We included HMH Into Math Grade 8 Answer Key PDF Module 11 Lesson 2 Prove the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 8 Module 11 Lesson 2 Answer Key Prove the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
I Can prove the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem and use it to determine if a triangle is a right triangle, and I can determine whether three side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Spark Your Learning
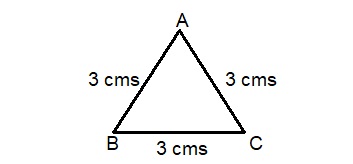
Previously, you used the Pythagorean Theorem equation with right triangles. Does the equation hold true for other types of triangles? Draw a non-right triangle and investigate.

Answer:
No, the equation will not hold true for other types of triangles,
Explanation:
Pythagorean theorem is used in only right angled triangles, So the equation will not hold true for other types of triangles, “Law of Cosines” that extends the Pythagorean theorem to
non-right-triangles by adding in a correction term. It says: If a, b, c are the sides of any triangle and C is the angle opposite side c, then a2 + b2 = c2 – 2ab cosC. Now lets take equilateral triangle where all sides are equal, Now applying Pythagorean Theorem ac2 = ab2 + bc2,
so ac2 = 32 + 32, ac2 = 9 + 9 = 18, now ac is equal to square root of 18 which is 4.24 which is not equal to 3 cms so Pythagorean theorem will not hold true for other types of triangles.
Turn and Talk Which type of triangle did you draw? Did the Pythagorean Theorem equation hold true?
Answer:
Equilateral triangle, No,
Explanation:
The type of triangle I did draw is Equilateral triangle, No, the Pythagorean Theorem
equation does not hold true as ac2 ≠ ab2 + bc2, 32 ≠ 32 + 32.
Build Understanding
Consider this statement: If I am in this class, then I am in the 8th grade. The converse of this statement is: If I am in the 8th grade, then I am in this class. The converse of a theorem reverses the hypothesis and the conclusion.

The Pythagorean Theorem states:
If a triangle is a right triangle, then the sum of the squares of the shorter sides is equal to the square of the longest side.
The converse of that statement is:
If the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides of a triangle is equal to the square of the longest side, then the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 1.
Show that, given a triangle ABC with side lengths a, b, and c, if a2 + b2 = c2, then the triangle is a right triangle with a right angle at C.
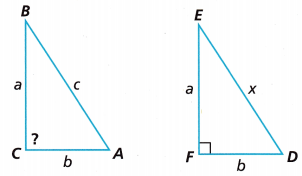
A. Let Triangle DEF be a triangle such that EF = a, DF = b, DE = x, and F is a right angle. We need to show that Triangles ABC and DEF are congruent.
Answer:
EF = a = BC, DF = b = CA, DE = x = AB and F, C are right angle,
ABC and DEF are congurent,
Explanation:
Congurent triangles :
1. If three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
2. If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
3. If two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
4. If two angles and the non-included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and
side of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
5. If the hypotenuse and one leg of one right-angled triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of another right-angled triangle, the two triangles are congruent.
As EF = a = BC,DF = b = CA, DE = x = AB and F, C are right angle,
So ABC and DEF are congurent,
B. Can we apply the Pythagorean Theorem to Triangle DEF1 Why or why not? If so, what can we conclude?
Answer:
Yes, a2 + b2 = x2,
Explanation:
As triangle DEF is a triangle such that EF = a, DF = b, DE = x, and F is a right angle,
Yes we can apply pythagorean theorem as it is right traingle therefore we conclude that a2 + b2 = x2.
C. How can we relate x to c?
Answer:
As it is hypotenuse side so x = c,
Explanation:
In triangle DEF a right triangle we relate x to c because in pythagorean theorem c is longest side and hypotenuse and in DEF x is longest side and hypotenuse side so x = c.
D. What can you conclude about the measure of Angle C? Explain, and include the classification for Triangle ABC.
Answer:
Angle C = 900 is right angle,
Explanation:
As triangles ABC and DEF are congruent and so we have EF = a = BC, DF = b = CA, DE = x = AB and F, C are right angle, Therefore angle F = angle C = 900 is right angle.
