This handy Spectrum Math Grade 7 Answer Key Chapter 6 Lesson 6.1 Sampling provides detailed answers for the workbook questions
Spectrum Math Grade 7 Chapter 6 Lesson 6.1 Sampling Answers Key
When a population, or data set, has a very large number of data points, sampling can be used to help summarize the data set.
To be sure that the description of the population is correct, random sampling should be used. If a summary is made based on biased sampling, the description of the population will not be accurate.
Diana is trying to find out what kind of music 7th graders prefer. If she was to interview the first 60 seventh graders to arrive at school one morning, she would be using random sampling because school arrival time has nothing to do with taste in music. If she was to interview 60 7th graders who are taking band, or who are at a concert for a specific band, she would be using biased sampling because both of those factors can affect someone’s taste in music.
Tell if each sample would be considered random or biased.
Question 1.
Charlie puts a deck of cards in a bag. He shakes the bag and pulls 4 cards out of the bag.
Answer:
random sampling.
Explanation:
A sample in which every person, object, or event has an equal chance of being selected is called a random sample. A random sample is more likely to be representative of the entire population than other types of samples.
Charlie pulls 4 cards out of the bag is a random sample form a deck of cards in a bag is random sampling.
Question 2.
Nicole wanted to know what 6th graders’ favorite movie of the year was. She asked 10 girls from her homeroom class.
Answer:
biased sampling.
Explanation:
A sampling method is called biased if it systematically favors some outcomes over others.
Nicole wanted to know what 6th graders’ favorite movie of the year was.
So, she asked 10 girls from her homeroom class is biased sampling.
Question 3.
A garden has 100 pepper plants. John wants to know the number of peppers that are on each of the plants. He counts the number of peppers on the plants in one of the outside rows.
Answer:
biased sampling.
Explanation:
A sampling method is called biased if it systematically favors some outcomes over others.
John wants to know the number of peppers that are on each of the plants of 100 pepper plants.
He counts the number of peppers on the plants in one of the outside rows is biased sampling.
Question 4.
Ben wants to know what time most 7th graders get on the bus in the morning. He surveys five students from each bus.
Answer:
random sampling.
Explanation:
A sample in which every person, object, or event has an equal chance of being selected is called a random sample. A random sample is more likely to be representative of the entire population than other types of samples.
Ben wants to know what time most 7th graders get on the bus in the morning.
He surveys five students from each bus is random sampling.
Question 5.
Anna wants to know how much middle school students weight. She weighs one student from each homeroom.
Answer:
random sampling.
Explanation:
A sample in which every person, object, or event has an equal chance of being selected is called a random sample. A random sample is more likely to be representative of the entire population than other types of samples.
She weighs one student from each homeroom. is random sampling.
As Anna wants to know how much middle school students weight.
Question 6.
Jordan wants to know which restaurant makes the best burger in town. He stands on a block between two different burger restaurants at dinner time and asks the first 25 people that walk by.
Answer:
biased sampling.
Explanation:
A sampling method is called biased if it systematically favors some outcomes over others.
Jordan wants to know which restaurant makes the best burger in town.
He stands on a block between two different burger restaurants at dinner time and asks the first 25 people that walk by, is biased sampling.
When sampling a data set, there are several approaches that can be used to create a random sample.
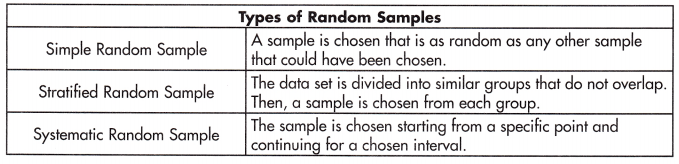
There are also different ways of creating a biased sample.
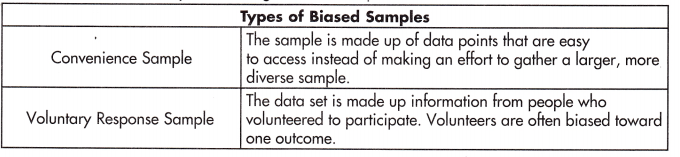
Name the type of sampling used in each situation.
Question 1.
At a factory, every 100th piece is taken off the assembly line to be inspected.
Answer:
systematic random sample.
Explanation:
Systematic random sampling :
The sample is chosen staring from a specific point and continuing for a chosen interval.
At a factory, every 100th piece is taken off the assembly line to be inspect is systematic random sampling.
Question 2.
A reporter for the school newspaper asks 10 students in the cafeteria who would make the best student council president.
Answer:
simple random sample.
Explanation:
In a simple random sample, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
In sampling frame should include the whole population.
A reporter for the school newspaper asks 10 students in the cafeteria who would make the best student council president is simple random sample.
Question 3.
Your math teacher calls on every 3rd name alphabetically to answer questions.
Answer:
systematic random sample.
Explanation:
Systematic random sampling :
The sample is chosen staring from a specific point and continuing for a chosen interval.
Systematic sampling is similar to simple random sampling, but it is usually slightly easier to conduct.
Every member of the population is listed with a number,
but instead of randomly generating numbers, individuals are chosen at regular intervals.
Math teacher calls on every 3rd name alphabetically to answer questions is systematic random sample.
Question 4.
15 students from your school get to represent your school at a news conference. Everybody’s names are put in a box by grade level and 5 names are drawn from each box.
Answer:
stratified random sample.
Explanation:
Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subpopulations that may differ in important ways.
It allows you draw more precise conclusions by ensuring that every subgroup is properly represented in the sample.
15 students from your school get to represent your school at a news conference.
Everybody’s names are put in a box by grade level and 5 names are drawn from each box is stratified random sample.
Question 5.
Shana announces to her class that she wants to know which new movie is their favorite. She calls on the first 10 people to raise their hands.
Answer:
voluntary random sample.
Explanation:
The data set is made up information from people who volunteered to participate.
Volunteers are often biased toward one outcome.
Shana wants to know which new movie is their favorite.
She calls on the first 10 people to raise their hands is voluntary random sample.