We included HMH Into Math Grade 8 Answer Key PDF Module 1 Lesson 4 Explore Rotations to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 8 Module 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key Explore Rotations
I Can identify and perform rotations, and describe a rotation on a coordinate plane algebraically.
Spark Your Learning
Use tracing paper to trace a copy of this recycling symbol.
Place the tip of your pencil in the center of the symbol and turn the paper about that point. You’ll see that the original design reappears three times in every full turn.
In the space provided, sketch a design that reappears every quarter of a full turn. Trace the shape on tracing paper, then turn it to check your work.

 Answer:
Answer:
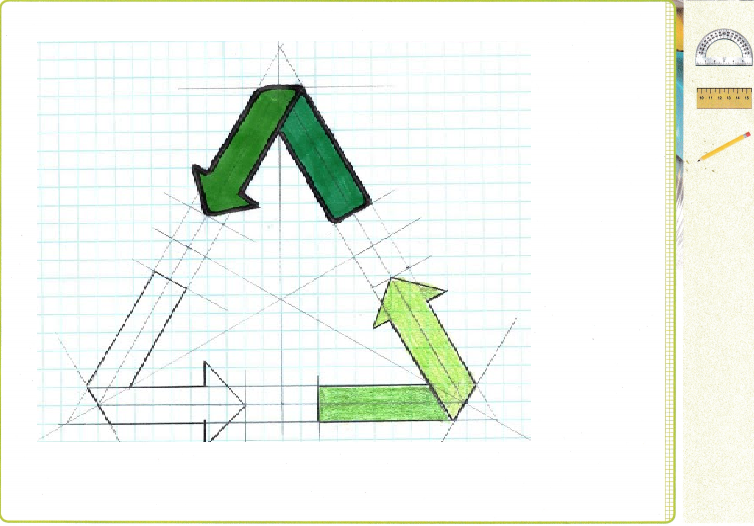
Explanation:
First place the tip of a pencil in the center of the symbol and turn the paper about that point.
Then the original design reappears every quarter of a full turn three times in every full turn.
A quarter turn is moving the image to right degrees as shown above.
Turn and Talk If the preimage and image of a figure look identical after being turned one-fourth turn clockwise or one-fourth turn counterclockwise, what must be true about the figure?
Answer:
The new figure is called the image and original figure is known as preimage.
Explanation:
A preimage is the original figure in a transformation.
A transformation is a change in the position, size, or shape of a new geometric figure.
The preimage of a transformation is the shape before the transformation.
The new figure is called the image and original figure is known as preimage.
Build Understanding
A. Use a ruler and protractor to complete the table.
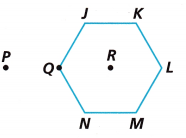
Connect to Vocabulary
A rotation is a transformation in which a figure is turned around a point. That point is called the center of rotation.
A. Use a ruler and protractor to complete the table.

Answer:
Explanation:
A rotation is a transformation in which a figure is turned around a point.
That point is called the center of rotation.
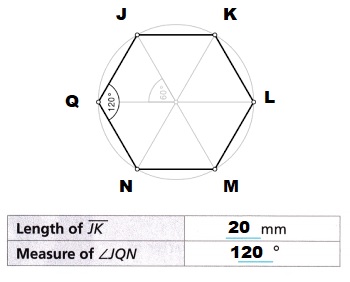
B. Place the tip of a pencil on Point R and rotate the hexagon 90° (one-fourth turn) clockwise about that point.
- What happens to the measure of ∠JQN?
- What happens to the length of \(\overline{J K}\)?
- Name a pair of parallel sides in the shape. What happens to the pair when the shape is rotated?
Answer:

Explanation:
Placing the tip of a pencil on Point R and rotate the hexagon 90° clockwise about that point.
i ) No change in the measure of angle ∠JQN in the above figure hexagon.
ii) No change to the length of \(\overline{J K}\), as before rotation same length.
iii) JK and NM a pair of parallel sides in the shape,
the pair JK and NM position changed, when the shape is rotated.