Step It Out
Question 2.
Given each set of side lengths, determine whether each triangle is a right triangle.

A. Side a measures 4 inches.
Side b measures 6 inches.
Side c measures 8 inches.
a2 + b2 = c2
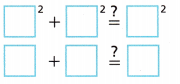
Circle the correct answers to complete the sentence.
The square of a plus the square of b (does / does not) equal the square of c, so the triangle (is/is not) a right triangle.
Answer:

Explanation:
Circled the correct answers and completed the sentence as the square of a plus the square of b does not equal the square of c, so the triangle is not a right triangle.
B. Side a measures 5 inches.
Side b measures 12 inches.
Side c measures 13 inches.
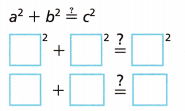
Circle the correct answers to complete the sentence.
The square of a plus the square of b (does / does not) equal the square of c, so the triangle (is/is not) a right triangle.
Answer:
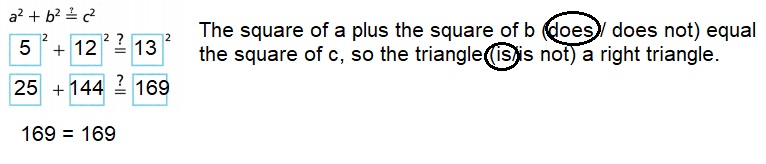
Explanation:
Circled the correct answers and completed the sentence as the square of
a plus the square of b does equal the square of c, so the triangle is a right triangle.
C. Side a measures 9 miles.
Side b measures 9 miles.
Side c measures 9 miles.
Circle the correct answers to complete the sentence.
The square of a plus the square of b (does/does not) equal the square of c, so the triangle (is / is not) a right triangle.
Answer:

Explanation:
Circled the correct answers and completed the sentence as the square of a plus the square of b does not equal the square of c, so the triangle is not a right triangle.
Turn and Talk Given the side lengths of a triangle, how can you determine whether it is a right triangle or not?
Answer:
If the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of
the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle,
Explanation:
If the side lengths of a triangle are given then the square of the length of the longest side of a
triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 3.
Determine whether each set of measurements is a Pythagorean triple. Remember, a Pythagorean triple is a set of three integers that can be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle.
A. Side a measures 5 inches.
Side b measures 16 inches.
Side c measures 20 inches.
Are the side lengths integers?
Does a2 + b2 = c2?
Is the triangle a right triangle?
This (is /is not) a Pythagorean triple.
Answer:
Yes, the side lengths are integers, 52 + 162 ≠ 202, Not a right triangle,
This is not a Pythagorean triple,
Explanation:
Given side a measures 5 inches, Side b measures 16 inches,
Side c measures 20 inches, The side lengths are integers as an integer is a number
with no decimal or fractional part, from the set of negative and positive numbers including zero.
As 52 + 162 = 25 + 256 = 281 ≠ 202 ≠ 400,
Therefore not a right triangle and not a Pythagorean triple.
B. Side a measures \(\sqrt {3}\) inches.
Side b measures \(\sqrt {4}\) inches.
Side c measures \(\sqrt {7}\) inches.
Are the side lengths integers?
Does a2 + b2 = c2?
Is the triangle a right triangle?
This (is / is not) a Pythagorean triple.
Answer:
Yes, the side lengths are integers, \(\sqrt {3}\)2 + \(\sqrt {4}\) 2 = \(\sqrt {7}\)2, A right triangle and a Pythagorean triple,
Explanation:
Given side a measures \(\sqrt {3}\) inches.
Side b measures \(\sqrt {4}\) inches. Side c measures \(\sqrt {7}\) inches.
The side lengths are integers as an integer is a number with no decimal or fractional part, from the set of negative and positive numbers including zero.
As \(\sqrt {3}\)2 + \(\sqrt {4}\) 2 = \(\sqrt {7}\)2,
3 + 4 = 7, So the triangle is a right triangle and a Pythagorean triple.
Check Understanding
For Problems 1-2, determine whether each set of measurements is a Pythagorean triple.
Question 1.
Side a measures 7 inches.
Side b measures 24 inches.
Side c measures 25 inches.
