We included HMH Into Math Grade 8 Answer Key PDF Module 1 Lesson 3 Explore Reflections to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 8 Module 1 Lesson 3 Answer Key Explore Reflections
I Can reflect a figure over either axis in the coordinate plane and describe the reflection algebraically.

Spark Your Learning
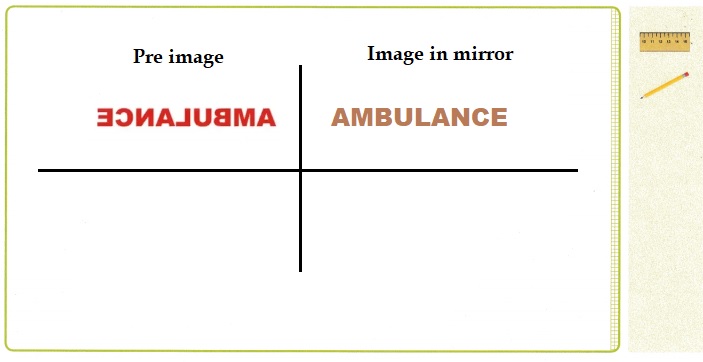
The word “AMBULANCE” is often written backward on the front of ambulances, so that it will appear forward in the rear-view mirrors of cars.

Use tracing paper to trace the word as it is shown above. What can you do with your result to make the word readable?
What effect do your actions have on the order of the letters, and what effect do your actions have on the individual letters themselves?

Answer:
Explanation:
An image is the resulting figure in a transformation.
A transformation is a change in the position, size, or shape of a new geometric figure.
The image of a transformation is the shape after the transformation.
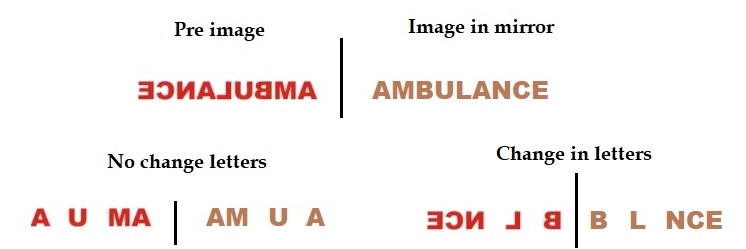
Turn and Talk As you change the word “AMBULANCE” so that it is readable, which letters change their appearance and which do not? What is different about the letters that remain the same after the transition, as opposed to the letters that change?
Answer:
Letters B, L, N, C and E change their appearance and letter A, M and U do not change as shown below.
Build Understanding
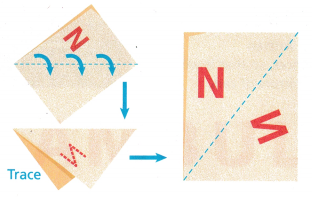
1. How can you reflect a figure using tracing paper? Draw the letter “N” on a piece of tracing paper, then fold the paper over the diagonal and trace the “N”. Unfold the paper, and you should see the original “N” and its reflection:
Connect to Vocabulary
A reflection is a transformation of a figure that flips the figure across a given line, called the line of reflection, so that each point on the preimage is the same distance from the line of reflection as the corresponding point on the image.
A. Find two line segments for the letter “N” that are parallel in the preimage. Are the corresponding segments in the image also parallel?
Answer:
Yes, the images are parallel.
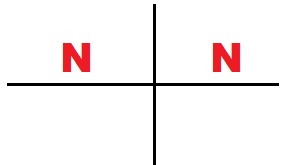
Explanation:
From the above image shown above, y – axis both two sides of letter N are parallel,
the corresponding segments in the image also parallel to preimage and image.
B. Use a ruler to measure the length of a line segment in the preimage. Then measure the length of the corresponding line segment in the image. What do you notice about the lengths of the two segments?
Answer:
No change in lengths,
Explanation:
The length of a line segment in the preimage and corresponding line segment in the image.
We notice that the lengths of the two segments are same, with no change.
C. Use a protractor to measure an angle in the preimage and the corresponding angle in the image. What do you notice?
Answer:
No change in the angles,
Explanation:
We observe that there is no change in the angles of a line segment in the preimage of letter N,
and corresponding line segment of letter N in the image.
We notice that the lengths of the two angles segments are same angles, no change.
D. What can you conclude about the way reflecting a figure affects side length, angle measure, and parallel line segments?
Answer:
A reflection on the coordinate plane takes a geometric figure such as a point, line segment, or shape and transforms it into a congruent geometric figure called the image.
