Students looking for the Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Answer Key Unit 8 Module 3 can find a better approach to solve the problems.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Answer Key Unit 8 Module 3
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 3 Session 1 Answer Key
Energy in Our Homes
Look around your home, and answer as many of the following questions as you can:
Question 1.
If you have an attic, ask an adult at home how much insulation it has.
![]() 6 inches or less
6 inches or less
![]() 7-11 inches
7-11 inches
![]() 12 inches or more
12 inches or more
Answer:
Answer may vary depending upon the houses.
Approx. 12 inches or more.
Explanation:
We know that insulation is a material used to fit the exposed pipes.
Simply multiply the length by the width to calculate the area of the home to insulation.
Question 2.
How many layers of glass do your windows have?
![]() Single pane with no storm windows
Single pane with no storm windows
![]() Single pane with storm windows or double pane
Single pane with storm windows or double pane
![]() Double pane with reflective coating or gas-filled
Double pane with reflective coating or gas-filled
Answer:
Answer may vary depending upon the choice of the house owner.
Double pane with reflective coating or gas-filled.
Explanation:
The two layers of glass and insulating gas significantly reduce the amount of outdoor noise pollution that enters home and the amount of noise that emanates from inside home.
Question 3.
Hold your hands up near where the window meets the ledge and the edge. Do you feel a draft?
![]() Yes
Yes
![]() No
No
Answer:
yes,
Explanation:
Drafty windows are no longer airtight, and they’re leaking cold air into home.
Question 4.
Hold your hand up against the window. Does it feel cold (in the winter) or hot (in the summer)?
![]() Yes
Yes
![]() No
No
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
Heat exchange in a home happens mostly through windows, when we hold hands up against the window.
So, feel hot in summer and cold in winter.
Question 5.
Open your front door and check the condition of the weatherstripping between the door and the door frame.
![]() None
None
![]() Worn out
Worn out
![]() Good condition
Good condition
Answer:
Good condition.
Explanation:
We know that,
The weather stripping is generally adhered to the doorframe,
so that when the door is closed, light and air are unable to leak through the opening.
Weatherstripping and sealing are used to protect outdoor elements that can impact indoor air quality.
These seals also work to prevent the costly leakage of heated indoor air.
Weatherstripping is typically used around moving building components like windows and doors
Question 6.
Do you use awnings or shades to cover your windows in the summer?
![]() Yes
Yes
![]() No
No
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
We know that,
A window awning function as a mini roof over a window or a door to keep excessive sunlight and precipitation away and the primary purpose of these are to conserve and protect our home from overbearing sunrays. Awnings provide shade, regardless if it’s hot or cold outside.
Question 7.
Are there deciduous trees on the south-facing side of your home?
![]() Yes
Yes
![]() No
No
Answer:
Yes, Answer may vary.
Explanation:
Deciduous trees helps to shade out the hot summer sun, and then when the leaves drop, to let in light and any warmth to be gained from the winter sun.
Question 8.
Count the number of compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs) you have in your home.
![]() 0 CFL bulbs
0 CFL bulbs
![]() 1-4 CFL bulbs
1-4 CFL bulbs
![]() 5 or more CFLs
5 or more CFLs
Answer:
Answer may vary depending upon the home.
Mostly 5 or more CFLs.
Explanation:
We know that,
Fluorescent lamps give light from a large glowing surface rather than a small intense source.
They reduce demand for electricity; and also release less greenhouse gas emissions.
Question 9.
How often do you turn lights off when you leave a room?
![]() Almost never
Almost never
![]() Sometimes
Sometimes
![]() Always
Always
Answer:
Always.
Answer may vary.
Explanation:
Turning off the lights when you leave a room can help to save energy.
It can also help reduce carbon emission and other harmful greenhouse gases.
Hence, turning off your lights is a simple way to help protect the environment and save the planet.
Question 10.
At what temperature do you set your thermostat when you are home and awake?
