We included HMH Into Math Grade 8 Answer Key PDF Module 10 Lesson 2 Investigate Roots to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 8 Module 10 Lesson 2 Answer Key Investigate Roots
I Can evaluate square roots and cube roots.
Spark Your Learning
Aaron plans to make origami cranes, which can be folded from a square piece of paper. He starts by drawing small squares with side lengths 1 inch, 2 inches, 3 inches, and 4 inches.
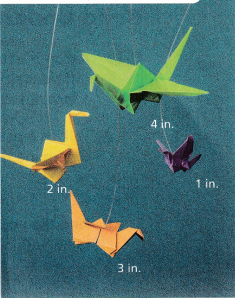
Find the area of each square. What do you notice about the relationship between the side lengths and the area of each square?
Answer:
Area of 1 inch square is 1 sqaure inch, Area of 2 inches square is 4 sqaure inches,
Area of 3 inches square is 9 sqaure inches, Area of 4 inches square is 16 sqaure inches,
Explanation:
Given Aaron plans to make origami cranes which can be folded from a square piece of paper.
He starts by drawing small squares with side lengths 1 inch, 2 inches, 3 inches, and 4 inches.
So the area of each sqaure is as follows area of 1 inch square is 1 sqaure inch,
area of 2 inches square is 4 sqaure inches area of 3 inches square is 9 sqaure inches,
area of 4 inches square is 16 sqaure inches,
Turn and Talk Consider a square with an area of 23 square inches. Explain how you would determine the length of each side for such a square.
Answer:
The length of each side is 4.795831 approximately 5,
Explanation:
Given a square with an area of 23 square inches. To determine the length of each side for such a square, we have area of given square using that we will find as area = square of length, so length of each side is square root of area which is sqaure root of 23 we will get as
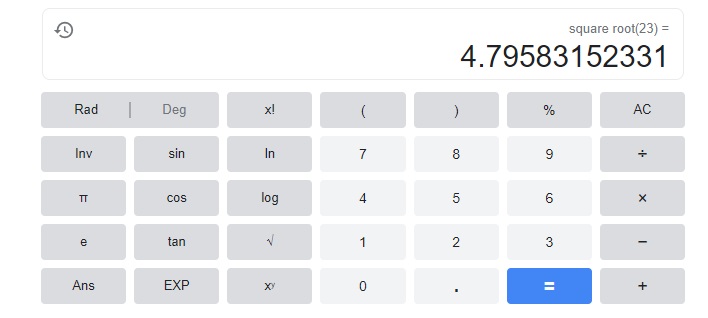
4.795831 approximately 5.
Build Understanding
Question 1.
Aaron is also planning to make origami cubes of different sizes. The edge lengths of the cubes are 1 inch, 2 inches, 3 inches, and 4 inches.
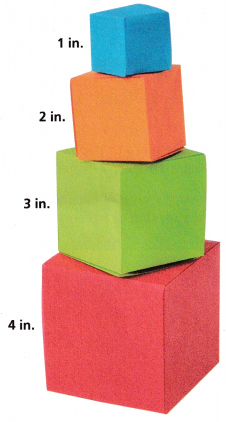
A. Talk to a partner, then write down a formula to determine the volume of a cube.
Answer:
Volume of cube is edge3,
Explanation:
The formula to determine the volume of a cube is edge3.
B. Find the volume of each of the cubes. Complete the table and look for patterns.
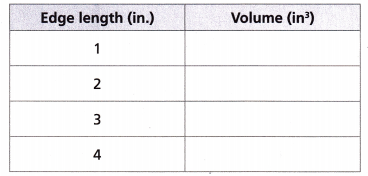
Answer:
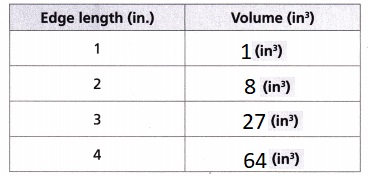
Explanation:
Founded the volume of each of the cubes and Completed the given table as shown above.
