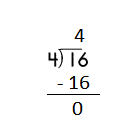This handy Spectrum Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 5 Lesson 5.5 Division Practice provides detailed answers for the workbook questions.
Spectrum Math Grade 4 Chapter 5 Lesson 5.5 Division Practice Answers Key
Divide.
Question 1.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 56 is divisible by 8, as we know that 8 × 7 = 56 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 7 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 56 ÷ 8 = 7, then 8 × 7 = 56 must be true.
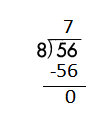
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 24 is divisible by 6, as we know that 6 × 4 = 24 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 4 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 24 ÷ 6 = 4, then 6 × 4 = 24 must be true.
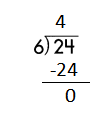
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 18 is divisible by 2, as we know that 2 × 9 = 18 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 18 ÷ 2 = 9, then 2 × 9 = 18 must be true.
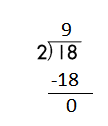
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 35 is divisible by 5, as we know that 5 × 7 = 35 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 7 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 35 ÷ 5 = 7, then 5 × 7 = 35 must be true.
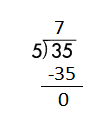
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 42 is divisible by 7, as we know that 7 × 6 = 42 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 6 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 42 ÷ 6 = 7, then 7 × 6 = 42 must be true.
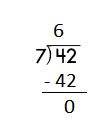
Question 2.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 48 is divisible by 6, as we know that 6 × 8 = 48 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 8 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 48 ÷ 6 = 8, then 6 × 8 = 48 must be true.
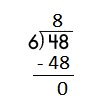
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 30 is divisible by 6, as we know that 6 × 5 = 30 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 5 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 30 ÷ 6 = 5, then 6 × 5 = 30 must be true.
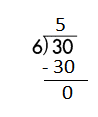
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 72 is divisible by 8, as we know that 8 × 9 = 72 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 72 ÷ 8 = 9, then 8 × 9 = 72 must be true.
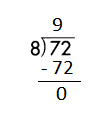
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 36 is divisible by 6, as we know that 6 × 6 = 36 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 6 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 36 ÷ 6 = 6, then 6 × 6 = 36 must be true.
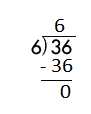
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 81 is divisible by 9, as we know that 9 × 9 = 81 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 81 ÷ 9 = 9, then 9 × 9 = 81 must be true.
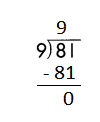
Question 3.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 54 is divisible by 9, as we know that 9 × 6 = 54 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 6 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 54 ÷ 9 = 6, then 9 × 6 = 54 must be true.
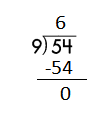
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 21 is divisible by 3, as we know that 3 × 7 = 21 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 7 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 21 ÷ 3 = 7, then 3 × 7 = 21 must be true.
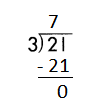
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 28 is divisible by 7, as we know that 7 × 4 = 28 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 4 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 28 ÷ 7 = 4, then 7 × 4 = 28 must be true.
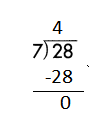
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 18 is divisible by 3, as we know that 3 × 6 = 18 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 6 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 18 ÷ 3 = 6, then 3 × 6 = 18 must be true.
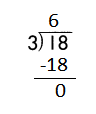
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 18 is divisible by 2, as we know that 2 × 9 = 18 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 18 ÷ 2 = 9, then 2 × 9 = 18 must be true.
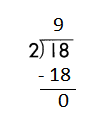
Question 4.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 45 is divisible by 5, as we know that 5 × 9 = 45 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 45 ÷ 5 = 9, then 5 × 9 = 45 must be true.
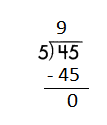
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 36 is divisible by 9, as we know that 9 × 4 = 36 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 4 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 36 ÷ 9 = 4, then 9 × 4 = 36 must be true.
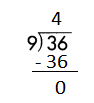
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 42 is divisible by 6, as we know that 6 × 7 = 42 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 7 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 42 ÷ 6 = 7, then 6 × 7 = 42 must be true.
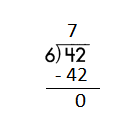
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 64 is divisible by 8, as we know that 8 × 8 = 64 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 8 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 64 ÷ 8 = 8, then 8 × 8 = 64 must be true.
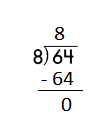
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 63 is divisible by 7, as we know that 7 × 9 = 63 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 63 ÷ 7 = 9, then 7 × 9 = 63 must be true.
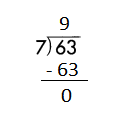
Question 5.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 24 is divisible by 3, as we know that 3 × 8 = 24 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 8 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 24 ÷ 3 = 8, then 3 × 8 = 24 must be true.
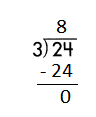
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 27 is divisible by 9, as we know that 9 × 3 = 27 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 3 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 27 ÷ 9 = 3, then 9 × 3 = 27 must be true.
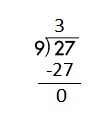
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 20 is divisible by 5, as we know that 5 × 4 = 20 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 4 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 20 ÷ 5 = 4, then 5 × 4 = 20 must be true.
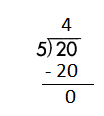
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 49 is divisible by 7, as we know that 7 × 7 = 49 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 7 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 49 ÷ 7 = 7, then 7 × 7 = 49 must be true.
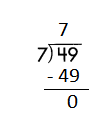
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 25 is divisible by 5, as we know that 5 × 5 = 25 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 5 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 25 ÷ 5 = 5, then 5 × 5 = 25 must be true.
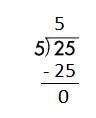
Question 6.
a.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 40 is divisible by 5, as we know that 5 × 8 = 40 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 8 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 40 ÷ 5 = 8, then 5 × 8 = 40 must be true.
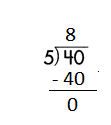
b.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 14 is divisible by 7, as we know that 7 × 2 = 14 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 2 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 14 ÷ 7 = 2, then 7 × 2 = 14 must be true.
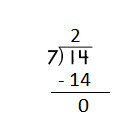
c.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 81 is divisible by 9, as we know that 9 × 9 = 81 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 9 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 81 ÷ 9 = 9, then 9 × 9 = 81 must be true.
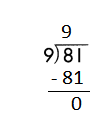
d.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: We know that, 9×0=0
Step 2: Write 0 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 0 ÷ 9 = 0, then 9 × 0 = 0 must be true.
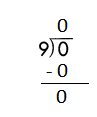
e.
![]()
Answer:
Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
Step 2: 16 is divisible by 4, as we know that 4 × 4 = 16 so, we go for it.
Step 3: Write 4 in the quotient.
Check:
Do the inverse operation to check your answer.
If 16 ÷ 4 = 4, then 4 × 4 = 16 must be true.