In heating seasons (winter):
![]() 73° or more
73° or more
![]() 70°-72°
70°-72°
![]() 69° or less
69° or less
In cooling seasons (summer):
![]() 74° or less
74° or less
![]() 75°-77°
75°-77°
![]() 78° or more
78° or more
Answer:
In heating seasons (winter): 69° or less
In cooling seasons (summer): 78° or more
Explanation:
When it comes to thermostat temperature settings,
The ideal thermostat temperature in the winter is 68 degrees Fahrenheit when you’re at home.
68 degrees is a good room temperature while you’re awake at home but recommends lowering it while you’re asleep or away.
The best thermostat setting for summer is 78 degrees Fahrenheit when you’re at home.
Programmable thermostats can help make monitoring your home’s temperature while you’re away.
The thermostat can be set to start cooling shortly before you arrive home,
so it’s the ideal temperature when you walk in the door.
Question 11.
Ask an adult at home how often your furnace filters were cleaned or changed in the last year.
![]() Not at all
Not at all
![]() 1-3 times
1-3 times
![]() 4 or more
4 or more
Answer:
Answer may vary.
Preferable to clean 4 or more times a year.
Explanation:
If the furnace filters are not replaced regularly, they eventually become clogged cause overheating and costly repairs.
As dirt and debris accumulate in filter air has trouble passing through, and furnace has to work increasingly hard.
Question 12.
At what water temperature do you wash your clothes?
![]() Mostly hot water
Mostly hot water
![]() Mostly warm water
Mostly warm water
![]() Mostly cold water
Mostly cold water
Answer:
Mostly warm water.
Explanation:
Most of your clothes can be washed in warm water.
A it results good cleaning without significant fading or shrinking.
Warm water: 90°-110° F (32°-43° C)
Question 13.
How much time do you spend in the shower?
![]() 15 minutes or more
15 minutes or more
![]() 10 minutes
10 minutes
![]() 5 minutes
5 minutes
Answer:
Answer may vary. 10 minutes.
Explanation:
The time that we spend in the shower depends on the bathing routine that one may follow.
The ideal time to shower is 10 minutes as it is enough time to cleanse and hydrate the skin.
Question 14.
What other things do you notice about how you use energy in your home?
Answer:
Answer may vary.
Explanation:
When we talk about residential uses of energy, these are the most basic uses of energy like watching television, washing clothes, heating and lighting the home, taking a shower, working from home on your laptop or computer, running appliances and cooking. Residential uses of energy account for almost forty percent of total energy use globally.
Question 15.
Consider the information you have gathered. Write a note to your parents explaining in what ways your home is energy efficient and what could be done to improve its efficiency.
Answer:
By following Energy Saving Tips.
1. Temperature.
When using your thermostat, reduce the temperature by 1°C and you could save 10% Temperature.
2. Timers & Controls.
Heat it when you need it – use timers or smart heating controls to fit your routine.
3. Switch Off.
Do not turn on lights until necessary and don’t forget to turn off when finished leaving a room.
Explanation:
The energy efficiency of a home impacts how much energy is required to power the home.
The better the energy efficiency, the less energy being used for the same tasks, and vice versa.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 3 Session 3 Answer Key
Drawing a House to Scale
Question 1.
One team in Ms. Vega’s class made a model house with dimensions 7″ wide by 10″ long by 8″ tall. They need to cut out windows that take up \(\frac{1}{8}\) of the surface area of the four walls.
a. How much area do they have for windows? Show your work.
Answer:
The area for windows is 51.5 sq in.
Explanation:
With reference to the above information, the dimensions of model houses are:
w = 7″ wide
l = 10″ long
h= 8″ tall.
The length (l), width (w), and height (h) of the cuboid and use the formula:
surface area (SA)=2lw+2lh+2hw.
SA = 2[7×10 + 10×8 + 8×7]
SA = 2[70 + 80 + 56]
SA = 2[206]
SA = 412 sq in.
So, they need to cut out windows that take up \(\frac{1}{8}\) of the surface area of the four walls.
\(\frac{1}{8}\) × 412
= \(\frac{412}{8}\)
= 51.5 sq in
b. Decide on the size and placement of the windows on the four walls. Make a quick sketch of each wall with windows.