C. What do you notice about how the volumes change as the edge length increases?
Answer:
Edge length increases,
Explanation:
I have noticed that as the edge length increases, The volume of the cube also increases.
D. If you are given the volume of a cube, how can you find the edge length?
Answer:
Cube root of the volume of a cube,
Explanation:
If the volume of a cube is given then to find the edge length i will be calculating the cube root
of the given volume.
E. What is the edge length of a cube with a volume of 125 cubic inches? Why is it difficult to express the edge length of a cube with a volume of 10 cubic inches?
Answer:
The edge length of a cube with a volume of 125 cubic inches is 5 inches,
10 cubic inches will have a irrational,
Explanation:
The edge length of a cube with a volume of125 cubic inches is cube root of 125 cubic inches which is
5, it difficult to express the edge length of a cube with a volume of 10 cubic inches because as it is
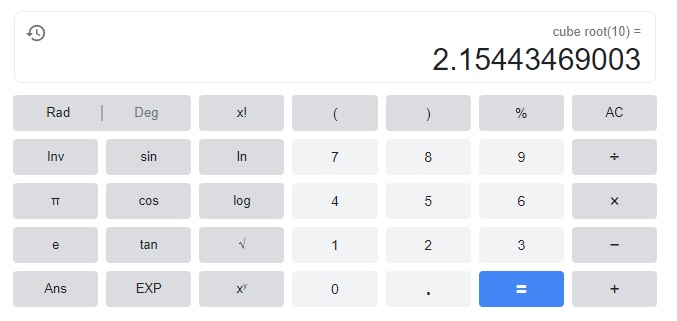
So as ∛10 = ∛(2 × 5) and it cannot be expressed as perfect cube or
in the form of p/q where q ≠ 0. Therefore, the value of the cube root of 10 is an irrational number and
are the real numbers that cannot be represented as a simple fraction.
Turn and Talk A student completed the above table and claimed it is impossible for a cube to have a volume of exactly 50 cubic centimeters since this number will not appear in the “Volume” column. Do you agree? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes agree,
Explanation:
Given a student completed the above table and claimed it is impossible for a cube to have a
volume of exactly 50 cubic centimeters since this number will not appear in the “Volume” column.
Yes, I do you agree as if we see the edge lengths of the cubes are 1 inch, 2 inches, 3 inches, and 4 inches and with volume 50 cubic centimeters the cube root of 50 cubic centimeters is
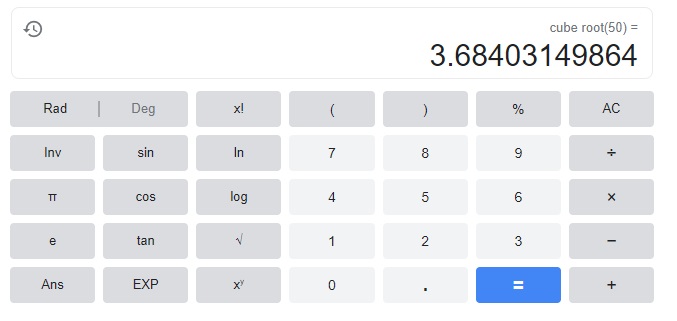
3.6840314 as we have not been given the edge lengths between 3 and 4 inches so it will not appear in the “Volume” column.
Step It Out
The square root of a positive number p is x when x2 = p. Note that every positive number has two square roots. For example, 32 = 9 and (-3)2 = 9, so the two square roots of 9 are 3 and -3. These are sometimes written together as ±3, and read as “plus or minus three.”
A perfect square is a whole number whose square roots are integers. For example, 16 is a perfect square since its square roots are the integers 4 and -4. The square root of any number that isn’t a perfect square is another example of an irrational number.
The symbol √ (radical symbol) is used to indicate the positive square root, or principal square root, of a number. So, \(\sqrt {16}\) = 4.