Explanation:
In this explainer, we will focus on three different types of reflection on the coordinate plane:
Reflection in the 𝑥-axis
Reflection in the 𝑦-axis
Reflection about the origin
E. Look again at the “N” and its image on the paper. Why do you think the word reflection is used to describe such an image?
Answer:
Letter N changes the shape of the letter as shown below,
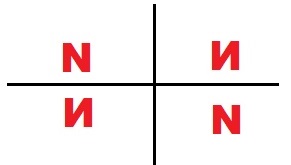
Explanation:
letter N changes the shape of the letter N,
but the lengths and angles between the side of the letter N remain same.
Turn and Talk Two students perform a reflection of the same shape. One reflects over a vertical line. The other reflects over a horizontal line. How are their reflections the same? How are they different?
Answer:
Letter N changes the shape of the letter N,
but the lengths and angles between the side of the letter N remain same as shown below.

Step It Out
2. How can you reflect a figure over the x-axis or y-axis?
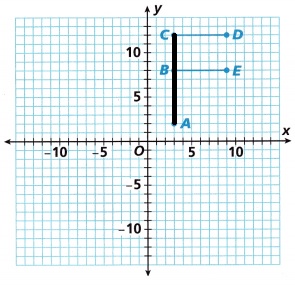
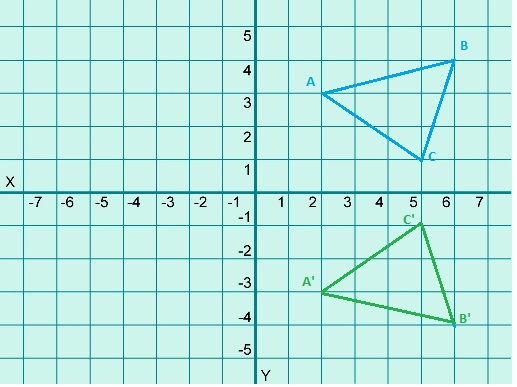
A. Reflect the image shown over the x-axis. Remember to keep each point of the image the same distance from the x-axis as the corresponding preimage point. For instance, Point C is 12 units from the x-axis, so Point C’ in the image must also be 12 units from the x-axis. Label the points using prime notation.
Answer:
Explanation:
An image is the resulting figure in a transformation.
A transformation is a change in the position, size, or shape of a new geometric figure.
The image of a transformation is the shape after the transformation.
B. The preimage is upright. Is the image also upright, or has it changed?
__________
Answer:
Image has changed,
Explanation:
The image is larger than the preimage.
The image and the preimage are congruent, but do not have the same orientation.
When the image is on the same side the object and the image distance is positive,
then the image is said to be real and inverted.
When the image of the object is behind then the image distance is negative,
the image is said to be virtual and upright.
C. Find the length of \(\overline{A C}\) in the preimage (in units). What do you expect the length of \(\overline{A^{\prime} C^{\prime}}\) to be? Find this length.
Answer:
10 units
Explanation:
The length of \(\overline{A C}\) in the preimage (in units) is 10 units.
The length of \(\overline{A^{\prime} C^{\prime}}\) to be 10 units.
D. The original letter “F” faces to the right. Reflect the original image over the y-axis. Does the new image face the same direction? If not, how is it different? Label the points using double-prime notation (“).
Answer:
No
Explanation:
Letter “F” faces to the right of the original image over the y-axis,
the new image face the opposite direction as shown below figure.
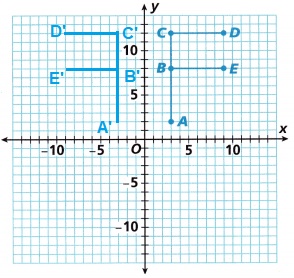
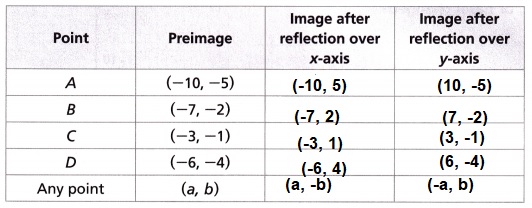
E. What are the coordinates of the points on the images corresponding to the labeled points on the preimage? Complete the table.