C. Move the center of rotation by placing the tip of your pencil on Point P. Rotate the shape about Point P. Describe the rotation. How is it different from the rotation in Part B?
Answer:
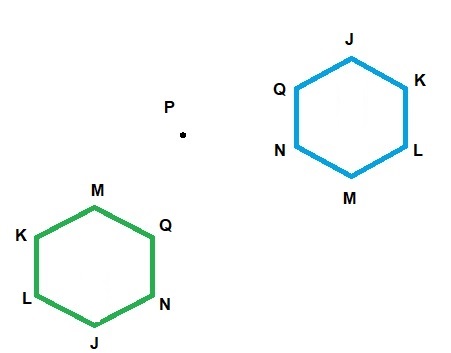
Explanation:
A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a point.
Rotation means the circular movement of an object around a center.
It is possible to rotate different shapes by an angle around the center point.
D. Draw an arrow inside your hexagon that points to the top of the shape. When you rotate the shape 180° (one-half turn), what happens to the direction of the arrow in the image, and why?
Answer:
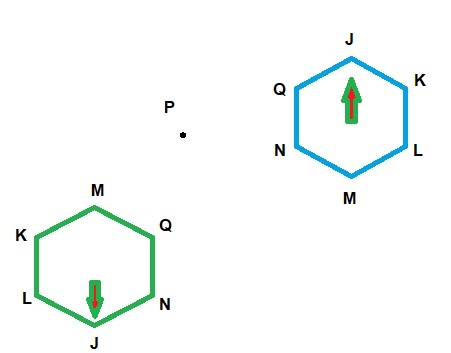
Explanation:
A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a point.
Rotation means the circular movement of an object around a center.
It is possible to rotate different shapes by an angle around the center point.
When we rotate the shape 180° (one-half turn), the resultant shape is shown below.
Turn and Talk Can you make your hexagon change its shape using a rotation? Why or why not?
Answer:
No,
Explanation:
The hexagon shape can not be changed by rotation.
A rotation is a transformation in which a figure is turned around a point.
That point is called the center of rotation.
Step It Out
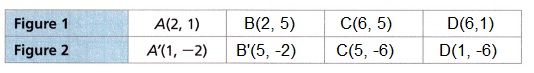
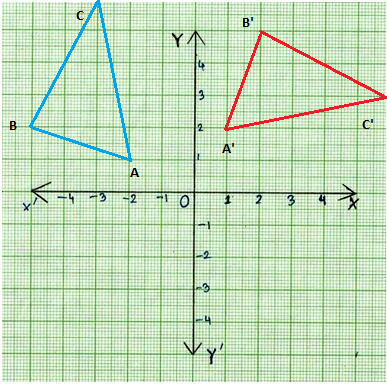
2. You can rotate the letter “N” and get the letter “Z.” Figure 2 was formed by rotating Figure 1 90° clockwise about the origin.
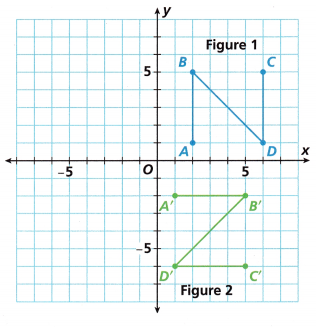
Answer:
(x, y) → (y, -x)
A(2, 1) → A'(1, – 2)
B(2, 5) → B'(5, -2)
C(6, 5) → C'(5, -6)
D(6, 1) → D'(1, -6)
Explanation:
Rotate the figure 90 degrees clockwise about a point,
every point(x, y) will rotate to (y, -x).
Let’s understand the rotation of 90 degrees clockwise about a point visually.
So, each point has to be rotated and new coordinates have to be found.
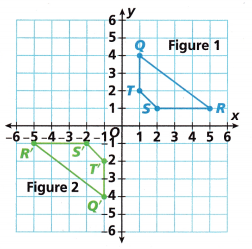
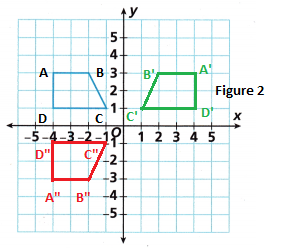
A. Use a ruler and protractor to measure the line segments and angles of both figures. What is the relationship between the side lengths and angle measures of the image and preimage?