Are the side lengths integers?
Does a2 + b2 = c2?
Is the triangle a right triangle?
Is the triple a Pythagorean triple?
Answer:
Yes, the side lengths are integers, 72 + 242 = 252, Is a right triangle,
This is a Pythagorean triple,
Explanation:
Given side a measures 7 inches, Side b measures 24 inches,
Side c measures 25 inches, The side lengths are integers as an integer is a number
with no decimal or fractional part, from the set of negative and positive numbers including zero.
As 72 + 242 = 252, 49 + 576 = 625, As 625 = 625,
Is a right triangle and a Pythagorean triple.
Question 2.
Side a measures \(\sqrt {3}\)inches.
Side b measures 2 inches.
Side c measures \(\sqrt {7}\) inches.

Are the side lengths integers?
Does a2 + b2 = c2?
Is the triangle a right triangle?
Is the triple a Pythagorean triple?
Answer:
Yes, the side lengths are integers, \(\sqrt {3}\)2 + 22 = \(\sqrt {7}\)2,
A right triangle and a Pythagorean triple,
Explanation:
Given side a measures \(\sqrt {3}\) inches. Side b measures 2 inches.
Side c measures \(\sqrt {7}\) inches. The side lengths are integers as an integer is a number
with no decimal or fractional part, from the set of negative and positive numbers including zero.
As \(\sqrt {3}\)2 + 22 = \(\sqrt {7}\)2, 3 + 4 = 7, So the triangle is a right triangle and a Pythagorean triple.
On Your Own
Question 3.
STEM A high school is converting an entry staircase into a ramp to increase accessibility. The entrance door is 7 feet off the ground. By law, a ramp this height needs to start 24 feet away from the building. If the length of the ramp is 25 feet, will the ramp form a right triangle with the building?
A. Fill in the measurements on the illustration shown.
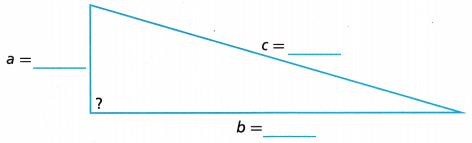
Answer:
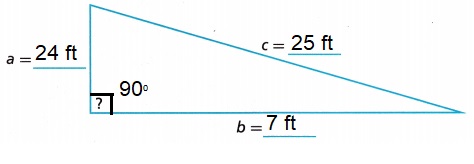
Explanation:
Given a high school is converting an entry staircase into a ramp to increase accessibility.
The entrance door is 7 feet off the ground.
By law, a ramp this height needs to start 24 feet away from the building. If the length of the ramp
is 25 feet, Yes, the ramp form a right triangle with the building,
as 72 + 242 = 252, 49 + 576 = 625, 625 = 625. Filled in the measurements on the illustration
as shown above.
B. Determine whether the ramp forms a right triangle.
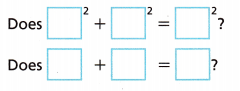
By the _____________, since the sum of the squares of the leg lengths equals the square of the hypotenuse length, the ramp __________ form a right triangle.
Answer:
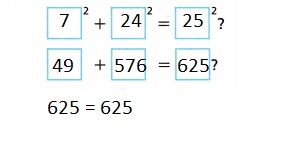
By the measurements, since the sum of the squares of the leg lengths equals the square of the hypotenuse length, the ramp will form a right triangle,
Explanation:
As 72 + 242 = 252, 49 + 576 = 625, 625 = 625. By the measurements,
Since the sum of the squares of the leg lengths equals the square of the hypotenuse length,
the ramp will form a right triangle.
For Problems 4-9, determine whether each set of side lengths form a right triangle.
Question 4.
4, 5, and 6 _______________
Answer:
Not form a right triangle 42 + 52 ≠ 62,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 4,5 and 6 we apply, Pythagorean theorem as 42 + 52 =
16 + 25 = 41 ≠ 62 ≠ 36, So not form a right triangle.
Question 5.
5, 12, and 13 _______________
Answer:
Form a right triangle,
52 + 122 = 132,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 5,12 and 13 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 52 + 122 =
25 + 144 = 169 = 132 = 169, So form a right triangle.