Question 2.
Use the information about roots to evaluate each expression.
A. Find the square roots of 81.
![]()
So, the square roots of 81 are ___________ and ___________.
Answer:
The square roots of 81 are 9 and -9,
Explanation:
Given to find the square roots of 81 as every positive number has two square roots therefore
√81 = √9 X 9 or √-9 X – 9, So the square roots of 81 are 9 and -9.
B. Find \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}}\)
Both  = \(\frac{4}{9}\) and
= \(\frac{4}{9}\) and 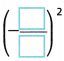 = \(\frac{4}{9}\)
= \(\frac{4}{9}\)
The square root symbol indicates the principal square root.
So, \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}}\) = ![]() .
.
Answer:
The square roots of \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}}\) are \(\frac{2}{3}\) and –\(\frac{2}{3}\),
Explanation:
Give to find sqaure root of \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}}\) as every positive number has two square roots therefore we have \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) and –\(\frac{2}{3}\).
Suppose Aaron wants a square piece of origami paper with an area of 2 square centimeters.
C. What is the length of one side of the piece of paper? Use a square root symbol in your answer.
____________ centimeters
Answer:
1.414213 centimeters,
Explanation:
Given Aaron wants a square piece of origami paper with an area of 2 square centimeters.
So the length of one side of the piece of paper is √2 which is equal to 1.414213 centimeters.
D. Is 2 a perfect square? Why or why not? (yes / no); There (is / is not) an integer whose square is 2.
Answer:
No, not a perfect square, There is not an integer whose square is 2,
Explanation:
No 2 is not a perfect sqaure, As a perfect square is a number that can be expressed as
the product of two equal integers.
The only way to accurately calculate if a number is a perfect square is to find the factors. Before we go through the trouble of finding the factors, there is a quick trick we can use to help to determine if we need even need to do the extra work. We try these steps first:
1. A number that is a perfect square never ends in 2, 3, 7 or 8. If your number ends in any of those numbers, We can stop here because your number is not a perfect square.
2. Obtain the digital root of the number. The digital root essentially is the sum of all of the digits.
If we’re lost, don’t worry, we’ll go over each step in more detail below.
3. All possible numbers that are a perfect square have a digital root of 1, 4, 7, 9.
There is not an integer whose square is 2. Because √2 is not an integer (2 is not a perfect square),
√2 must therefore be irrational.
E. Is the square root of 2 rational or irrational? (rational / irrational); \(\sqrt {2}\) (can / cannot) be written as a ratio of two integers.
Answer:
Square root of 2 is irrational, \(\sqrt {2}\) cannot be written as a ratio of two integers,
Explanation:
As square root of 2 is 1.414213 so it is irrational \(\sqrt {2}\) cannot be written as a ratio
of two integers as it is not rational and cannot be represented as \(\frac{p}{q}\) form.
The cube root of a positive number p is x when x3 = p. Every positive number has one cube root. For example, 43 = 64, so the cube root of 64 is 4. The symbol for a cube root is similar to the symbol for square root, and written as \(\sqrt[3]{}\). \(\sqrt[3]{64}\) = 4 is read out loud as, “The cube root of 64 equals 4.”
A perfect cube is a whole number whose cube root is an integer. For example, 64 is a perfect cube since its cube root is an integer, 4.
Question 3.
Find the cube root of \(\frac{8}{27}\).
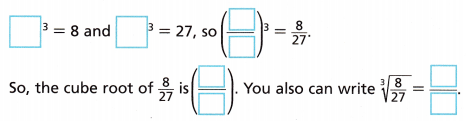
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{3}\),
Explanation:
Given to find the cube root of \(\frac{8}{27}\) which is equal to cube root of \(\frac{2 X 2 X 2}{3 X 3 X 3}\) we get \(\frac{2}{3}\).
Question 4.
Solve each problem.