Answer:
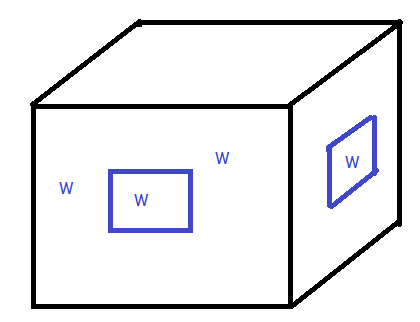
Explanation:
With reference to the above information,
They need to cut out windows that take up \(\frac{1}{8}\) of the surface area of the four walls.
\(\frac{1}{8}\) × 412
= \(\frac{412}{8}\)
= 51.5 sq in.
Question 2.
Draw side views of the 4 walls and a bird’s-eye view roof for this team of students, using a scale factor of \(\frac{1}{3}\).
Answer:
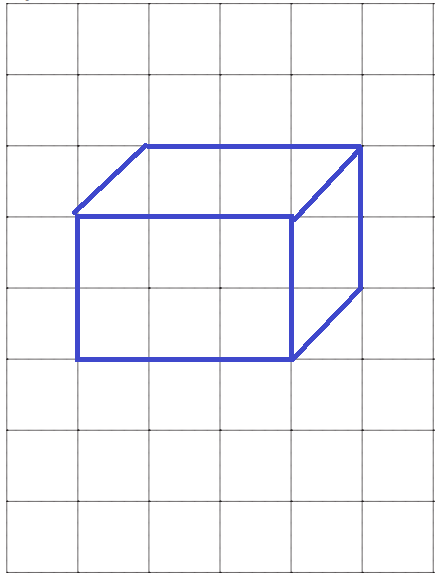
Explanation:
With reference to the above information,
a view from a high angle as if seen by a bird in flight.
We know that,
The scale factor is a measure by which the size of any geometrical figure could be varied with respect to original shape.
So, Scale factor = Dimension of the new shape ÷ Dimension of the original shape.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Home Connections Unit 8 Module 3 Session 5 Answer Key
Designing a Solar House
Question 1.
Design and sketch several views of a solar house. Include and label at least three solar energy features. The features can be active or passive. On the next page, describe how you incorporated the solar energy features into your design.
Answer:
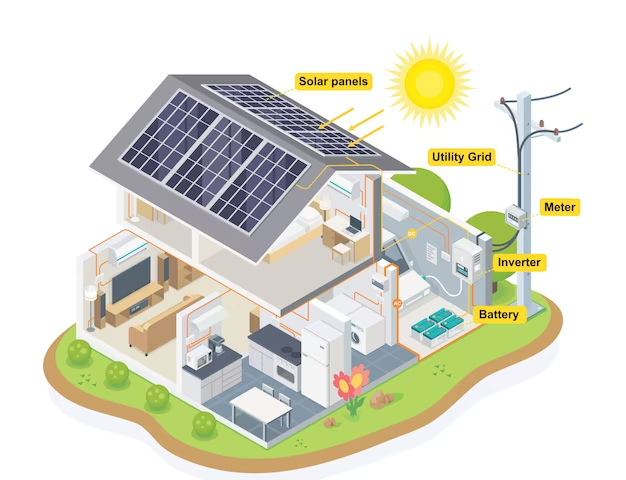
Explanation:
Passive solar heating involves designing structures to take advantage of heat and light from the sun without the aid of mechanical devices, where as active solar heating uses collectors, storage devices, and heat pumps to collect solar energy and distribute it throughout a home or building.
So, Solar cells, are an active system in which small panels faced with semiconducting material turn sunlight into electricity.
Question 2.
Describe how you incorporated solar energy features into your house design.
Answer:
The sun provides more than enough energy to meet the whole world’s energy needs, and unlike fossil fuels, it won’t run out anytime soon, hence it energy is limitless.
Explanation:
The following are some of the incorporated solar energy features into your house design:
Solar energy – a clean source. No greenhouse gas emissions are released into the atmosphere when you use solar panels to create electricity.
No fuel to burn.
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal
1. Grid-tied (On-Grid system)
2. Grid-tied with battery backup.
3. Off Grid System