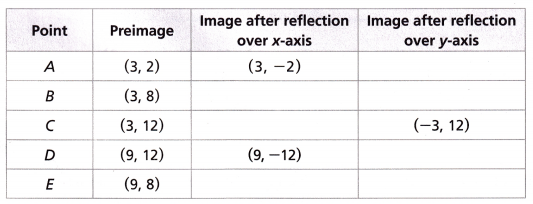
Answer:
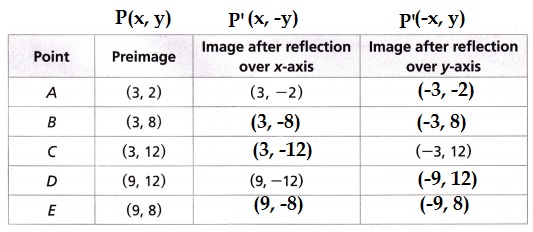
Explanation:
The formula for reflecting a point or line segment is as follows:
A point (x,y) being reflected over the x-axis will be reflected to the point (x,−y) .
The x-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the coordinate changes signs.
A point (x,y) being reflected over the y-axis will be reflected to the point (-x, y) .
The y-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the coordinate changes signs.
F. Look at your table. In general:

A point (a, b) reflected over the x-axis has the coordinates ![]()
Answer:
𝑃(a, b) → 𝑃′(a, −b).
Explanation:
A reflection in the 𝑥-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point 𝑃′ by keeping the 𝑥-coordinate,
the same and changing the sign of the 𝑦-coordinate.
The effect is that the position of 𝑃′ will mirror that of 𝑃,
on the opposite side of the 𝑥-axis (which is the line with equation 𝑦=0),
and at the same perpendicular distance from the 𝑥-axis as 𝑃.
Since the 𝑥-axis acts like a mirror, it is called the line of reflection (or mirror line).
A point (a, b) reflected over the y-axis has the coordinates 𝑃(a, b) → 𝑃′(a, −b).
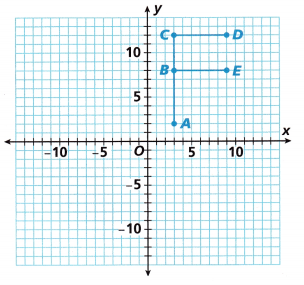
Turn and Talk On the grid, draw \(\overline{D E}\) and \(\overline{D^{\prime} E^{\prime}}\). Find the areas of Rectangle BCDE and Rectangle B’C’D’E’. What do you notice about these areas?
Answer:
Area = 24 units
Explanation:
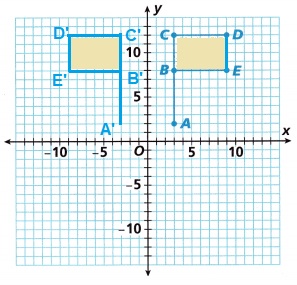
No change in the areas of Rectangle BCDE and Rectangle B’C’D’E’,
we notice that the areas are same as shown in the above figure.
3. On a piece of graph paper, draw a parallelogram in the third quadrant of the coordinate plane as shown.
A. Reflect this preimage over the x-axis and describe the location of the image after reflection.
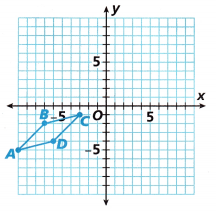 |
|
Answer:
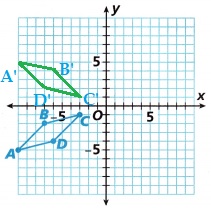
Explanation:
The above given preimage is drawn reflected image with respect to the x-axis,
and describe the location of the image after reflection.
B. Reflect the preimage over the y-axis and describe the location of the image after reflection.
Answer:
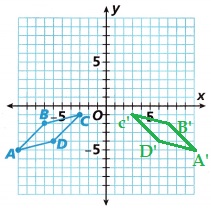
Explanation:
The above given preimage is drawn reflected image with respect to the y-axis,
and describe the location of the image after reflection.
C. Fill in the table with the coordinates of the vertices.
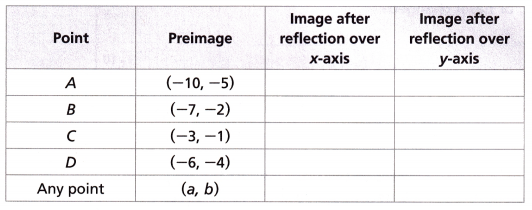
Answer:
Explanation:
The formula for reflecting a point or line segment is as follows:
A point (x,y) being reflected over the x-axis will be reflected to the point (x,−y) .