A. What is the side length of the square picture frame shown?
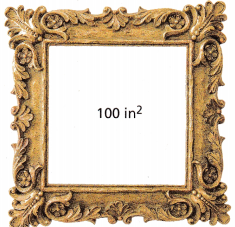
x2 = 100 Write the equation.
x = ±\(\sqrt {100}\) Apply the definition of square root.
x = ± ___________ Find integers that when squared equal 100.
The side length of the picture frame is ___________ inches.
Note that the square root -10 is not used since it is not a possible length for a real-world object.
Answer:
The side length of the picture frame is 10 inches,
Explanation:
Given the area of the square picture as 100 square inches,
So the side length of the picture frame is the square root of 100 we get a square root of 10 X 10
which is equal to 10 inches.
B. Solve for y: y3 = \(\frac{1}{14}\).
y = \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{14}}\) Apply the definition of cube root.
Since no rational number when cubed equals \(\frac{1}{14}\), ___________ represents the solution to y3 = \(\frac{1}{14}\).
Answer:
y = 0.07142857142,
Explanation:
Given to solve for y: y3 = \(\frac{1}{14}\),
Applying the definition of cube root.
Since no rational number when
cubed equals \(\frac{1}{14}\), as it is
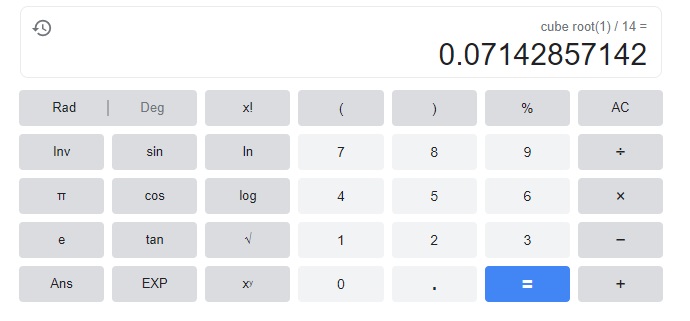
the solution to y3 = \(\frac{1}{14}\) is y = 0.07142857142.
Check Understanding
Question 1.
Solve each equation.
A. x2
x = ____________
Answer:
x,
Explanation:
Given to solve x2 ,So x = sqaure root of x2 = sqaure root of x X x = x,
therefore square root of x2 is x.
B. x3 = \(\frac{1}{64}\)
x = _____________
Answer:
x3 = \(\frac{1}{4}\),
Explanation:
Given to find x3 = \(\frac{1}{64}\) it is
x3 = \(\frac{1}{4 x 4 x 4}\) = 4.
For Problems 2-4, find the indicated root.
Question 2.
\(\sqrt{121}\)
Answer:
11,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt{121}\) it is \(\sqrt{11 X 11}\) = 11.
Question 3.
\(\sqrt{\frac{16}{25}}\),
Answer:
\(\sqrt{\frac{4}{5}}\),
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt{\frac{16}{25}}\), it is \(\sqrt{\frac{4 x 4}{5 x 5}}\) so the result is \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{5}}\).
Question 4.
\(\sqrt[3]{125}\)
Answer:
5,
Explanation:
Given to find cube root of 125 it is cube root of 5 X 5 X 5 which is equal to 5.
On Your Own
Question 5.
A band stores its equipment in a large cube. The cube has sound-dampening foam designed to allow the drummer to play inside the cube when the band is practicing.

A. Is 125 a perfect cube? Why or why not?
Answer:
125 is a perfect cube,
Explanation:
Given to find is 125 a perfect cube, yes it is as the number 125 is called a perfect cube number,
since its cube root value is a whole number 5.
B. What is the edge length of the band’s cube? Explain.
Answer:
The edge length of the band’s cube is 5 feet,
Explanation:
Given a band stores its equipment in a large cube. The cube has sound-dampening foam designed to allow the drummer to play inside the cube when the band is practicing. It has volume as 125 cubic feet, So the edge length of the band’s cube is cube root of 125 which is 5 feet.