Question 6.
8, 15, and 17 _______________
Answer:
Form a right triangle 82 + 152 = 172,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 8,15 and 17 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 82 + 152 =
64 + 225 = 289 = 172 = 289, So form a right triangle.
Question 7.
5, 8, and 12 _______________
Answer:
Not form a right triangle 52 + 82 ≠ 122
Explanation:l
Given side lengths as 5,8 and 12 we apply Pythagorean theorem as
52 + 82 = 25 + 64 = 89 ≠ 122 ≠ 144, So not form a right triangle.
Question 8.
6, 8, and 10 _______________
Answer:
Form a right triangle 62 + 82 = 102,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 6,8 and 10 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 62 + 82 =
36 + 64 = 100 = 102 = 100, So form a right triangle.
Question 9.
9, 40, and 41 _______________
Answer:
Form a right triangle 92 + 402 = 412,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 9,40 and 41 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 92 + 402 =
81 + 1,600 = 1,681 = 412 = 1,681 So form a right triangle.
Question 10.
Open-Ended List one set of three side lengths not used in Problems 4-9 that form a right triangle, and one set that form a triangle but not a right triangle.
Answer:
1. Form a right triangle: 20, 21 and 29,
2. Form a triangle but not a right triangle: 7, 11 and 14,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 20,21 and 29 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 202 + 212 =
400 + 441 = 841 = 292 = 841, So form a right triangle and 7, 11 and 14 form a triangle but not a right triangle as we apply Pythagorean theorem as 72 + 112 = 49 + 121 = 170 ≠ 142 ≠ 196, So not form a right triangle but form a triangle.
Question 11.
Use each number from the box exactly once to complete each Pythagorean triple.
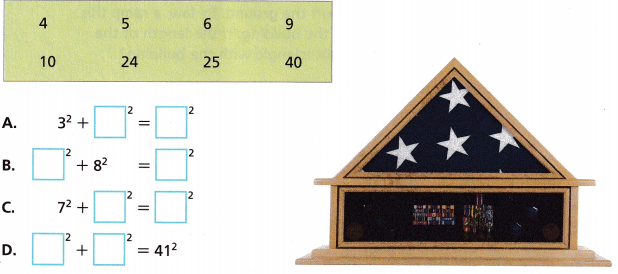
Answer:
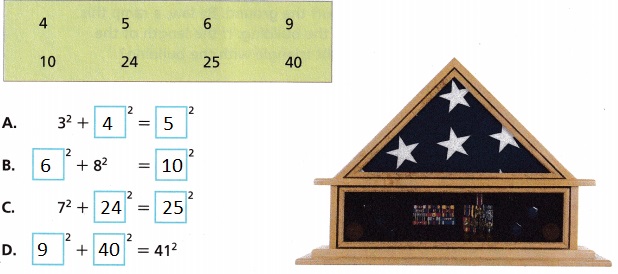
Explanation:
Given to use each number from the box exactly once to complete each Pythagorean triple so done as
A. 32 + 42 = 52, 9 + 16 = 25 =25,
B. 62 + 82 = 102, 36 + 64 = 100 = 100,
C. 72 + 242 = 252, 49 + 576 = 625 = 625,
D. 92 + 402 = 412, 81 + 1,600 = 1,681 = 1,681.
Question 12.
Determine whether each set of three side lengths forms a right triangle.
A. 9, 12, and 15
Answer:
Form a right triangle 92 + 122 = 152,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 9,12 and 15 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 92 + 122 =
81 + 144 = 225 = 152 = 225, So form a right triangle.
B. 1.5, 2, and 2.5
Answer:
Form a right triangle 1.52 + 22 = 2.52,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 1.5, 2 and 2.5 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 1.52 + 22 =
2.25 + 4 = 6.25 = 2.52 = 6.25, So form a right triangle.
C. 12, 35, and 37
Answer:
Form a right triangle 122 + 352 = 372,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 12, 35 and 37 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 122 + 352 =
144 + 1,225 = 1,369 = 372 = 1,369, So form a right triangle.
