Students can use the Spectrum Math Grade 8 Answer Key Chapter 4 Lesson 4.7 Constructing Function Models as a quick guide to resolve any of their doubts.
Spectrum Math Grade 8 Chapter 4 Lesson 4.7 Constructing Function Models Answers Key
Function models can be constructed by observing points on a graph, calculating the rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
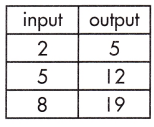
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change. \(\frac{19-5}{8-2}\) = \(\frac{14}{6}\) = \(\frac{7}{3}\)
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(5) = (\(\frac{7}{3}\))(2) + b
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = 5 – \(\frac{14}{3}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = \(\frac{7}{3}\)x + (\(\frac{1}{3}\))
Construct a function model, or equation, for each table below.
Question 1.
a.
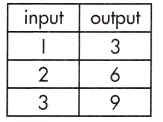
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = 3x
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation,
y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{9-3}{3-1}\)
= \(\frac{6}{2}\) = 3
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(3) = 3 (1) + b
b = 3 – 3 = 0
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = 0
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = 3x + 0
y = 3x
b.
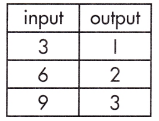
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{3 – 1}{9 – 3}\)
= \(\frac{2}{6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(1) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) (3) + b
b = 1 – 1 = 0
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = 0
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 0
y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x
c.
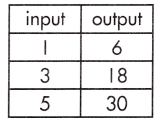
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = 6x
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{30 – 6}{5 – 1}\)
= \(\frac{24}{4}\)
= 6
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(6) = 6 (1) + b
b = 6 – 6
b = 0
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = 0
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = 6x + 0
y = 6x
Question 2.
a.
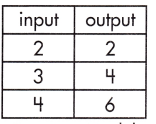
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = 2x – 2
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{6 – 2}{4 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{4}{2}\)
= 2
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(2) = 2 (2) + b
b = 2 – 4
b = -2
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = -2
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = 2x – 2
b.
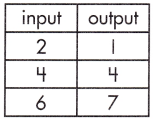
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = \(\frac{3}{2}\)x – 2
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{7 – 1}{6 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{6}{4}\)
= \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(1) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) (2) + b
b = 1 – 3
b = -2
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = -2
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = \(\frac{3}{2}\)x – 2
c.
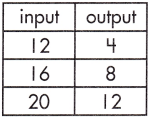
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = x – 8
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{12 – 4}{20 – 12}\)
= \(\frac{8}{8}\)
= 1
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(4) = 1 (12) + b
b = 4 – 12
b = -8
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = -8
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = 1x – 8
y = x – 8
Question 3.
a.
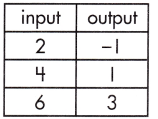
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = x – 3
Explanation:
the rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{3 – (-1)}{6 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{4}{4}\)
= 1
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(3) = 1 (6) + b
b = 3 – 6
b = -3
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = -3
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = x – 3
b.
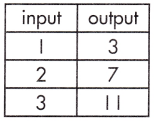
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = 4x – 1
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{11 – 3}{3 – 1}\)
= \(\frac{8}{2}\)
= 4
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(3) = 4 (1) + b
b = 3 – 4
b = -1
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = -1
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = 4x – 1
c.
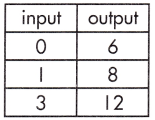
Function Model:
_________
Answer:
y = 2x + 6
Explanation:
The rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{12 – 6}{3 – 0}\)
= \(\frac{6}{3}\)
= 2
Step 2: Substitute known values of x and y into the slope-intercept form of the equation.
y = mx + b
(6) = 2 (0) + b
b = 6 – 0
b = 6
Step 3: Solve to find the initial value of the output variable (b).
b = 6
Step 4: Write the equation using the found values of m and b.
y = mx + b
y = 2x + 6
Function models can be constructed by observing points on a graph, calculating the rate of change (or slope), and plugging known values into the equation, y = mx + b.
Step 1: Find and name two points on (4, 6) and (2, 4) the line.
Step 2: Calculate the rate of change. \(\frac{4-6}{2-4}\) = \(\frac{-2}{-2}\) = 1
Step 3: Use the found points and calculated slope to find the initial value of the output if it cannot be determined based on the graph.
Based on the graph, the initial value of the output variable is 2.
Step 4: Write the formula for all values of x and y using the equation. y = (1)x + 2
y = x + 2
Use the graphs to write function models, or equations, in the form of y = mx + b.
Question 1.
a.