Question 6.
Find the square roots of 400.
Answer:
20,
Explanation:
Given to find square root of 400, let it be x, So x2 = 400 which is equal to x2 = 20 x 20,
therefore x = sqaure root of 20 X 20 = 20.
Question 7.
Find the cube root of \(\frac{8}{125}\). Show how you can check that you found the cube root correctly.
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{5}\),
Explanation:
Given to find \(\frac{8}{125}\) it is \(\frac{2 X 2 X 2}{5 X 5 X 5}\) = \(\frac{2}{5}\), There the cube root of \(\frac{8}{125}\) is \(\frac{2}{5}\).
Question 8.
Reason A student claimed 7 and -7 are the two cube roots of 343. Do you agree or disagree? Explain.
Answer:
Disagree,
Explanation:
Given a student claimed 7 and -7 are the two cube roots of 343. I disagree as (7)3 = 343 but not
(-7)3 = -343 not 343.
Question 9.
Solve the equation x2 = 196. Show your work and explain your steps.
Answer:
14,
Explanation:
Given to find x2 = 196, it is x2 = 14 x 14 = x2 = 14.
Question 10.
Solve the equation z3 = \(\frac{125}{216}\). Show your work and explain your steps.
Answer:
z3 = \(\frac{5}{6}\),
Explanation:
Given to find z3 = \(\frac{125}{216}\) it is z3 = \(\frac{5 X 5 X 5}{6 X 6 X 6}\) =
z3 = \(\frac{5}{6}\).
Question 11.
Open-Ended A square tile has an area of less than 1 square foot. The area and length are rational numbers. What is a possible area for the tile in square feet? What is the corresponding edge length?

Answer:
Possible area for the tile in square feet is \(\frac{1}{4}\),
The corresponding edge length is \(\frac{1}{2}\),
Explanation:
Given a square tile has an area of less than 1 square foot. The area and length are rational numbers.
So the possible area for the tile in square feet is \(\frac{1}{4}\) and the corresponding edge length is \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Question 12.
Use Repeated Reasoning What do perfect squares have in common?
A. Complete the table of squares.
Answer:
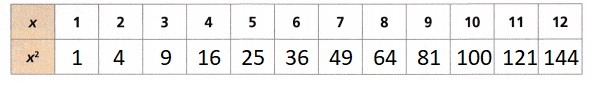
Explanation:
Completed the given table of squares as shown above.
B. What do you notice about the ones digit in each of the perfect squares in your table?
Answer:
The digits 1,4,6 and 9 are repeating,
Explanation:
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of two equal integers now if we see the ones digit in each of the perfect squares in my table numbers 1,4,6 and 9 are repeating.
C. Suppose you extend the table and continue to find perfect squares. Do you think the number 10,402 will eventually appear in the x2 row? Explain.
Answer:
No,
Explanation:
Suppose if I extend the table and continue to find perfect squares. I think the number 10,402 will eventually not appear in the x2 row as 10,402 is not a perfect square.
Question 13.
Does the square root of 0 exist? What about the cube root of 0? Explain your answers.
Answer:
Yes square root of 0 exists The cube root of 0 is 0,
Explanation:
Zero has one square root which is 0. So 0 has square root,
The cube root of 0 is 0 as cube root of 0 is cube root of 0 X 0 X 0 which equals to 0.
For Problems 14-16, find each root.
Question 14.
\(\sqrt{225}\)
Answer:
15,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt{225}\) it is \(\sqrt{15 X 15}\) = 15.
Question 15.
\(\sqrt[3]{729}\)
Answer:
9,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt[3]{729}\) it is \(\sqrt[3]{9 X 9 X 9}\) = 9.
Question 16.
\(\sqrt[3]{\frac{64}{343}}\)
Answer:
\(\sqrt[3]{\frac{4}{7}}\),
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{64}{343}}\) it is \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{4 X 4 X 4}{7 X 7 X 7}}\) = \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{4}{7}}\).