D. 8, 11, and 13
Answer:
Not form a right triangle 82 + 112 ≠ 132,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 8,11 and 13 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 82 + 112 =
64 + 121 = 185 ≠ 132 ≠ 169, So not form a right triangle.
E. 7, 10, and 12
Answer:
Not form a right triangle 72 + 102 ≠ 122,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 7,10 and 12 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 72 + 102 =
49 + 100 = 149 ≠ 122 ≠ 144, So not form a right triangle.
F. 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5
Answer:
Form a right triangle 0.32 + 0.42 = 0.52,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 0.32 + 0.42 = 0.09 + 0.16 = 0.25 = 0.52 = 0.25, So form a right triangle.
G. Construct Arguments Consider which of these sets of side lengths forms a right triangle. Which set(s) of lengths do not form a Pythagorean triple? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Forms right triangle:
A. 9, 12, and 15, B. 1.5, 2, and 2.5 C. 12, 35, and 37 and F. 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5,
Do not form a Pythagorean triple: D. 8, 11, and 13, E. 7, 10, and 12,
Explanation:
As Pythagorean theorem states that for all right-angled triangles,
‘The square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides’. So all these sets forms right triangle: A. 9, 12, and 15, B. 1.5, 2, and 2.5, C. 12, 35, and 37 and
F. 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 and sets do not form a Pythagorean triple: D. 8, 11, and 13 and E. 7, 10, and 12.
I’m in a Learning Mindset!
How did I apply the feedback I was given about the Pythagorean Theorem to my understanding of the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem?
Answer:
The converse of the Pythagorean theorem is used to determine if the given
triangle is a right triangle or not,
Explanation:
The converse of the Pythagorean theorem states that for a triangle, if the square of the largest side is equal to the sum of the squares of the two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle.
This means that the converse of the Pythagorean theorem is used to determine if the triangle
given is a right triangle or not.
Lesson 11.2 More Practice/Homework
Question 1.
Given the side lengths, determine whether or not they form a right triangle.
Side a measures 36 inches.
Side b measures 77 inches.
Side c measures 85 inches.
This triangle __________ a right triangle because _______________.
Answer:
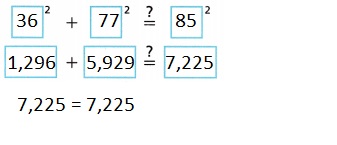
This triangle form a right triangle because of Pythagorean theorem,
Explanation :
Given the side lengths, to determine whether or not they form a right triangle. Side a measures 36 inches Side b measures 77 inches, Side c measures 85 inches,
As Pythagorean theorem is true as we apply Pythagorean theorem as 362 + 772 =
1,296 + 5,929 = 7,225 = 852 = 7,225, So form a right triangle.
Question 2.
Determine whether the set of measurements is a Pythagorean triple.

Side a measures 5 feet.
Side b measures 16 feet.
Side c measures 20 feet.
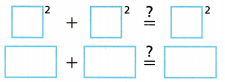
Is this a Pythagorean triple? ___________
Answer:
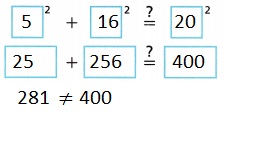
Not a Pythagorean triple,
Explanation:
Given side a measures 5 feet, side b measures 16 feet side c measures 20 feet. We apply
Pythagorean theorem as 52 + 162 = 25 + 256 = 281 ≠ 202 ≠ 400, So not form a right triangle or
Pythagorean triple.
Question 3.
Critique Reasoning Winston says that a triangle with side lengths measuring 25, 36, and 64 must be a right triangle because all of the sides are perfect squares. Is he correct? Why or why not?
Answer:
No Winston is incorrect 252 + 362 ≠ 642, Not a right triangle,
Explanation:
Given Winston says that a triangle with side lengths measuring 25, 36, and 64 must be a right triangle
because all of the sides are perfect squares.
He is incorrect as we apply Pythagorean theorem 252 + 362 = 625 + 1,296 = 1,921 ≠ 642 ≠ 4,096,
So not form a right triangle.
Question 4.
