Students looking for the Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Answer Key Unit 8 Module 1 can find a better approach to solve the problems.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Answer Key Unit 8 Module 1
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 1 Session 1 Answer Key
Looking for Solar Energy in Our Neighborhood
Note to Families
We are beginning a unit of study about solar energy. Please take some time to locate examples of solar energy devices. Some examples include solar yard lights, solar-powered mobile device power sources, swimming pool covers, greenhouses, and certain streetlights and traffic signals. You might find them in your neighborhood, or you can take a drive around your town or city. If you are unable to find local examples of solar use, you can look in books, in magazines, or on the Internet. Take time to talk about each type of device, its purpose, and any special features the device might have.
Question 1.
Look around your neighborhood for solar energy devices. Examples might include solar water heaters, photovoltaic panels, photovoltaic signs and lights, and swimming pools with solar covers.
a. For each solar device, record the type, location, and special features on the chart. Photograph or sketch devices you find in the world. Clip or print out pictures of devices you find in magazines, books, or on the Internet.
Answer:
Answers may vary.
Explanation:
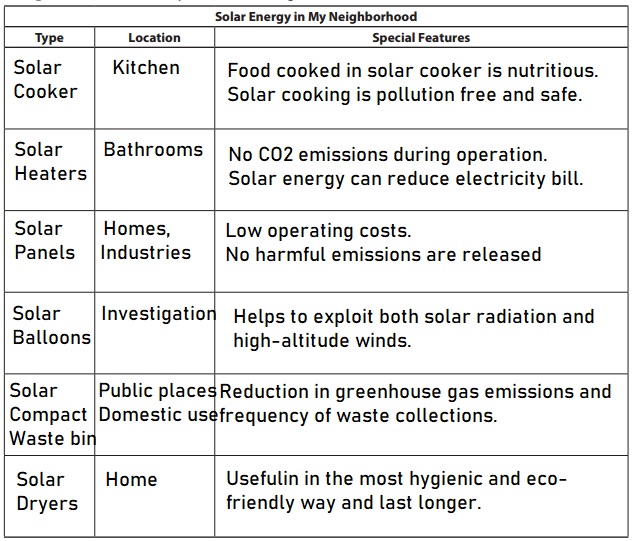
Question 2.
Sketch or glue pictures of the devices on your chart in the space below.
Answer:

Explanation:
Solar Dryer used to eliminate the moisture content from crops, vegetables, and fruits. The solar dryer consists of a box made up of easily available and cheap material like cement, galvanized iron, brick, and plywood.
Solar balloons can only support around a 2.7kg payload because there is a limited volume the sun can heat.
Solar balloons are usually black in color, in which solar radiation is used to heat directly the air in a hot-air flying balloon, can be used as a mixed power system that exploits both solar radiation and high-altitude winds.
Solar Heater is a device that captures sunlight to heat water. It can be an economical way to generate hot water It not only enables substantial energy savings as solar power is free in contrast to natural gas or fuel oil.
Solar Cooker is a type of solar thermal collector which traps the Sun’s thermal energy. Heat is produced when high frequency light is converted into low frequency infrared radiation.
Solar Compacting Waste Bins is a smart device that reads a waste bin’s fill-level in real-time and triggers an automatic compaction of the waste, effectively increasing the bin’s capacity by up to 5-8 times. The compaction mechanism runs on a battery, which is charged by the solar panel.
Solar Panel convert sunlight into electrical energy either through photovoltaic panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation. This energy can be used to generate electricity or be stored in batteries or thermal storage.
Question 3.
If you can’t find evidence of solar use in your neighborhood, list several places a solar energy device could be helpful.
Answer:
Answer may vary.
Explanation:
Solar energy is commonly used for solar water heaters and house heating in and around the neighborhood.
A part from this we see several places a solar energy device could be helpful in the production of chemicals, food, textiles, warm greenhouses, swimming pools, and livestock buildings.
Question 4.
CHALLENGE Interview someone who uses solar energy, and find out about the benefits and challenges of using it.
Answer:
Answers may vary.
Explanation:
The following are some of the benefits and challenges of using it.
Solar energy is a renewable energy source and reduces carbon emissions.
Solar energy can reduce electricity bill.
Homes with solar panels installed may improve the value of home.
But, one of the biggest problems that solar energy technology poses is that energy is only generated while the sun is shining that means nighttime and overcast days can interrupt the supply.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 1 Session 3 Answer Key
Solar Reflection & Absorption Hunt
Question 1.
On a sunny day, go outside and find the following items. Sketch and describe each item you find.
a. A surface that reflects solar energy.