For Problems 17-19, solve each equation.
Question 17.
x2 = \(\frac{1}{49}\)
Answer:
x2 = \(\frac{1}{7}\),
Explanation:
Given to find x2 = \(\frac{1}{49}\) it is x2 = \(\frac{1}{7 X 7}\) = x2 = \(\frac{1}{7}\).
Question 18.
n3 = 19
Answer:
n = 2.66840164872,
Explanation:
Given to find cube root of 19 which is
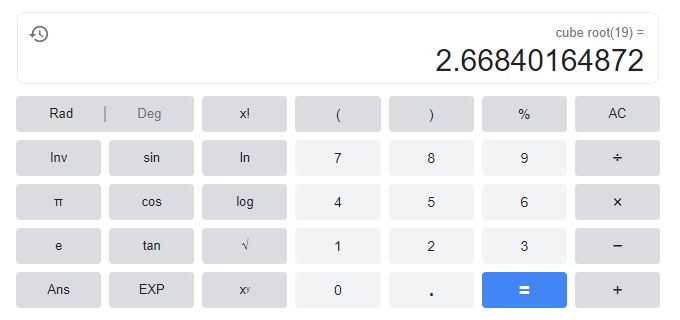
n = 2.66840164872.
Question 19.
y3 = \(\frac{27}{125}\)
Answer:
y3 = \(\frac{3}{5}\),
Explanation:
Given to find y3 = \(\frac{27}{125}\) it is y3 = \(\frac{3 X 3 X 3}{5 X 5 X 5}\),
so y = cube root of \(\frac{3 X 3 X 3}{5 X 5 X 5}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\).
I’m in a Learning Mindset!
How did I provide constructive feedback when solving Problem 12?
Answer:
A perfect square is always positive,
Explanation:
The constructive feedback when solving Problem 12 is a perfect square is an integer which is the square of another integer n that is n2.
Since a negative times a negative is positive a perfect square is always positive.
Lesson 10.2 More Practice/Homework
Question 1.
A puzzle maker built the cube puzzle shown.
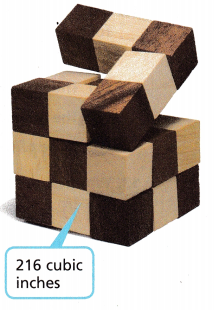
A. What is the edge length of the cube puzzle? Explain.
Answer:
The edge length of the cube puzzle is 6,
Explanation:
Given volume of the cube as 216 cubic inches let the edge length of cube puzzle be x, we have
now x3 = 216 it is x3 = 6 X 6 X 6, so x = 6, Therefore, the edge length of the cube puzzle is 6 cubic inches.
B. Suppose the puzzle maker wants to build a larger cube puzzle and wants the volume to be a perfect cube when measured in cubic inches. If the volume must be less than 1000 cubic inches, what are some volumes the puzzle maker could use? Explain.
Answer:
1 inch, 8 inches, 27 inches, 64 inches, 125 inches,
216 inches, 343 inches, 512 inches and 729 inches,
Explanation:
Given the puzzle maker wants to build a larger cube puzzle and wants the volume to be a perfect cube when measured in cubic inches. If the volume must be less than 1000 cubic inches, some volumes the puzzle maker could use are listed below as cube root of 1 x 1 x 1 = 1 inch,
cube root of 2 × 2 × 2 = 8 inches, cube root of 3 × 3 × 3 = 27 inches,
cube root of 4 × 4 × 4 = 64 inches, cube root of 5 × 5 × 5 = 125 inches,
cube root of 6 × 6 × 6 = 216 inches, cube root of 7 × 7 × 7 = 343 inches,
cube root of 8 × 8 × 8 = 512 inches and cube root of 9 × 9 × 9 = 729 inches.
Question 2.
Find the square roots of 169. Then find \(\sqrt {169}\). Explain why the answers are not exactly the same.