The x-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the signs of the coordinate change.
A point (x,y) being reflected over the y-axis will be reflected to the point (-x, y) .
The y-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the signs of the coordinate change.
Check Understanding
Question 1.
The coordinates of the vertices of a triangle are (2, 3), (5, 1), and (6, 4). After one reflection, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle’s image are (2, -3), (5, -1), and (6, -4). Over what line has the triangle been reflected?
Answer:
Over x axis line has the triangle been reflected.
The coordinates of the vertices of a triangle are,
(2, 3), (5, 1), and (6, 4).
the vertices of the triangle’s image are,
(2, -3), (5, -1), and (6, -4).
𝑃(x, y) → 𝑃′(x, −y).
Explanation:
A reflection in the 𝑥-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point 𝑃′ by keeping the 𝑥-coordinate,
and changing the sign of the 𝑦-coordinate.
The effect is that the position of 𝑃′ will mirror that of 𝑃,
on the opposite side of the 𝑥-axis (which is the line with equation 𝑦=0),
and at the same perpendicular distance from the 𝑥-axis as 𝑃.
Since the 𝑥-axis acts like a mirror, it is called the line of reflection (or mirror line).
Question 2.
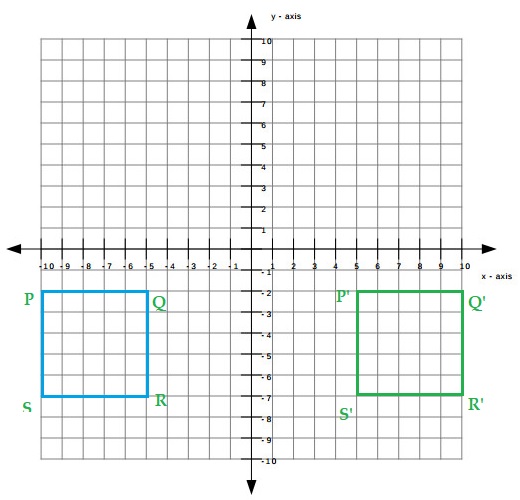
The coordinates of the vertices of a square are (-10, -2), (-5, -2), (-5, -7), and (-10, -7). The square is reflected over the y—axis.
A. What are the coordinates of the vertices of the image?
______________________
Answer:
(-10, -2), (-5, -2), (-5, -7), and (-10, -7)
𝑃(x, y) → 𝑃′(-x, y).
(10, -2), (5, -2), (5, -7), and (10, -7)
Explanation:
A reflection in the 𝑦-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point 𝑃′ by changing the sign of the 𝑥-coordinates,
and keeping the 𝑦-coordinate as the same.
The effect is that the position of 𝑃′ will mirror that of 𝑃,
on the opposite side of the 𝑦-axis (which is the line with equation 𝑥=0),
and at the same perpendicular distance from the 𝑦-axis as 𝑃.
Since the 𝑦-axis acts like a mirror, it is called the line of reflection (or mirror line).
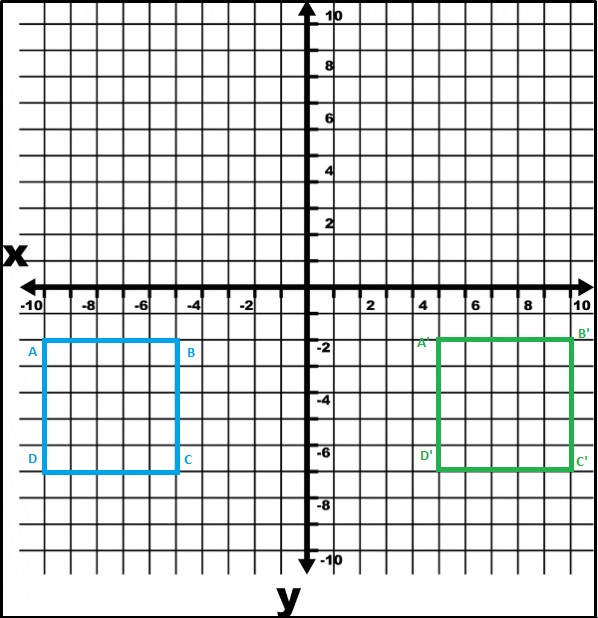
B. Show that the image still has parallel sides and has the same angles as the preimage: The image’s sides are segments of the lines y = ____, y = ____, x = ____, which meet at ___ angles.
Answer:
The image’s sides are segments of the lines y = y, x = -x, which meet at 90 degrees angles.