Answer:
The length of line segments is 2 centimeters,
and the angle between the line segments is 45° in both the figures.
Explanation:
The relationship between the side lengths and angle measures of the image and preimage on horizontal line segments become vertical line segment and the angle between the line segments is 45°.
B. In Figure 1, \(\overline{A B}\) is parallel to \(\overline{D C}\). What is the relationship between \(\overline{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}\) and \(\overline{D^{\prime} C^{\prime}}\) in Figure 2?
Answer:
\(\overline{A^{\prime} B^{\prime}}\) and \(\overline{D^{\prime} C^{\prime}}\) are also parallel, as shown in the below figure, darked blue and green lines are parallel lines.
Explanation:
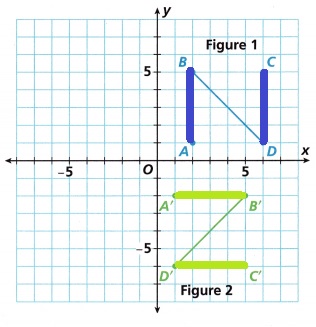
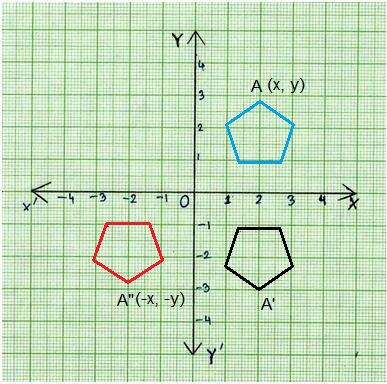
C. Fill in the coordinates for each point.

Answer:
Explanation:
A point (x, y) being reflected over the x-axis will be reflected to the point (x,−y) .
The x-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the coordinate changes signs.
A point (x, y) being reflected over the y-axis will be reflected to the point (-x, y) .
The y-value of the coordinate is unchanged and the y-value of the coordinate changes signs.
D. Look at the relationship between the coordinates of the vertices of Figure 1 and Figure 2. Write a rule to find the coordinates of the vertices of any figure rotated 90° clockwise about the origin.
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
To rotate the figure 90 degrees clockwise about a point, every point(x, y) will rotate to (y, -x).
Let’s understand the rotation of 90 degrees clockwise about a point visually.
So, each point has to be rotated and new coordinates have to be found.
E. Rotate Figure 2 180° counterclockwise about the origin. Label the result as Figure 3. Then fill in the table.

Answer:

Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x,-y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
F. Write a rule that represents the change in coordinates of any figure rotated 180° counterclockwise about the origin.
![]()
Answer:
Rule : ![]()
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y). S
o all we do is make both x and y negative.
G. If you rotate the letter “W” 180° clockwise, what letter does it resemble? ___________
Answer:
Letter M
Explanation:
(-4, 3) is (4, -3)
(-2, 1) is (2, -1)
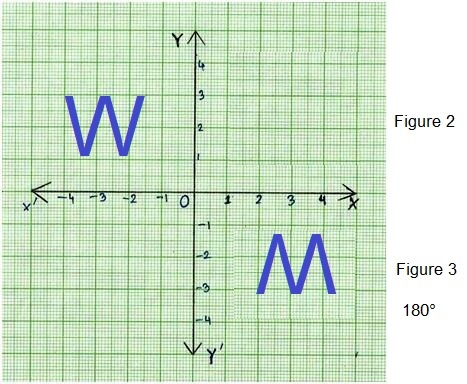
Turn and Talk Identify which uppercase letters look the same after a 180° rotation.
Answer:
In English alphabet, there are 7 capital letters that look the same after being rotated 180°.
Those letters are H, I, N, O, S, X, and Z.
