We included HMH Into Math Grade 7 Answer Key PDF Module 7 Lesson 5 Two-Step Equations to Find Angle Measures to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 7 Module 7 Lesson 5 Answer Key Two-Step Equations to Find Angle Measures
I Can identify angle relationships, and use them to write and solve equations.
Step It Out
You previously learned that a right angle measures 90°. In this lesson, you will also work with pairs of angles called complementary angles and supplementary angles.
Connect to Vocabulary
Two angles whose measures have a sum of 90° are called complementary angles. Two angles whose measures have a sum of 1800 are called supplementary angles.
Question 1.
Use the diagram for Parts A-H.
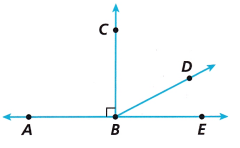
A. Name the right angles. ∠ ____________ and ∠ ____________
Answer:
∠CBE and ∠CBA
Explanation:
The right angles are ∠CBE and ∠CBA.
B. Name a pair of complementary angles. ∠ ____________ and ∠ ____________
Answer:
∠DBE and ∠CBD.
Explanation:
A pair of complementary angles. ∠DBE and ∠CBD.
C. What is the measure of ∠ABE? ____________
Answer:
∠180°
Explanation:
The measure of ∠ABE is ∠180°
D. Name a pair of supplementary angles.
∠____________ and ∠ _____________
Answer:
∠ABD and ∠CBE.
Explanation:
A pair of supplementary angles is ∠ABD and ∠CBE.
E. If the measure of ∠CBD is equal to (5x)° and the measure of ∠DBE is 40°, use what you know about complementary angles to write an equation to solve for x. Then solve it.
![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]()
x = ![]()
Answer:
x = 10°
Explanation:
Given,
∠CBD = 5x° and ∠DBE is 40°
∠CBD + ∠DBE = 90°
5x° + 40° = 90°
5x° = 90 – 40
5x° = 50°
x = 50°÷ 5
x = 10°
F. If the measure of ∠ABD is (5y + 15)° and the measure of ∠DBE is 40°, write an equation and solve for y.
![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]()
y = ![]()
Answer:
y = 25°
Explanation:
Given,
∠ABD = (5y + 15)° and ∠DBE is 40°
∠ABD + ∠DBE = 180°
(5y + 15) + 40° = 180°
5y + 15 = 180 – 40
5y + 15 = 140
5y = 140 – 15
5y = 125°
y = 125° ÷ 5
y = 25°
Turn and Talk If ∠ABD were the only known angle measure, how could you determine the measures of the other angles in the diagram?
Answer:
∠ABD was given, ∠ABC = 90° we can find ∠DBE
∠ABD + ∠ABC + ∠DBE = 180°
With these measures of angles, we can find angles in the diagram.
Question 2.
Use Figure 1 for Parts A-C and Figure 2 for Parts D-F.
Connect to Vocabulary
Vertical angles are opposite angles formed by intersecting lines. Vertical angles are congruent.
A. Name two pairs of vertical angles.
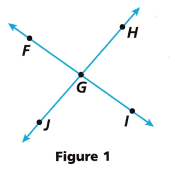
∠____________ and ∠ _____________
∠ ___________ and ∠ ____________
Answer:
∠FGJ and ∠HGI
∠FGH and ∠JGI
Explanation:
The two pairs of vertical angles are ∠FGJ and ∠HGI, ∠FGH and ∠JGI
B. Vertical angles (are / are not) congruent.
Answer:
Vertical angles are congruent.
C. Given ∠FGH measures (6x – 24)° and ∠JGl measures 96°, write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x. Solve for x.
![]() =
= ![]() and x =
and x = ![]()
Answer:
Given,
(6x – 24)° = 96°
Let us solve the equation
6x – 24 = 96
6x = 96 + 24
6x = 120
x = 120 ÷ 6
x = 20
D. Name a pair of adjacent angles in Figure 2.
Answer:
∠FGB and ∠BGJ are a pair of adjacent angles.