Answer:
Water in swimming pools, lakes, ponds etc., will reflect to solar energy.
Explanation:
There are many surfaces that reflect to the solar energy.
Snow reflects more of the sun’s energy because it is white and more ‘reflective’ than the darker ground surface beneath.
Mirrors are being explored as a reflective surface to reflect solar radiation and cool temperatures.
b. Two objects that absorb solar energy.
Answer:
Opaque and Black objects.
Explanation:
The opaque objects such as wood, coal, organic matter, etc. are capable of absorbing solar energy.
Black objects like coal, charcoal, sand etc. are capable of absorbing solar energy.
As black color is usually considered to be a good absorbent of light radiations.
c. An item that stays cool even when it is sunny out.
Answer:
Cotton clothes or material.
Explanation:
Cotton acts as a great thermal insulator and helps to stay cool in sunny.
d. Something that casts a shadow from the sun.
Answer:
Opaque objects.
Explanation:
Shadows are formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light.
Anything that obstructs sunlight casts a shadow.
For example, Trees, dogs, buildings, people
Question 2.
What temperature do you think it is outside in degrees Fahrenheit? Record your estimate and explain your thinking.
Answer:
40°
Explanation:
We know that,
A measurement of temperature on a standard in which 32° is the temperature at which water freezes and 212° that at which it boils is known as Fahrenheit. degrees.
Question 3.
Use the formula below to find your estimated temperature in degrees Celsius.
C = (F – 32) × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
Answer:
5°
Explanation:
With reference to the above information, F = 40°
C = (F – 32) × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
C = (40° – 32) × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
C = 8 × \(\frac{5}{9}\)
C = \(\frac{45}{9}\)
C = 5°
Question 4.
At what time of day do you think it gets the hottest? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
At noon around 3 p.m.
Explanation:
The hottest time of the day is around 3 p.m. heat continues building up after noon.
When the sun is highest in the sky, as long as more heat is arriving at the earth than leaving.
Question 5.
Draw a diagram showing where the sun is in the sky in the morning, at noon, and in the afternoon. Label your diagram.
Answer:
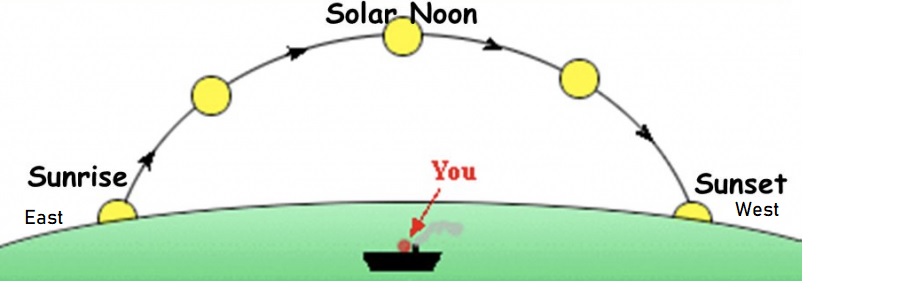
Explanation:
We know that, the sun rises from the east, the location of the sun during the morning is towards the east.
If the sun is compared in the afternoon by the morning sun, it moves a little west since the sun sets in the west in the evening.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 1 Session 5 Answer Key
Volume of Boxes
Mr. Ivy’s class is conducting a solar collection experiment and wants to make boxes that have a volume of 32 cubic inches.
Question 1.
List all the sets of dimensions (length, width, and height) a box with a volume of 32 cubic inches could have.
ex: 1″ × 1″ × 32″ = 32 cubic inches
Answer:
2″ × 2″ × 8″ = 32 cubic inches.
4″ × 4″ × 2″ = 32 cubic inches.
Explanation:
With reference to the above given information, 1″ × 1″ × 32″ = 32 cubic inches.
The possible sets of dimensions (length, width, and height) of a box with a volume of 32 cubic inches could have.
2″ × 2″ × 8″ = 32 cubic inches.
4″ × 4″ × 2″ = 32 cubic inches.
Question 2.
The class needs patterns to help them make the boxes. Choose one of the boxes you listed above. Sketch and label a model that would help someone know how to measure and cut a piece of tagboard that could be folded and taped to make a box (without a lid) with the dimensions you chose. You can include directions for making the box if you like.
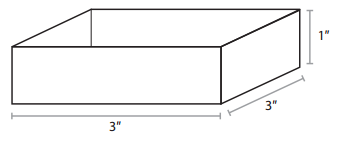
Note: Your sketch will be smaller than the actual measurements. For example, here is a sketch that would help someone know how to measure and cut a piece of tagboard that could be folded and taped to make a 3″ × 3″ × 1″ box.