3. Figure 1 is rotated to form Figure 2.
A. Describe the rotation.
______________
Answer:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
B. Fill in the table of vertex coordinates.

Answer:
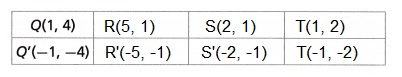
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
C. Write a rule that represents the change in coordinates of any figure rotated 180° about the origin.
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
4. A triangle has vertices (2, 4), (5, 1), and (1, 2).
A. Graph the triangle and label it Figure 1.
Answer:
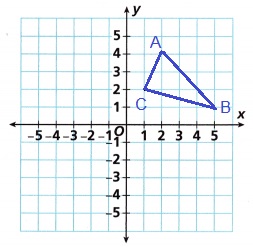
Explanation:
Draw a triangle on the graph using the vertices (2, 4), (5, 1), and (1, 2) as shown above.
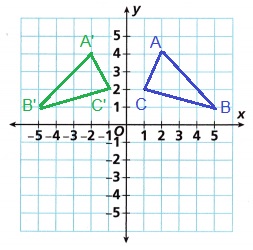
B. Rotate Figure 1 by the rule (x, y) → (y, -x) and label the image Figure 2. Complete the sentence about the rotation:
To form Figure 2, Figure 1 underwent a rotation of 90° ____ about the origin.
Answer:
90° clockwise about the origin.
Explanation:
rule (x, y) → (y, -x)
(2, 4), (5, 1), and (1, 2).
(4, -2), (1, -5) and (2, -1)
C. Rotate Figure 1 by the rule (x, y) → (-y, x) and label the image Figure 3. Complete the sentence about the rotation:
Answer:
Rotate Figure 1 by the rule (x, y) → (-y, x) and label the image Figure 3.
Explanation:
(2, 4), (5, 1), and (1, 2).
(-4, 2), (-1, 5), and (-2, 1).
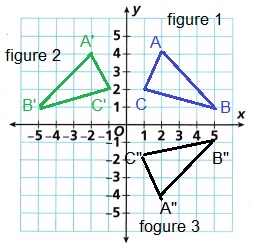
To form Figure 3, Figure 1 underwent a rotation of____ counterclockwise about the origin.
Answer:
To form Figure 3, Figure 1 underwent a rotation of 90° counterclockwise about the origin.
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-y, x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
Check Understanding
Question 1.
Antoine and Bobby each rotated a pentagon about Point P, but they each got a different image. Which rotation is correct? Why?
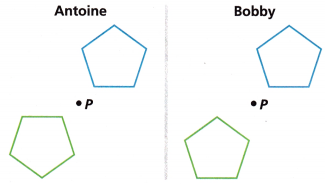
Answer:
Antoine is correct, each rotated a pentagon about Point P.
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
rotated with 180 degrees rotation
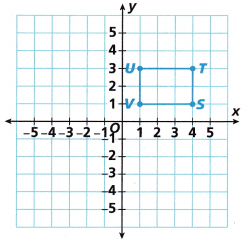
Question 2.
A. Draw rotations of Rectangle STUV 90°, 180°, and 270° clockwise about the origin.
Answer:
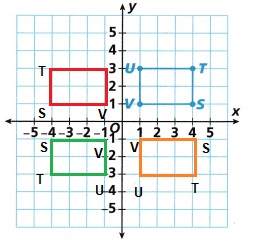
Explanation:
90° clockwise rotation: (x,y) becomes (y,-x)
180° clockwise and counterclockwise rotation: (x, y) becomes (-x,-y)
270° clockwise rotation: (x,y) becomes (-y,x)
B. What do all four figures have in common? They all have ___ side lengths and ____ angle measures, and their ___ sides are parallel.
Answer:
All four figures have in common center origin point.
Explanation:
A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a point.
They all have same side lengths and same angle measures,
and their opposite sides are parallel.
On Your Own
Question 3.
Victor rotated his initial, V, about Point P. What stayed the same between the preimage and image? What changed?
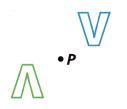
Answer:
180 degrees rotation.
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y) becomes A'(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative rotated with 180 degrees rotation.
Question 4.