Connect to Vocabulary
The word adjacent means “next to” or “connected to.” Adjacent angles are two angles in the same plane with a common vertex and a common side, but no common interior points.
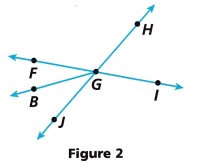
∠ __________ and ∠ __________
Answer:
∠FGB and ∠BGJ are adjacent angles.
E. Given m∠FGJ = 84°, m∠FGB = (4x)°, and m∠JGB (5x + 3)°, write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x. Solve for x.
 +
+ ![]() =
=  and x =
and x = 
Answer:
The value of x = 9
4x = 36°
(5x + 3) = 48°
Explanation:
Given,
m∠FGJ = 84°, m∠FGB = (4x)° and m∠JGB (5x + 3)°
m∠FGB + m∠JGB = m∠FGJ
4x° + (5x + 3)° = 84°
4x + 5x + 3 = 84
9x + 3 = 84
9x = 84 – 3
9x = 81
x = 81 ÷ 9
x = 9°
4x = 4 × 9 = 36°
(5x + 3) = ((5 × 9) + 3)
= 45 + 3
= 48°
F. Explain why ∠FGJ and ∠FGB are not adjacent.
Answer:
Adjacent angles must be next to each other and they do share a common line but the given angles overlap each other. Hence ∠FGJ and ∠FGB are not adjacent.
Turn and Talk Explain why ∠FGB does not have a vertical angle in Figure 2.
Answer:
When two lines meet each other at a point that is called a vertical angle. The angle ∠FGB does not meet at any point. So ∠FGB does not have a vertical angle.
Question 3.
In Figure 3, ∠AOD measures (3x + 15)°.
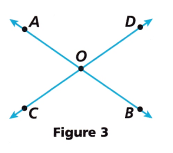
A. What is the sum of the measures of ∠AOD and ∠DOB?
Answer:
The sum of the measures of ∠AOD and ∠DOB is 25°.
Explanation:
Given ∠AOD = (3x + 15)° ∠DOB = 90°
We need to find the sum of the measures of ∠AOD and ∠DOB.
∠AOD + ∠DOB = 180°
(3x + 15)° + 90° = 180°
(3x + 15)° = 180° – 90°
(3x + 15)° = 90°
3x = 90° – 15°
3x = 75°
x = 75 ÷ 3
x = 25°
B. If the measure of ∠DOB is (2x + 15)°, write an equation to determine the value of x.
![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]()
Answer:
(2x + 15)° + (3x + 15)° = 90°
Explanation:
Given,
∠DOB = (2x + 15)°
∠AOD = (3x + 15)°
Sum of complimentary angles = 180
∠DOB + ∠AOD = 180°
(2x + 15)° + (3x + 15)° = 180°
C. Solve for x.
x = ___________
Answer:
x = 30°
Explanation:
∠DOB + ∠AOD = 180°
(2x + 15)° + (3x + 15)° = 180°
2x + 3x + 15 + 15 = 180°
5x + 30 = 180
5x = 180 – 30
5x = 150
x = 150 ÷ 5
x = 30°
D. What is the measure of ∠AOD?
Answer:
∠AOD = 105°
Explanation:
∠AOD = (3x + 15)°
∠AOD = ((3 × 30)) + 15
∠AOD = 90 + 15
∠AOD = 105°
E. What angle makes vertical angles with ∠AOD? What is its measure?
m ___________ = ____________
Answer:
∠BOC and its measure is 105°.
Explanation:
The angle that makes vertical angles with ∠AOD is ∠BOC.
F. What two angles are adjacent to ∠AOD? What are their angle measures?
m ___________ = _____________
m ___________ = ____________
Answer:
∠AOC = 75° and ∠DOB = 75°
Explanation:
Given,
∠DOB = (2x + 15)°
x = 30°
(2 × 30) + 15
60 + 15 = 75
∠DOB = 75°
Check Understanding
Question 1.