Math on the Spot Lynnette is buying a triangular parcel of land. If the lengths of the three sides are 300 yards, 400 yards, and 500 yards, will the parcel of land have a right angle? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, the parcel of land have a right angle,
Explanation:
Given Lynnette is buying a triangular parcel of land.
If the lengths of the three sides are 300 yards, 400 yards and
500 yards applying Pythagorean theorem as 3002 + 4002 =
90,000 + 160,000 = 250,000 = 5002 = 250,000,
So form a right triangle. Therefore the parcel of land have a right angle.
For Problems 5-8, determine whether each set of three side lengths could form a right triangle.
Question 5.
10, 24, and 26
Answer:
Form a right triangle 102 + 242 = 262,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 10, 24 and 26 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 102 + 242 =
100 + 576 = 676 = 262 = 676, So form a right triangle.
Question 6.
8, 16, and 24
Answer:
Not form a right triangle 82 + 162 ≠ 242,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 8,16 and 24 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 82 + 162 =
64 + 256 = 320 ≠ 242 ≠ 576, So not form a right triangle.
Question 7.
5, 5, and 5
Answer:
Not form a right triangle,
52 + 52 ≠ 52,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 5,5 and 5 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 52 + 52 = 25 + 25 = 50 ≠ 52 ≠ 25, So not form a right triangle.
Question 8.
20, 21, and 29
Answer:
Form a right triangle 202 + 212 = 292,
Explanation:
Given side lengths as 20, 21 and 29 we apply Pythagorean theorem as 202 + 212 =
400 + 441 = 841 = 292 = 841, So form a right triangle.
Test Prep
Question 9.
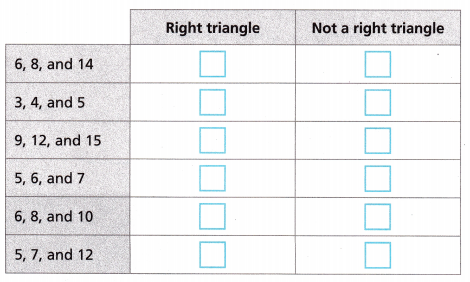
Identify in the table whether the measurements could be the side lengths of a right triangle or not.
Answer:
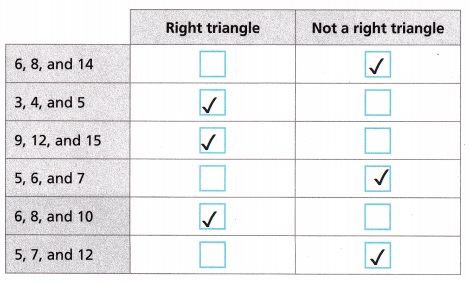
Explanation:
Given to identify in the table whether the measurements could be the side lengths of a right triangle or not, So Applying Pythagorean theorem as 1. 6, 8 and 14, 62 + 82 = 102,
36 + 64 = 100 ≠ 142 ≠ 196, Not a right triangle, 2. 3, 4 and 5, 32 + 42 = 52,
9 + 16 = 25 = 52 = 25, Is a right triangle 3. 9, 12 and 15, 92 + 122 = 152,
81+ 144 = 225 = 152 = 225, Is a right triangle 4. 5, 6 and 7, 52 + 62 = 72,
25 + 36 = 61 ≠ 72 ≠ 49, Not a right triangle, 5. 6, 8 and 10, 62 + 82 = 102,
36 + 64 = 100 = 102 = 100, Is a right triangle and 6. 5, 7 and 12, 52 + 72 = 122,
25 + 49 = 74 ≠ 122 ≠ 144, Not a right triangle and identified the given table above.
Question 10.
Which of the following are Pythagorean triples? Select all that apply.