Use Tools Sketch a rotation of the Figure WXYZ. Use Point W as the center of rotation.
A. What is the same about the two images?
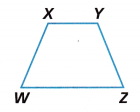
Answer:
A rotation of the Figure WXYZ 180 degrees rotation by use Point W as the center of rotation.
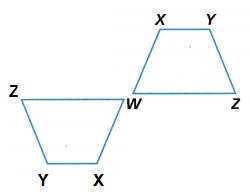
Explanation:
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point (x, y) becomes ‘(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
Question 5.
Model with Mathematics Elias graphed the movement of one quarter-turn of a ceiling fan.
A. Continue the rotation and draw the fan blade in the third and second quadrants after two more rotations of 90° each.
Answer:
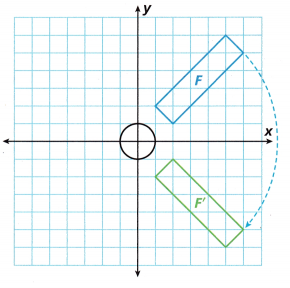
Explanation:
A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a point.
They all have same side lengths and same angle measures,
and their opposite sides are parallel.
B. Describe the rotation of the fan blade from F to F’.
Answer:
90 Degree Rotation.
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point F(x, y) becomes F'(-y, x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
C. Describe the rotation from F to F’ in mapping notation.
Answer:
Point F(x, y) becomes F'(-y, x).
(x, y) → (-y, x)
(2, 1) → (2, -1)
(6, 5) → (6, -5)
(5, 6) → (5, -6)
(1, 2) → (1, -2)
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point F(x, y) becomes F'(-y, x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
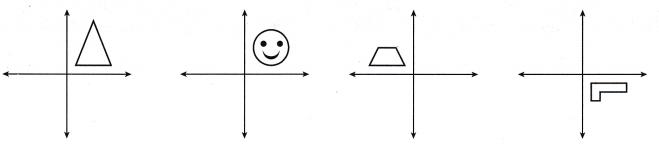
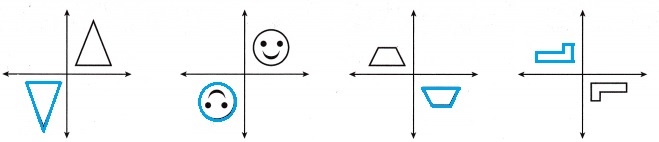
Question 6.
Attend to Precision Rotate each figure 180° about the origin.
Answer:
Explanation:
Each rotated a pentagon about Point P.
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point (x, y) becomes ‘(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
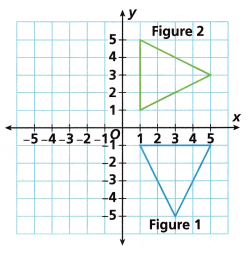
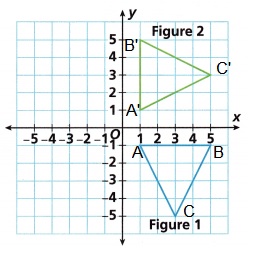
Question 7.
Describe the transformation of Figure 1 to Figure 2 using mapping notation.
Answer:
F1(x, y) → F2(x, -y)
(1, -1) → (1, 1)
(5, -1) → (1, 5)
(3, -5) → (5, 3)
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point F(x, y) becomes F'(-y, x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
(x, y) → (x, -y)
(1, -1) → (1, 1)
(5, -1) → (1, 5)
(3, -5) → (5, 3)
Question 8.
∆JKL has an area of 3.25 square units. What happens to its area when it is rotated 180° about Point J?
Answer:
No change in area,
Explanation:
The area remains same as 3.25 square units and the point J is changed in the location,
as shown in the below figure after rotating 180° about Point J.
Question 9.
The vertices of the preimage of a triangle are (-2, 1), (-5, 2), and (-3, 6). The triangle is rotated and its image has vertices at (1, 2), (2, 5), and (6, 3).
A. Describe the rotation that resulted in the image.
Answer:
The rule for a rotation by 90° about the origin is (x, y) → (−y, x).