Explanation:
The image PQRS still has parallel sides and has the same angles as the preimage P’Q’R’S’,
as shown in the below figure.
The image’s sides are segments of the lines y = y, x = -x, which meet at 90 degrees angles.
C. Does the image have the same side lengths as the preimage? Explain.
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
As shown in the below figure the side lengths and the angles are same.
Question 3.
In your own words, describe the meaning of a reflection.
______________________
Answer:
A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line.
Explanation:
A reflection is known as a flip which is a mirror image of the shape.
An image will reflect through a line, known as the line of reflection.
A figure is said to reflect the other figure,
then every point in a figure is equidistant from each corresponding point in another figure.
On Your Own
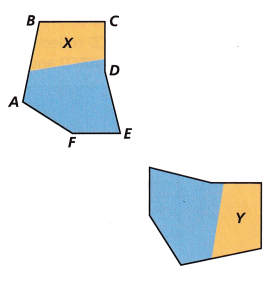
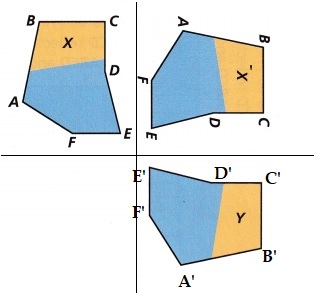
Use the figures to answer Problems 4—7.
Figure Y is a reflection of Figure X.
Question 4.
\(\overline{A B}\) is 3 centimeters long. What is the length of the corresponding side of Figure Y? How do you know?
Answer:
3 centimeters long.
Explanation:
\(\overline{A B}\) is 3 centimeters long in the reflected image also as shown in the below figure.
A’B’ of 3 centimeter is the length of the corresponding side of Figure Y.
Question 5.
Angle A measures 115°. What is the measure of the corresponding angle in Figure Y?
Answer:
115°
Explanation:
The measure of the corresponding angle in Figure Y is also 115°
no change in lengths and angles in the reflected figure.
Question 6.
\(\overline{F E}\) is parallel to \(\overline{B C}\) Are the corresponding sides in Figure Y also parallel?
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
The measure of the corresponding lengths in Figure Y,
\(\overline{F E}\) is parallel to \(\overline{B C}\).
Are the corresponding sides in Figure Y also parallel,
no change in lengths and angles in the reflected figure.
Question 7.
Use Tools Draw the line of reflection between Figures X and Y.
Answer:

Explanation:
A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line.
A reflection is known as a flip which is a mirror image of the shape.
An image will reflect through a line, known as the line of reflection.
A figure is said to reflect the other figure,
then every point in a figure is equidistant from each corresponding point in another figure.
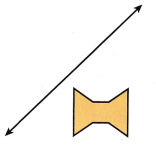
Question 8.
Use Tools Draw a reflection of the preimage over the line shown.
Answer:
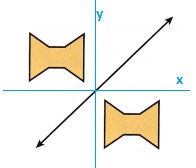
Explanation:
The reflection over a given line can be drawn as shown in the above figure,
first shifting the given figure to left side with reference to the y axis,
and then the reflection with reference to to the x axis is the reflected image.
A reflection in the 𝑦-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point 𝑃′ by changing the sign of the 𝑥-coordinate,
and keeping the 𝑦-coordinate as same.
The effect is that the position of 𝑃′ will mirror that of 𝑃,
on the opposite side of the 𝑦-axis (which is the line with equation 𝑥=0),
and at the same perpendicular distance from the 𝑦-axis as 𝑃.
Since the 𝑦-axis acts like a mirror, it is called the line of reflection (or mirror line).
Question 9.
Marie is practicing her reflections on graph paper.
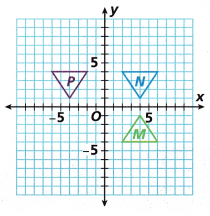
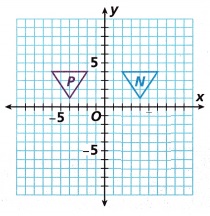
A. Is Figure P a reflection of Figure N over the y-axis?
_______________
Answer:
yes,
Explanation:
figure P is a reflection of figure N over y axis,
a reflection in the 𝑦-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point N.
By changing the sign of the 𝑥-coordinate and keeping the 𝑦-coordinate the same.
The effect is that the position of N will mirror that of 𝑃,on the opposite side of the 𝑦-axis.