Two angles are complementary. The first angle measures (2x + 15)°, and the second measures (4x + 9)°. Write an equation to determine the value of x. Then solve your equation and find the measures of both angles.
Answer:
x = 11°, (2x + 15)° = 37° and (4x + 9)° = 53°
Explanation:
Given,
First angle = (2x + 15)° and second angle = (4x + 9)°
And the two angles are complementary
(2x + 15)° + (4x + 9)° = 90°
2x + 4x + 15 + 9 = 90°
6x + 24 = 90°
6x = 90 – 24
6x = 66
x = 66 ÷ 6
x = 11°
First angle = (2x + 15)°
= (2 × 11) + 15
= 22 + 15
= 37°
Second angle = (4x + 9)°
= (4 × 11) + 9
= 44 + 9
= 53°
Question 2.
∠A and ∠B are adjacent. The sum of their measures is 92°. ∠A measures (2x + 5)°. ∠B is three times the size of ∠A. Write an equation to determine the value of x. Then solve your equation and find the measures of both angles.
Answer:
x = 9°, ∠A = 23° and ∠B = 69°
Explanation:
Given,
∠A = (2x + 5)°, ∠B = 3(2x + 5)°
The sum of their measures is 92°
∠A + ∠B = 92°
(2x + 5)° + 3(2x + 5)° = 92°
(2x + 5)° + 6x + 15 = 92°
2x + 6x + 5 + 15 = 92°
8x + 20 = 92°
8x = 92° – 20
8x = 72
x = 72 ÷ 8
x = 9°
∠A = (2x + 5)°
= (2 × 9) + 5
= 18 + 5
= 23°
∠B = 3(2x + 5)°
= 6x + 15
= (6 × 9) + 15
= 54 + 15
= 69°
On Your Own
Question 3.
Angles A and B are adjacent angles and are supplementary. The measure of ∠A is (3x + 10)°, and the measure of ∠B is (12x + 35)°.
A. Write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x.
Answer:
∠A + ∠B = 180°
(3x + 10)° + (12x + 35)° = 180°
Explanation:
An equation that can be used to determine the value of x is (3x + 10)° + (12x + 35)° = 180°.
B. What is the value of x?
Answer:
The value of x is 9°
Explanation:
Given equation is
(3x + 10)° + (12x + 35)° = 180°
3x + 12x + 10 + 35 = 180°
15x + 45° = 180°
15x = 180° – 45°
15x = 135°
x = 135° ÷ 15
x = 9°
C. What is the measure of ∠A?
Answer:
∠A = 37°
Explanation:
Given,
∠A = (3x + 10)°
x = 9°
= (3 × 9) + 10
= 27 + 10
= 37°
Question 4.
Describe ∠COA in relation to ∠DOB
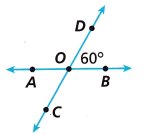
Answer:
∠COA and ∠DOB are vertically opposite angles.
∠DOB = 60°
Therefore ∠COA = ∠DOB
∠COA = 60°
Question 5.
Attend to Precision ∠A is complementary to ∠B. The measure of ∠A is (8x + 12)°. The measure of ∠B is half the measure of ∠A. Write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x. Then solve for x.
Answer:
x = 6
Explanation:
∠A is complimentry to ∠B
∠A + ∠B = 90°
∠A = (8x + 12)°, ∠B = (8x + 12) ÷ 2
∠B = (4x + 6)
(8x + 12) + (4x + 6) = 90°
8x + 4x + 12 + 6 = 90°
12x + 18 = 90°
12x = 90° – 18°
12x = 72°
x = 72 ÷ 12
x = 6°
For Problems 6-7, use Figure 4.
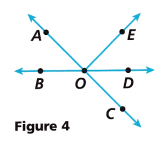
Question 6.
Describe the relationship between ∠BOC and ∠COD. What is the sum of their angle measures?
Answer:
∠BOC and ∠COD are adjacent angles.
The sum of their angle is ∠BOC + ∠COD = 180°
Question 7.