Answer:
One is square root and Other is arithmetic square root,
Explanation:
Given to find the square roots of 169 which is ±13, Then finding \(\sqrt {169}\)
which is 13 as the answers are not exactly the same because one is sqaure root and other is arithmetic square root.
Question 3.
Solve the equation y3 = \(\frac{64}{729}\). Show your work and explain your steps.
Answer:
y = \(\frac{4}{9}\),
Explanation:
Given to find y3 = \(\frac{64}{729}\), it is y3 = \(\frac{4 X 4 X 4}{9 X 9 X 9}\),
so y = \(\frac{4}{9}\).
Question 4.
Math on the Spot Solve each equation for x.
A. x2 = 81
Answer:
x = 9,
Explanation:
Given to find x2 = 81, it is x2 = 9 X 9, so x = square root of 9 X 9 = 9.
B. x2 = \(\frac{25}{144}\)
Answer:
x = \(\frac{5}{12}\),
Explanation:
Given to find x2 = \(\frac{25}{144}\), it is x2 = \(\frac{5 X 5}{12 X 12}\) so
x = square root of \(\frac{5}{12}\) X \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{12}\).
For Problems 5-10, find each root.
Question 5.
\(\sqrt{289}\)
Answer:
17,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt{289}\), it is \(\sqrt{17 X 17}\) = 17.
Question 6.
\(\sqrt[3]{512}\)
Answer:
8,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt[3]{512}\), it is \(\sqrt[3]{8 X 8 X 8}\) = 8.
Question 7.
\(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{1000}}\)
Answer:
10,
Explanation:
Given to find \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{1000}}\) it is \(\sqrt[3]{\frac{1}{10 X 10 X 10}}\) = 10.
Question 8.
z2 = \(\frac{81}{121}\)
Answer:
z = \(\frac{9}{11}\),
Explanation:
Given to find z which is sqaure root of z2 = \(\frac{81}{121}\) it is z = square root \(\frac{9 X 9}{11 X 11}\) = \(\frac{9}{11}\).
Question 9.
x3 = 343
Answer:
x = 7,
Explanation:
Given to find x as x3 = 343 it is x3 = 7 X 7 X 7, So x = cube root of 7 X 7 X 7 = 7.
Question 10.
y3 = \(\frac{8}{729}\)
Answer:
y = \(\frac{2}{9}\),
Explanation:
Given to find y where y3 = \(\frac{8}{729}\) it is y3 = \(\frac{2 X 2 X 2}{9 X 9 X 9}\),
so y = cube root of \(\frac{2 X 2 X 2}{9 X 9 X 9}\) = \(\frac{2}{9}\).
Test Prep
Question 11.
Which of the following is NOT a perfect cube?
(A) 1
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 27
Answer:
(C) 9,
Explanation:
Given to check which of the following is not a perfect cube as bit (A) = 1 it is perfect cube of 1 only,
bit (B) = 8 which is perfect cube of 2 as 2 X 2 X 2 = 8, bit (C) = 9 which is not a perfect cube as it has 2.08008, bit (D) = 27 which is a perfect cube of 3, therefore bit (C) 9 matches.
Question 12.
Iris wrote a square root of 144 on a piece of paper. Which one of the following must be true about the number she wrote?
(A) The number is 12.
(B) The number is -12.
(C) The number multiplied by itself equals 144.
(D) None of the above is true.
Answer:
(A) The number is 12,
Explanation:
Given Iris wrote a square root of 144 on a piece of paper.
To check which one of the following must be true about the number she wrote is bit (A).
The number is 12 it is true as square root of 144 is 12. Bits (B), (C) and (D) are not true.
Question 13.
Which of the following is an irrational number?