Explanation:
Rotate a figure of 90 degrees clockwise about the origin,
each point of the given figure has to be changed from (x, y) to (y, -x),
and graph the rotated figure as shown below.
vertices of the preimage of a triangle are,
(-2, 1), (-5, 2), and (-3, 6).
(x, y) → (−y, x).
The triangle is rotated and its image has vertices at,
(1, 2), (2, 5), and (6, 3).
B. If the image is then rotated 90 degrees clockwise, what are the coordinates of the new image?
Answer:
The triangle is rotated and its image has vertices at,
(1, 2), (2, 5), and (6, 3).
Explanation:
vertices of the preimage of a triangle are,
(-2, 1), (-5, 2), and (-3, 6).
(x, y) → (−y, x).
The triangle is rotated and its image has vertices at
(1, 2), (2, 5), and (6, 3).

Question 10.
Attend to Precision Rotate the shape by the rule (x, y) → (y, -x). Then rotate the new image according to the rule (x, y) → (-x, -y).
Answer:
Rotate the shape by the rule (x, y) → (y, -x) is Figure 2
Rotate the shape by the rule (x, y) → (-x, -y) is Figure 3
Explanation:
Rotate the shape by the rule (x, y) → (y, -x) is Figure 2
Rotation by 90° about the origin:
The rule for a rotation by 90° about the origin is (x, y) → (−y, x).
rotate a figure of 90 degrees clockwise about the origin, each point of the given figure has to be changed from (x, y) to (y, -x) and graph the rotated
Rotate the shape by the rule (x, y) → (-x, -y) is Figure 3
Rotation by 180° about the origin:
A rotation by 180° about the origin is shown.
The rule for a rotation by 180° about the origin is (x, y) → (−x, −y)
I’m in a Learning Mindset!
Do I have a fixed-mindset voice or growth-mindset voice in my head when I’m working with rotations? How can I tap into my growth-mindset voice?
Answer:
Someone with a growth mindset views intelligence, abilities, and talents as learnable and capable of improvement through effort.
On the other hand, someone with a fixed mindset views those same traits as inherently stable and unchangeable over time.
Lesson 1.4 More Practice/Homework
Question 1.
Which shape shows a rotation of the shaded figure following the rule (x, y) → (-x, -y)?
Answer:
Figure B
Explanation:
A rotation of the shaded figure follows the rule (x, y) → (-x, -y)
So, figure B of co-ordinates (-4, -3) and (-2, -1) shows the shaded figure.
Question 2.
Sarika uses rotations to make designs. What characteristics of the design indicate it is a rotation?
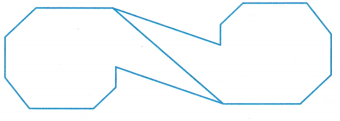
Answer:
A rotation preserves lengths of segments and measures of angles.
A rotation is a transformation that turns a figure about a point.
Rotation means the circular movement of an object around a center.
It is possible to rotate different shapes by an angle around the center point.
(X, Y) (X, -Y)
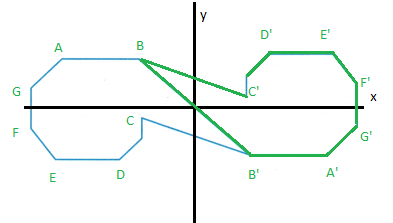
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin,
our point A(x,y) becomes A'(-y,x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
A rotation maps a line to a line, a ray to a ray, a segment to a segment, and an angle to an angle.
Question 3.
A triangle has vertices at (-3, 4), (-1, 0), and (-4, 0). What are the coordinates of the vertices after it is rotated 180° about the origin?
Answer:
The co-ordinates will remain same as (3, -4), (1, 0), and (4, 0).
Explanation:
There is a change in the co-ordinates of the vertices after it is rotated 180° about the origin.
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point (x, y) becomes ‘(-x, -y).
So all we do is make both x and y negative.
Question 4.