(A) 12, 16, 20
(B) 10, 12, \(\sqrt {19}\)
(C) 21, 28, 35
(D) 7, 14, 21
(E) 5, 10, 15
(F) 4, 14, 25
(G) 1, 2, \(\sqrt {5}\)
Answer:
(A) 12, 16, 20,
(C) 21, 28, 35 and
(G) 1, 2, \(\sqrt {5}\),
Explanation:
Checking which of the following are Pythagorean triples as Pythagorean theorem states that the sum of the squares on the other two sides is equal to the square on the hypotenuse,
Checking with bit (A) 12, 16, 20, 122 + 162 = 202,
144 + 256 = 400 = 202 = 400, Is a Pythagorean triple,
Checking with bit (B) 10, 12, \(\sqrt {19}\),
102 + 122 = \(\sqrt {19}\)2, 100 + 144 = 244 ≠ \(\sqrt {19}\)2 ≠ 19,
Is not a Pythagorean triple, Checking with bit (C) 21, 28, 35, 212 + 282 = 352,
441 + 784 = 1,225 = 352 = 1,225, Is a Pythagorean triple, Checking with bit (D) 7, 14, 21,
72 + 142 = 212, 49 + 196 = 245 ≠ 212 ≠ 441 Is not a Pythagorean triple,
Checking with bit (E) 5, 10, 15, 52 + 102 = 152, 25 + 100 = 125 ≠ 152 ≠ 225,
Is not a Pythagorean triple, Checking with bit (F) 4, 14, 25, 42 + 142 = 252,
16 + 196 = 212 ≠ 252 ≠ 625, Is not a Pythagorean triple, Checking with bit (G) 1, 2, \(\sqrt {5}\), 12 + 22 = \(\sqrt {5}\)2, 1 + 4 = 5 = \(\sqrt {5}\)2 = 5,
Is a Pythagorean triple, therefore following are Pythagorean triples bits (A) 12, 16, 20,
(C) 21, 28, 35 and (G) 1, 2, \(\sqrt {5}\).
Question 11.
Amber claims a triangle with sides measuring 3 inches, 6 inches, and 9 inches is a right triangle because 3 + 6 = 9. Explain her error.
Answer:
Error is it must be true for 32 + 62 = 92 not 3 + 6 = 9,
Explanation:
Given Amber claims a triangle with sides measuring 3 inches, 6 inches, and 9 inches is a right triangle
because 3 + 6 = 9. But is error as if its as right triangle according to Pythagorean theorem the sum of the squares on the other two sides is equal to the square on the hypotenuse, So it should be 32 + 62 = 92 not 3 + 6 = 9.
Question 12.
The square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 625. Which could be the side lengths?
(A) 4 and 27
(B) 49 and 576
(C) 100 and 525
(D) 7 and 24
Answer:
(D) 7 and 24,
Explanation:
Given the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 625.
The side lengths could be applying Pythagorean theorem
and checking with bit (A) 4 and 27, 42 + 272 = 16 + 729 = 745 ≠ 252 ≠ 625,
checking with bit (B) 49 and 576, 492 + 5762 = 2,401 + 331,776 = 334,177 ≠ 252 ≠ 625,
checking with bit (C) 100 and 525, 1002 + 5252 = 10,000 + 275,625 = 285,625 ≠ 252 ≠ 625,
checking with bit (D) 7 and 24, 72 + 242 = 49 + 576 = 625 = 252 = 625,
therefore bit (D) 7 and 24 could be the side lengths.
Spiral Review
Question 13.
Which of {10, \(3 . \overline{31}\), 4.2123417 ……, \(\frac{16}{3}\)} are rational, and which are irrational?
Answer:
10, \(\frac{16}{3}\) are rational and \(3 . \overline{31}\), 4.2123417 are irrational,
Explanation:
Rational : A rational number is any number that can be written as a fraction, where both the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number)
are integers and the denominator is not equal to zero or p/q form,
Irrational : Irrational numbers are those real numbers that cannot be represented in the form of a ratio. In other words, those real numbers that are not rational numbers are known as irrational numbers. Irrational numbers consist of non-terminating and non-recurring decimals,
therefore 10, \(\frac{16}{3}\) are rational and \(3 . \overline{31}\), 4.2123417 are irrational.
Question 14.
Charles placed a number of identical blocks on a table in a square shape with no gaps or holes. What is a possible number of blocks that could have been used? Explain how you know.
Answer:
4 blocks,
Explaantion:
Given Charles placed a number of identical blocks on a table in a square shape with no gaps or holes.
Let n be the possible number of blocks that could have been used are as perimeter of square is 4 X side, 4 X 1 = 4, So number of blocks n = 4.