(A) \(\sqrt[3]{1}\)
(B) \(\sqrt{2}\)
(C) \(\sqrt[3]{27}\)
(D) \(\sqrt{25}\)
Answer:
(B) \(\sqrt{2}\),
Explanation:
Asked which one of the following is an irrational number so bit (A) \(\sqrt[3]{1}\) = 1 which is rational bit (B) \(\sqrt{2}\) = 1.414213 which is irrational,
bit (C) \(\sqrt[3]{27}\) = 3 which is rational, bit (D) \(\sqrt{25}\) = 5 which is rational therefore bit (B) \(\sqrt{2}\) matches.
Question 14.
Which number when squared makes 26?
(A) 52
(B) 13
(C) 5.5
(D) \(\sqrt{26}\)
Answer:
(D) \(\sqrt{26}\),
Explanation:
Asking which number when squared makes 26 as it equal to 5.09901 checking with
bit (A) 52 not equal to squared 26, bit (B) 13 which is not eqaul to squared 26,
bit (C) 5.5 which is not eqaul to squared 26, bit (D) \(\sqrt{26}\) equals to
squared 26 therefore bit (D) \(\sqrt{26}\) matches.
Question 15.
A square flower bed has an area of \(\frac{169}{36}\) square yards. What is the perimeter of the flower bed?
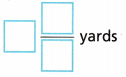
Answer:
8\(\frac{4}{6}\) yards,
Explanation:
Given a square flower bed has an area of \(\frac{169}{36}\) square yards.
So its side length is square root of \(\frac{169}{36}\) = square root of \(\frac{13 X 13}{6 X 6}\) = \(\frac{13}{6}\), Now the perimeter of the flower bed is
4 X \(\frac{13}{6}\) = \(\frac{52}{6}\) as numerator is greater we write in mixed fraction as 8\(\frac{4}{6}\) yards.
Spiral Review
Use the information and graph to solve Problems 16-17.
Ava is comparing the pricing at two different parking lots in the downtown area of her city. Both lots charge a fixed fee as well as an hourly rate. Ava makes the graph shown to compare the lots.
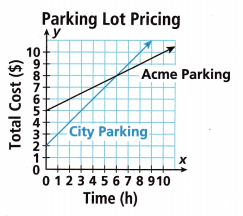
Question 16.
Which parking lot charges a greater hourly rate? Explain.
Answer:
Acme parking,
Explanation:
Given Ava is comparing the pricing at two different parking lots in the downtown area of her city.
Both lots charge a fixed fee as well as an hourly rate.
Ava has made the graph shown to compare the lots above it shows for City parking for 1 hour it is $3,
for 2 hours it is $4, for 3 hours it is $5 for 4 hours it is $6, for 5 hours it is $7 and so on,
Now for Acme parking it is 1 hour it is $5.5 for 2 hours it is $6, for 3 hours it is $6.5,
for 4 hours it is $7, for 5 hours it is $7.5 and so on, So when compairing parking lot charges of
Acme parking have greater hourly rate than City parking as $5.5 > $3, $6 > $4, $6.5 > $5.
Question 17.
Which parking lot charges a greater fixed fee? Explain.
Answer:
City parking,
Explanation:
As seen both City parking and Acme parking the lot charges of city parking has greater fixed fee
if we compare city parking for every 1 hour the fee increases $1 where as for acme parking
for every 1 hour the fee increases $0.5 so city parking has a greater fixed fee compared to other parking.
Question 18.
Is the number 0.575757… rational or irrational? If it is rational, express it as a fraction in the simplest form. If it is irrational, explain why.
Answer:
Rational,
Explanation:
Given to check is number 0.575757… rational or irrational, It is rational as we can express it as fraction as
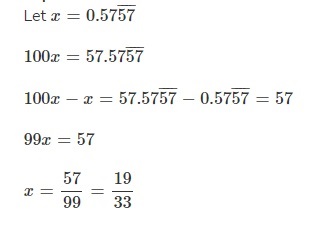
Therefore \(0 . \overline{57}\) as a fraction or mixed number in simplest form is \(\frac{19}{33}\).