A. Graph Rectangle ABCD with vertices at A(1, 5), B(3, 6), C(5, 2), and D(3, 1). Then draw a rotation of the rectangle 90° counterclockwise about the origin and list the coordinates of the vertices of the result.
Answer:
When we rotate a figure of 90 degrees counterclockwise,
each point of the given figure has to be changed from (x, y) to (-y, x),
and graph the rotated figure as shown below.
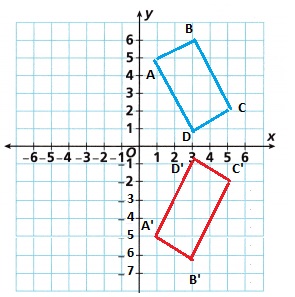
B. Describe the rotation in mapping notation.
Answer:
figure has to be changed from (x, y) to (-y, x) and graph the rotated figure.
Explanation:
The mathematical notation for rotation is written as R (center, rotation),
where the center is the point of rotation and the rotation is given in degrees.
Often, rotations are written using coordinate notation,
which means that their coordinates on the coordinate plane are given.
Test Prep
Question 5.
Draw a rotation of the parallelogram 90° counterclockwise about the origin.
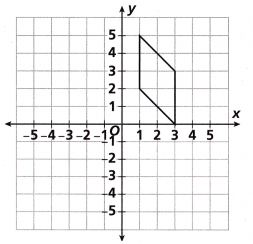
Answer:
Explanation:
When rotating a point 90 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point A(x, y)
becomes as A'(-y,x).
In other words, switch x and y and make y negative.
Question 6.
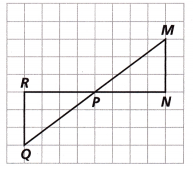
What rotation of ∆MNP about Point P could have produced ∆PQR?
A. 90° clockwise
B. 180° clockwise
C. 270° counterclockwise
D. 360° counterclockwise
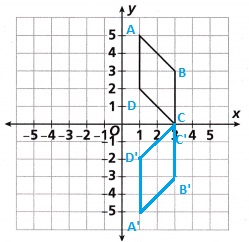
Answer:
180° clockwise.
Explanation:
The rule for a rotation by 180° about the origin is (x, y)→(−x, −y).
(x, y)→(−x, −y).
Question 7.
A pentagon has vertices at (-1, -1), (-5, -2), (-6, -4), (-4, -7), and (-2, -3). If the pentagon is rotated 180° clockwise about the origin, what are the coordinates of the vertices of the image?
Answer:
(1, 1), (5, 2), (6, 4), (4, 7), and (2, 3).
Explanation:
There is a change in the co-ordinates of the vertices after pentagon is rotated 180° about the origin.
When rotating a point 180 degrees counterclockwise about the origin our point (-x, -y) becomes ‘(x, y).
So all we do is make both x and y positive.
Spiral Review
Question 8.
A figure has two pairs of parallel sides and four right angles. The figure is translated 4 units down. How many parallel sides does the image have?
Answer:
The resultant figure is also has two pairs of parallel sides and four right angles.
After the figure is translated 4 units down as shown below figure
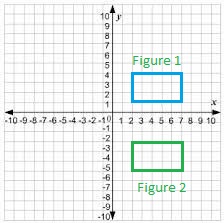
Explanation:
When the figure is translated 4 units down also,
there is no change in the resultant figure as shown above.
Question 9.
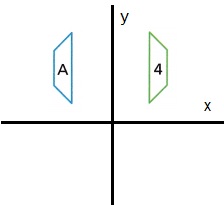
Identify which of the figures is a reflection of Figure A, and describe the reflection(s).
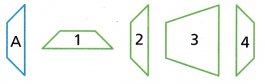
Answer:
Figure 4 is a reflection of across a vertical line of figure A,
and figure 2 is a reflection across horizontal line of figure A.
Explanation:
A reflection is a transformation that flips a figure across a line.
A reflection is known as a flip which is a mirror image of the shape.
An image will reflect through a line, known as the line of reflection.
A figure is said to reflect the other figure,
then every point in a figure is equidistant from each corresponding point in another figure.