Describe the relationship between ∠AOB and ∠COD. Are their measures equal?
Answer:
∠AOB and ∠COD are vertically opposite angles. And their measures are equal.
Question 8.
STEM A rocket blasts off at a 90° angle from Earth. A second rocket launches at a different angle as shown in the diagram.
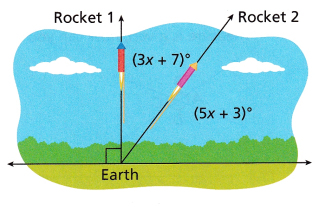
A. Write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x.
Answer:
(3x + 7) + (5x + 3) = 90°
B. What is the value of x?
Answer:
x = 10°
Explanation:
Given equation
(3x + 7) + (5x + 3) = 90°
Let us solve the given equation
3x + 5x + 7 + 3 = 90°
8x + 10 = 90°
8x = 90 – 10
8x = 80°
x = 80 ÷ 8
x = 10°
C. What is the measure of the angle of the second rocket launch in relation to Earth?
Answer:
The measure of the angle of the second rocket launch in relation to Earth is 53°
Explanation:
Given angle for second rocket is (5x + 3)
x = 10°
(5x + 3) = (5 × 10) + 3
= 50 + 3
= 53°
Question 9.
Two lines intersect to form an X. The measure of one angle is 58°.
A. What is the measure of one of the angles sharing a side with the 58° angle? Explain.
Answer:
122°
Explanation:
A straight line forms a flat angle.
180° – 58° = 122°
B. Since the angles are sharing a side, what are they called?
Answer:
As the angles are sharing a side they are called adjacent angles.
Model with Mathematics For Problems 10-12, write an equation that can be used to determine the value of x.
Question 10.
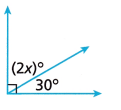
Answer:
2x° + 30° = 90°
Explanation:
An equation that can be used to determine the value of x is 2x° + 30° = 90°.
Question 11.
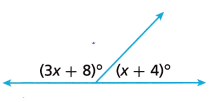
Answer:
(3x + 8)° + (x + 4)° = 180°
Explanation:
An equation that can be used to determine the value of x is (3x + 8)° + (x + 4)° = 180°.
Question 12.
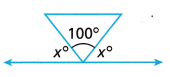
Answer:
x° + x° + 100° = 180°
Explanation:
An equation that can be used to determine the value of x is x° + x° + 100° = 180°.
Question 13.
Look for Repeated Reasoning Based on the diagram, if one angle measure is given, how can you determine all of the other angle measures?
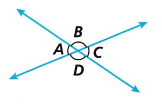
Answer:
∠A = ∠C and ∠B = ∠D
These are vertically opposite angles.
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
For Problems 14-15, use the expressions given for the measures of complementary angles to solve for x. Then find the angle measures.
Question 14.
(5x + 14)° and (3x + 20)°
Answer:
Given expression
(5x + 14)° and (3x + 20)°
Let us solve the given equation
Sum of two complementary angles is 90°
5x + 14 + 3x + 20 = 90°
8x + 34 = 90°
8x = 90° -34°
8x° = 56°
x° = 56 ÷ 8
x° = 7
5x° = 5 × 7 = 35°
8x° = 8 × 7 = 56°
Question 15.
(4x + 3)° and (4x + 7)°
Answer:
x = 10°
4x = 4 × 10 = 40°
Explanation:
Let us solve the given equation
The Sum of two complementary angles is 90°
(4x + 3)° + (4x + 7)° = 90°
4x + 4x + 3 + 7 = 90°
8x + 10 = 90°
8x = 90 – 10
8x = 80°
x = 80 ÷ 8
x = 10°
4x = 4 × 10 = 40°
For Problems 16-17, use the expressions given for the measures of supplementary angles to solve for x. Then find the angle measures.
Question 16.