B. Is Figure P a reflection of Figure M over the y-axis and then over the x-axis?
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
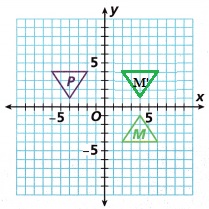
Reflection over x axis first, then y axis.
figure P is a reflection of figure M over x axis,
a reflection in the x-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point M.
By changing the sign of the y-coordinate and keeping the x-coordinate the same.
The effect is that the position of M will mirror that of 𝑃,on the opposite side of the x-axis.
C. Is Figure P a reflection of Figure M over the x-axis and then over the y-axis?
Answer:
yes,
Explanation:
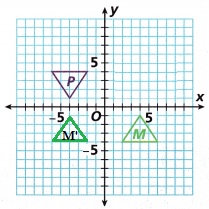
Reflection over y axis first, then x axis.
A reflection in the x-axis maps point 𝑃 onto its image point M.
By changing the sign of the x-coordinate and keeping the y-coordinate the same.
The effect is that the position of M will mirror that of 𝑃,on the opposite side of the y-axis.
Question 10.
Figure ABCD is a trapezoid in the second quadrant.
A. Attend to Precision On the given graph, draw the image of Figure ABCD reflected across the y-axis. What are the coordinates of the vertices of ABCD and A’B’C’D
Answer:
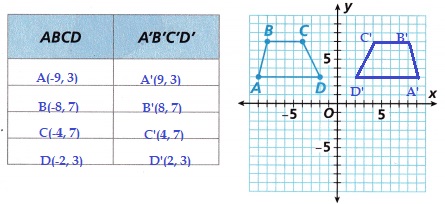
Explanation:
P(x, y) is changed to P'(-x, y) the image of Figure ABCD reflected across the y-axis.
the coordinated are shown in the above table.
B. Given any point (x, y) on ABCD, what are the coordinates of the corresponding point on A’B’C’D’?
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
P(x, y) is changed to P'(-x, y) the image of Figure ABCD reflected across the y-axis.
The image of Figure ABCD reflected across the y-axis, are the coordinates of the vertices of ABCD and A’B’C’D.
C. Is A’B’C’D’ facing the same direction as ABCD? Explain.
Answer:
yes,
Explanation:
A’B’C’D’ facing the same direction as ABCD,
a reflection in its image ABCD by changing the sign of the 𝑥-coordinate and keeping the 𝑦-coordinate as same. The effect is that the position of A’B’C’D’ will mirror that of ABCD on the opposite side of the 𝑦-axis.
Question 11.
Use Tools Draw a square with sides that are horizontal and vertical on a piece of paper.
A. If you reflect the square over a vertical line, does it look any different? If you reflect the square over a horizontal line, does it look any different?
_______________
Answer:
No,
Explanation:
The reflected square over image over a vertical line,
does not have any different with reference to original image.
B. In your original square, draw a right-angle mark in one corner. Reflect this square over a horizontal line. Does it look any different? If so, what is different?
Answer:
yes,
Explanation:
The right angle marked position is changed after the reflection, as shown below figure.
Right angle mark at bottom left corner will be top left corner shifted.
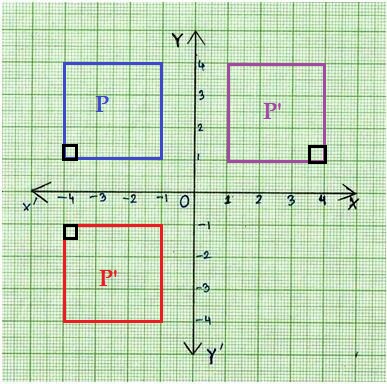
C. If you reflect the square from Part B over a vertical line, does it look any different? If so, what is different?
Answer:
yes, the difference is the right angle marked corner shifted.
Explanation:
There is difference in the shape and size of the square over a vertical line,
the difference to the right angle corner is shifted in the image with reference to preimage.
I’m in a Learning Mindset!
How does my mindset affect my confidence with performing reflections?
Answer:
Thinking over the preimage and image changes in the positions of the image,
with reference to the preimage and rule given will effect the mind set.
Lesson 1.3 More Practice/Homework
Use the tiger images to answer Problems 1—3.
Question 1.
Construct Arguments Could Tiger 2 be an image of Tiger 1 after one reflection? Explain. Tiger 1 Tiger 3
Answer:

Answer:
Tiger 1 is a pre image of image tiger 2,
tiger 2 is reflected over vertical line y-axis.