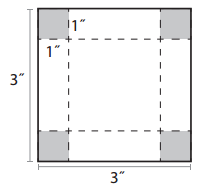
Start with a square of tagboard 5″ on each side. Cut a 1″ × 1″ square out of each corner. Fold along the dotted lines and tape the corners to make a box with a base of 3″ × 3″ and a height of 1″.
Here is what the 3″ × 3″ × 1″ box from the example sketch looks like after it is built.
Answer:
Explanation:
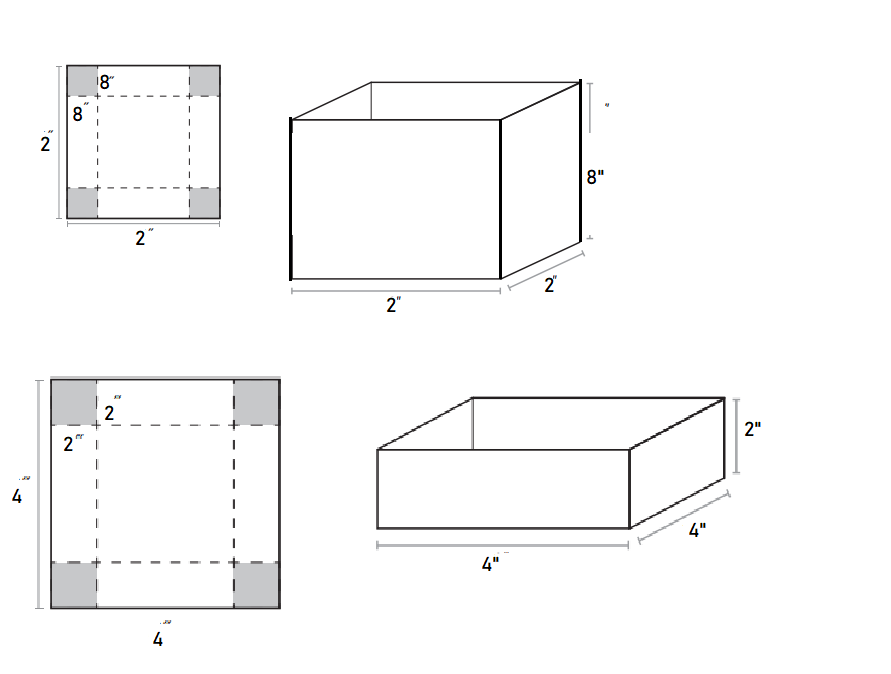
A square of tagboard 32″ on each side. Cut a 2″ × 2″ square out of each corner.
Fold along the dotted lines and tape the corners to make a box with a base of 2″ × 2″ and a height of 8″.
Here is what the dimensions of a box 2″ × 2″ × 8″
A square of tagboard 32″ on each side.
Cut a 4″ × 4″ square out of each corner.
Fold along the dotted lines and tape the corners to make a box with a base of 4″ × 4″ and a height of 2″.
Here is what the dimensions of a box 4″ × 4″ × 2″
Question 3.
Now draw and label a picture to show what the box you chose will look like after it is built.
Answer:
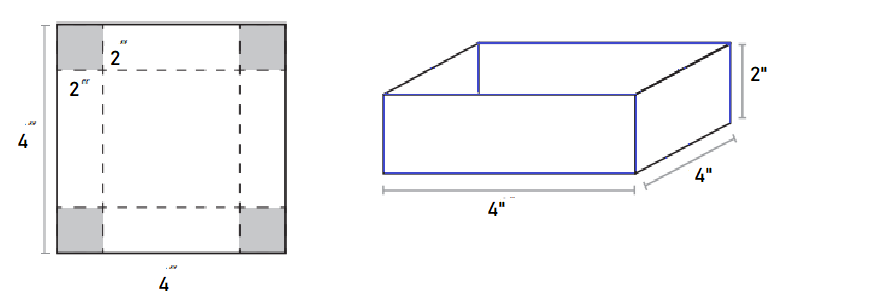
Explanation:
A square of tagboard 32″ on each side. Cut a 4″ × 4″ square out of each corner.
Fold along the dotted lines and tape the corners to make a box with a base of 4″ × 4″ and a height of 2″.
Here is what the dimensions of a box 4″ × 4″ × 2″
Question 4.
Which of the sides of this box you just sketched will collect the most solar energy when the box is set out in the sun? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Top side of the box, will collect the most solar energy, when the box is set out in the sun.
Explanation:
As sun light comes form top, the top layer of the box collect the solar energy.