(9x + 17)° and (6x + 13)°
Answer:
x = 10°
9x = 9 × 10 = 90°
6x = 6 × 10 = 60°
Explanation:
Given equation is
(9x + 17)° and (6x + 13)°
The sum of two supplementary angles is 180°
9x + 17 + 6x + 13 = 180°
15x + 30 = 180
15x = 180 – 30
15x = 150
x = 150 ÷ 15
x = 10°
9x = 9 × 10 = 90°
6x = 6 × 10 = 60°
Question 17.
(6x + 7)° and (5x + 8)°
Answer:
x = 15°
6x = 6 × 15 = 90°
5x = 5 × 15 = 75°
Explanation:
Given (6x + 7)° and (5x + 8)°
The sum of two supplementary angles is 180°
(6x + 7)° + (5x + 8)° = 180°
6x + 5x + 7 + 8 = 180°
11x + 15 = 180°
11x = 180° – 15°
11x = 165°
x = 165° ÷ 11
x = 15°
6x = 6 × 15 = 90°
5x = 5 × 15 = 75°
Question 18.
An angle measures (2x + 11)°.
A. What is the measure of an angle that is vertical to the given angle?
Answer:
(79 – 2x)°
Explanation:
90 – (2x + 11)° =
90 – 11 = 2x
2x = 79
(79 – 2x)°
B. Write an expression to represent the measure of an angle supplementary to the given angle.
Answer:
(169 – 2x)°
Explanation:
180° – (2x + 11)°
= (169 – 2x)°
Question 19.
The diagram shows a right angle. What does x equal? What are the angle measures?
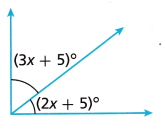
Answer:
x = 16°, (3x + 5)° = 53, (2x + 5)° = 37°
Explanation:
Sum of angles = 90°
(3x + 5)° + (2x + 5)° = 90°
5x + 10 = 90
5x = 90° -10°
5x = 80°
x = 80°÷5
x = 16°
(3x + 5)° = ((3 × 16) + 5)°
(48 + 5)°
53°
(2x + 5)° = ((2 × 16) + 5)°
= 32 + 5
= 37°
Lesson 7.5 More Practice/Homework
Question 1.
Libby is putting together a piece of furniture. She notices that two of the pieces form a right angle. If these right angles are cut in half, or bisected, by another bar, what would each angle measure within that right angle?

Answer:
Each angle within that right angle measures 45 degrees.
Explanation:
The given pieces of furniture form Right angle.
We need to find each angle measure within that right angle
The furniture is attached such that the angle between them is a right angle.
The right angle measures 90°.
Another bar bisects the right angle.
Bisecting the right angle means it is divided into two halves.
So \(\frac{90}{2}\) = 45°
So each angle within that right angle measures 45 degrees.
Question 2.
The diagram shows a right angle. Write an equation to determine the value of x. Solve for x.
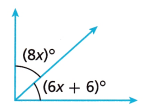
Answer:
x = 6°, 8x° = 48, (6x + 6)° = 40°
Explanation:
The given diagram is a right angle triangle that has 90°
8x° + (6x + 6)° = 90°
8x° + 6x + 6 = 90°
14x + 6 = 90°
14x = 90 – 6
14x = 84
x = 84 ÷ 14
x = 6°
8x = 6 × 8 = 48
(6x + 6)° = ((6 × 6) + 6)°
= 36 + 6
= 40°
Question 3.
A given angle measures 30°, and the measure of its vertical angle is expressed as (5x + 5)°.
A. Write an equation to determine the value of x. Solve for x.
Answer:
The required equation is 5x + 5 = 30
5x + 5 = 30
x = 5
B. If the measure of an angle adjacent to the given angle is represented by the expression (24x + 30)° using the same value for x, what is the measure of the adjacent angle?
Answer:
Vertically opposite angles are equal, then
5x + 5 = 30
5x = 30 – 5
5x = 25
x = 25 ÷ 5
x = 5
The required equation is 5x + 5 = 30
Question 4.
Attend to Precision Ms. Baumgartner draws a pair of supplementary angles and tells the class that the angle measures are (4x + 30)° and (2x + 6)°.