Tiger 3 is also a reflected image with a dilation factor d =\(\frac{1}{k}\)
Question 2.
Construct Arguments Could Tiger 3 be an image of Tiger 1 after one reflection? Explain.
Answer:
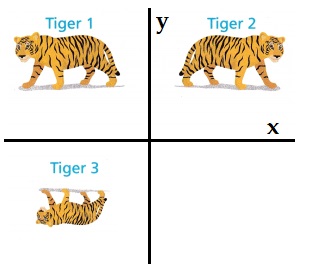
Explanation:
Tiger 3 is also a reflected image with a dilation factor d = \(\frac{1}{k}\)
reduction ratio factor k = 2
d = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 3.
Construct Arguments Could Tiger 4 be an image of Tiger 1 after one reflection? Explain.
Answer:
No,
Explanation:
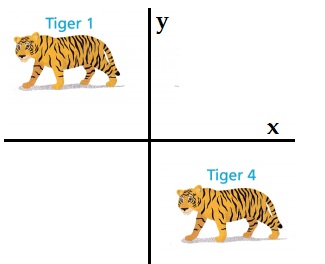
Both the tigers are same in shape and size,
but the tiger 4 is not reflection image of tiger 1.
Question 4.
The grid shows Figure R, a pair of arrows forming a right angle. On the grid, draw a reflection of R so that any point (a, b) on the preimage becomes (-a, b) on the image, R’.
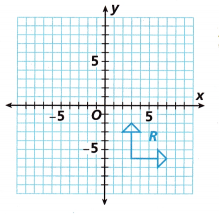
A. Over what line did you reflect R?
_______________
Answer:
With reference to y axis or vertical line letter R is reflected,
as shown in the below figure.
Explanation:
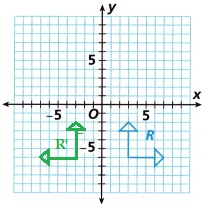
P(x, y) is changed to P'(-x, y) the image of Figure R reflected across the y-axis,
with reference to y axis or vertical line letter R is reflected.
B. Both arrows in Figure R are 4 units long. How long are the arrows in Figure R’?
Answer:
4 units long.
Explanation:
P(x, y) is changed to P'(-x, y) the image of Figure R reflected across the y-axis,
with reference to y axis or vertical line letter R is reflected,
and the lengths are 4 units long in the R’ reflected figure.
C. What are the coordinates of the tips of the arrows on R
Answer:
(3, -2) and (7, -6 )
Explanation:
The coordinates of the tips of the arrows on R (x, y) are,
(3, -2) and (7, -6 )
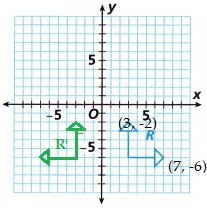
D. On the same grid, reflect R’ over the x-axis to arrive at Figure R”. In which quadrant is R”?
Answer:
The image is in the second quadrant is R”
Explanation:
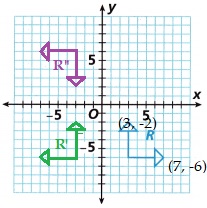
The same grid, reflect R’ over the x-axis to arrive at Figure R”,
it is in the second quadrant is R”.
E. What are the coordinates of the point at which the arrows intersect in R”?
Answer:
(-3, 2) and (-7, 6 )
Explanation:
The coordinates of the tips of the arrows on R (x, y) are,
(-3, 2) and (-7, 6 ).
F. In which directions do the arrows point in Figure R”?
Answer:
Left and Down direction of arrows.
Explanation:
With reference to the x axis in the direction of the arrows are Left and Down direction of arrows.
Test Prep
Question 5.
Select all the figures that could represent an image of the given figure after one reflection over a horizontal or vertical line through its center.

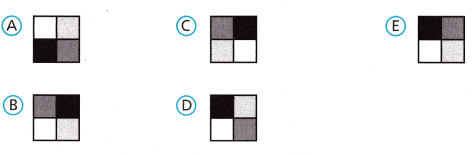
Answer:
A and C are the images after reflection.
Explanation:
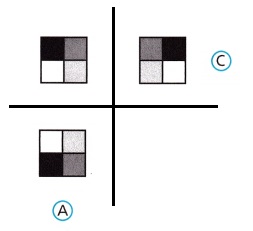
With reference to the horizontal line image A is form by reflecting the preimage.
With reference to the vertical line image C is form by reflecting the preimage.