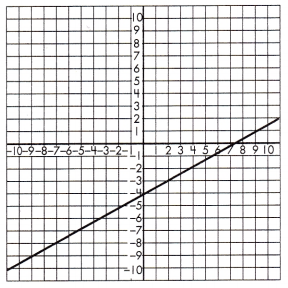
Function Model:
____________
Answer:
y = \(\frac{5}{9}\)x – 4\(\frac{1}{9}\)
Explanation:
Step 1: Find and name two points on (-5, -7) and (4, -2) the line.
Step 2: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{-2 – (-7)}{4- (-5)}\)
= \(\frac{5}{9}\)
Step 3: Use the found points and calculated slope to find the initial value of the output if it cannot be determined based on the graph.
Based on the graph, the initial value of the output variable for a value (x, y)
Step 4: Write the formula for all values of x and y using the equation.
y = mx + b
-7 = \(\frac{5}{9}\)(-5)+ b
-7 – \(\frac{25}{9}\) = b
b = \(\frac{63 – 25}{9}\)
b = \(\frac{63 – 25}{9}\)
b = \(\frac{38}{9}\)
b = 4\(\frac{2}{9}\)
y = mx + b
y = \(\frac{5}{9}\)x – 4\(\frac{2}{9}\)
b.
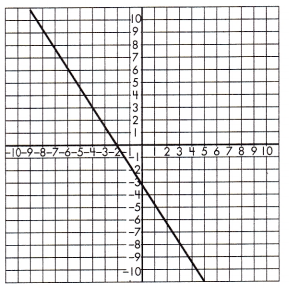
Function Model:
____________
Answer:
y = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)x – 3
Explanation:
Step 1: Find and name two points on (-6, 6) and (-2, 0) the line.
Step 2: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{0 – 6}{-2- (-6)}\)
= \(\frac{-6}{4}\)
= – \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Step 3: Use the found points and calculated slope to find the initial value of the output if it cannot be determined based on the graph.
Based on the graph, the initial value of the output variable for a value (x, y)
Step 4: Write the formula for all values of x and y using the equation.
y = mx + b
6 = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)(-6) + b
6 – 9 = b
b = -3
y = mx + b
y = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)x – 3
Question 2.
a.
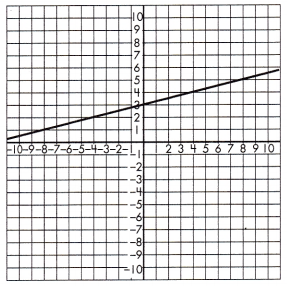
Function Model:
____________
Answer:
y = \(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 3
Explanation:
Step 1: Find and name two points on (-4, 2) and (4, 4) the line.
Step 2: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{4-2}{4-(-4)}\)
= \(\frac{2}{8}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Step 3: Use the found points and calculated slope to find the initial value of the output if it cannot be determined based on the graph.
Based on the graph, the initial value of the output variable for a value (x, y)
Step 4: Write the formula for all values of x and y using the equation.
y = mx + b
4 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)(4)+ b
4 – 1 = b
b = 3
y = mx + b
y = \(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 3
b.
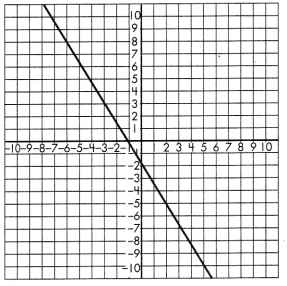
Function Model:
____________
Answer:
y = – \(\frac{5}{3}\)x – 1\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
Step 1: Find and name two points on (5, -10) and (2, -5) the line.
Step 2: Calculate the rate of change.
\(\frac{-5 +10}{2 – 5}\)
= –\(\frac{5}{3}\)
Step 3: Use the found points and calculated slope to find the initial value of the output if it cannot be determined based on the graph.
Based on the graph, the initial value of the output variable for a value (x, y)
Step 4: Write the formula for all values of x and y using the equation.
y = mx + b
-10 = –\(\frac{5}{3}\)(5)+ b
-10 – \(\frac{25}{3}\) = b
b = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
b = 1\(\frac{2}{3}\)
y = mx + b
y = – \(\frac{5}{3}\)x – 1\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Function models can be constructed when two points on the line representing the function are given, provided the function is linear. First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given. Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m. m = \(\frac{3-6}{2-5}\) = \(\frac{-3}{-3}\) = 1
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 3) and (5, 6).
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b. 3 = (1) (2) + b
3 = 2 + b
1 = b
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = 1x + 1
y = x + 1
Use the points given to find the function model for the linear function they represent.
Question 1.
a. (3, 4) and (5, 8)
y = ______
Answer:
y = 2x – 2
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m.
m = \(\frac{8-4}{5-3}\)
= \(\frac{4}{2}\)
= 2
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (3, 4) and (5, 8).