A. Write an equation to determine the value of x. Solve for x.
Answer:
(4x + 30)° + (2x + 6)° = 180°
x = 24
Explanation:
An equation to determine the value of x is (4x + 30)° + (2x + 6)° = 180°
Now let us solve the given equation
4x + 2x + 30 + 6 = 180°
6x + 36 = 180°
6x = 180° – 36°
6x = 144°
x = 144° ÷ 6°
x = 24°
4x + 30 = ((4 × 24) + 30)
= 96 + 30
= 126°
2x + 6 = ((2 × 24) + 6)
= (48 + 6)
= 54°`
B. What does the larger angle measure? What does the smaller angle measure?
Answer:
The larger angle measure is 126°. The smaller angle measures 54°.
Question 5.
Math on the Spot Use the diagram to find m∠2 if m∠1 = 105°.
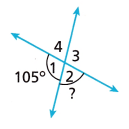
Answer:
m∠2 = 75°
Explanation:
Given m∠1 = 105°
sum of supplementary angles = 180°
m∠1 + m∠2 = 180°
105° + m∠2 = 180°
m∠2 = 180° – 105°
m∠2 = 75°
Test Prep
Question 6.
Consider adjacent angles that measure (2x + 45)° and (3x + 55)°. The sum of the measures of these two angles is 135°.
A. Write and solve an equation to find the value of x.
Answer:
The equation to find the value of x is (2x + 45)° + (3x + 55)° = 135°.
Value of x = 11°
Explanation:
Given angles are (2x + 45)° and (3x + 55)°
sum of the measures of these two angles is 135°
(2x + 45)° + (3x + 55)° = 135°
2x + 3x + 45 + 35 = 135°
5x + 80° = 135°
5x = 135° – 80°
5x = 55°
x = 55 ÷ 5
x = 11°
B. Using the value of x, what is the angle measure represented by the expression (2x + 45)°?
Answer:
The angle measure represented by the expression (2x + 45)° is 67°.
Explanation:
Given x = 11°
Angle given is (2x + 45)°
(2 × 11) + 45
22 + 45
67°
Question 7.
An angle has a measure of (3x + 5)°, and its complementary angle has a measure of (2x + 5)°. Which is the correct equation to find x?
(A) 5x + 10 = 180
(B) 5x = 180 + 10
(C) 5x + 10 = 90
(D) 5x = 90 + 10
Answer:
The correct equation to find x is 5x + 10 = 90°.
Explanation:
Given angles are (3x + 5)° and (2x + 5)°
Sum of complementary angles are 90°
3x + 5 + 2x + 5 = 90°
5x + 10 = 90°
Question 8.
Vertical angles have the same measure. True or False?
Answer:
True.
Explanation:
vertical angles are always in pairs. They have a common vertex but they cannot share a side. Vertical angles are congruent, which means they have equal measure.
Question 9.
The sum of the measures of adjacent angles is always 90°. True or False?
Answer:
False.
Explanation:
The sum of the measures of adjacent angles is 180°.
Question 10.
Draw lines to match.

Answer:
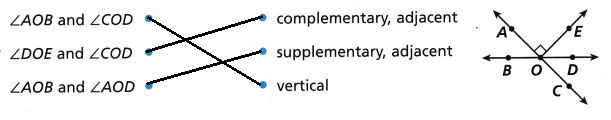
Spiral Review
Question 11.
Frankie and Marcel are picking apples. Frankie has 18 apples, which is 4 times plus 2 more apples than Marcel has. How many apples does Marcel have?
Answer:
Marcel has 4 apples.
Explanation:
Frankie has 18 apples that are 4 times more and 2 more apples of what marcel has then the equation is
(18 – 2) ÷ 4
16 ÷ 4
= 4
Question 12.
Is 10 a solution of the inequality x ≥ 12?
Answer:
No
Explanation:
Given inequality x ≥ 12
If x = 10
10 is not greater than 12
10 ≥ 12 The inequality is wrong.