Question 6.
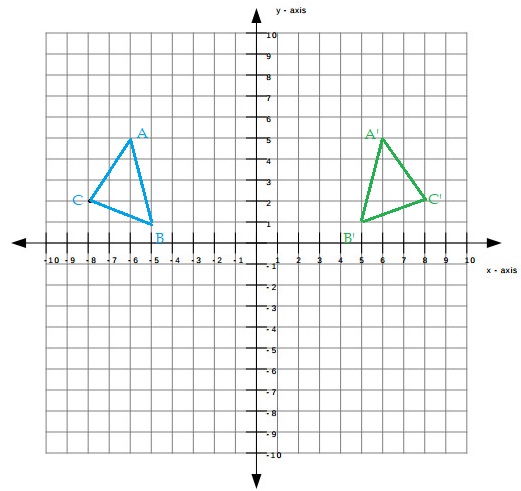
A triangle with vertices at (-6, 5), (-5, 1), and (-8, 2) is reflected over the y-axis. What are the coordinates of the vertices of the image?
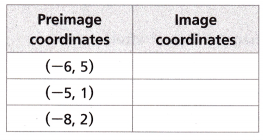
Answer:
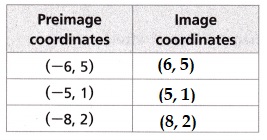
Explanation:
With reference to the y axis the pre image is reflected,
and the coordinated of triangle are,
P(x, y) → P'(-x, y)
A(-6, 5) → A'(6, 5)
B(-5, 1) → B'(5, 1)
C(-8, 2) → C'(8, 2)
Question 7.
Which of the following is a rule that represents what happens to the coordinates of any point on a figure after it is reflected over the x-axis and then the y-axis?
A. (x, y) → (x, -y)
B. (x, y) → (-x, y)
C. (x, y) → (y, x)
D. (x, y) → (-x, -y)
Answer:
Option (A) and Option (B)
Explanation:
Option (A)
(x, y) → (x, -y) the coordinates of any point on a figure after it is reflected over the x-axis.
Option (B)
(x, y) → (-x, y) the coordinates of any point on a figure after it is reflected over the y-axis.
Spiral Review
Question 8.
Albert works at a farmers’ market. He recently sold 18 pieces of fruit, 6 of which were oranges. What is the experimental probability that the next piece of fruit Albert sells will be an orange?
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
18 pieces of fruit, 6 of which were oranges.
The probability that the next piece of fruit Albert sells will be an orange,
\(\frac{6}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 9.
What is the surface area of a cube that has edges 3 centimeters long?
Answer:
54 cm2
Explanation:
Total surface area of a cube = 2AB + 2BC + 2 CA
Cube of edge length 3 cm,
the surface area of a cube if its height is 3 cm,
Surface area = 18 x 3 = 54 cm2
Question 10.
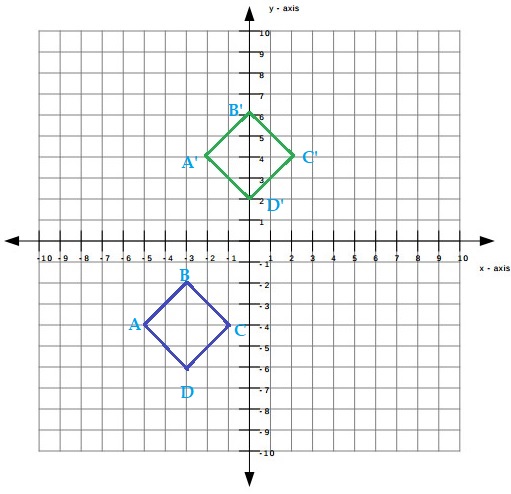
A diamond figure has vertices with coordinates at (-5, -4), (-3, -2), (-1, -4), and (-3, -6). If the figure is translated 3 units right and 8 units up, what are the coordinates of the vertices of the image?
Answer:
(-2, 4), (0, 6), (2, 4), (0, 2)
Explanation:
(-5, -4), (-3, -2), (-1, -4), and (-3, -6)
the figure is translated 3 units right and 8 units up,
the coordinates of the vertices of the image are,
(x, y) → (x + 3, y + 8)
(-5 + 3, -4 + 8) = (-2, 4)
(-3 + 3, -2 + 8) = (0, 6)
(-1 + 3, -4 + 8) = (2, 4)
(-3 + 3, -6 + 8) = (0, 2)