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
4 = (2) (3) + b
4 = 6 + b
4 – 6 = b
b = -2
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 2x – 2
b. (4, 5) and (8, 3)
y = ______
Answer:
y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 7
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (4, 5) and (8, 3)
m = \(\frac{3-5}{8-4}\)
= \(\frac{-2}{4}\)
= –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (4, 5) and (8, 3)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
5 = –\(\frac{1}{2}\) (4) + b
5 = -2 + b
5 + 2 = b
b = 7
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 7
c. (1, 2) and (5, 10)
y = ______
Answer:
y = 2x
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (1, 2) and (5, 10)
m = \(\frac{10 – 2}{5 – 1}\)
= \(\frac{8}{4}\)
= 2
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (1, 2) and (5, 10)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
2 = 2 (1) + b
2 – 2 = b
b = 0
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 2x + 0
y = 2x
Question 2.
a. (2, 7) and (0, 1)
y = ______
Answer:
y = 3x + 1
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (2, 7) and (0, 1)
m = \(\frac{1 – 7}{0 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{-6}{-2}\)
= 3
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 7) and (0, 1)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
7 = 3 (2) + b
7 – 6 = b
b = 1
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 3x + 1
b. (2, 0) and (0, 3)
y = ______
Answer:
y = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)x + 3
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (2, 0) and (0, 3)
m = \(\frac{3-0}{0-2}\)
= \(\frac{3}{-2}\)
= –\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 0) and (0, 3)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
0 = –\(\frac{3}{2}\) (2) + b
0 = -3 + b
0 + 3 = b
b = 3
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = –\(\frac{3}{2}\)x + 3
c. (-1, 2) and (7, 6)
y = ______
Answer:
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 2\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (-1, 2) and (7, 6)
m = \(\frac{6 – 2}{7 + 1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{8}\)
= –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (-1, 2) and (7, 6)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (-1) + b
2 = –\(\frac{1}{2}\) + b
2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = b
b = \(\frac{4 + 1}{2}\)
b = \(\frac{5}{2}\)
b =2\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 2\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 3.
a. (1, 1) and (3, 5)
y = ______
Answer:
y = 2x – 1
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (1, 1) and (3, 5)
m = \(\frac{5 – 1}{3 – 1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{2}\)
= 2
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (1, 1) and (3, 5)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
1 = (2) 1 + b
1 – 2 = b
-1 = b
b = -1
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 2x – 1
b. (1, 3) and (2, 4)
y = ______
Answer:
y = x + 2
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (1, 3) and (2, 4)
m = \(\frac{4 – 3}{2 – 1}\)
= \(\frac{1}{1}\)
= 1
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (1, 3) and (2, 4)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
3 = (1) 1 + b
3 – 1 = b
2 = b
b = 2
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = x + 2
c. (2, 6) and (-2, 4)
y = ______
Answer:
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 5
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (2, 6) and (-2, 4)
m = \(\frac{4 – 6}{-2 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{-2}{-4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 6) and (-2, 4)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
6 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) 2 + b
6 – 1 = b
b = 5
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 5
Question 4.
a. (2, 16) and (-1, 7)
y = ______
Answer:
y = 3x + 10
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (2, 16) and (-1, 7)
m = \(\frac{7 – 16}{-1 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{-9}{-3}\)
= 3
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 16) and (-1, 7)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
16 = (3) 2 + b
16 – 6 = b
b = 10
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 3x + 10
b. (2, 13) and (1, 8)
y = ______
Answer:
5x + 3
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (2, 13) and (1, 8)
m = \(\frac{8 – 13}{1 – 2}\)
= \(\frac{-5}{-1}\)
= 5
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (2, 13) and (1, 8)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
8 = (5) 1 + b
8 – 5 = b
b = 3
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = 5x + 3
c. (4, 3) and (8, 1)
y = ______
Answer:
y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 5
Explanation:
The function is linear.
First, calculate the rate of change, or slope, using the points given.
Then, plug one set of the known x and y values into the equation, y = mx + b, to find the initial value of the output variable.
Step 1: Find the rate of change, or slope, m for given points (4, 3) and (8, 1)
m = \(\frac{1 – 3}{8 – 4}\)
= \(\frac{-2}{4}\)
= –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Find the equation of a line that runs through points (1, 1) and (3, 5)
Step 2: Plug in known values of x and y to calculate b.
y = mx + b
1 = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)(8) + b
1 + 4 = b
b = 5
Step 3: Write the equation that will allow all values of x and y to be found.
y = mx + b
y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 5