We included HMH Into Math Grade 7 Answer Key PDF Module 14 Lesson 2 Find Experimental Probability of Simple Events to make students experts in learning maths.
HMH Into Math Grade 7 Module 14 Lesson 2 Answer Key Find Experimental Probability of Simple Events
I Can find an experimental probability and its complement.
Spark Your Learning
Toss a paper cup a number of times and record the different ways that the cup lands on a table. Describe each way that the cup lands as likely or unlikely. Organize your results in a table.
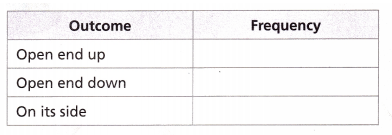
Answer:
Turn and Talk How do you think increasing the number of times you toss the cup would change your results?
Answer:
Build Understanding
Question 1.
Conduct an experiment by flipping a coin. Record your results in the table. Repeat until you have conducted the experiment 20 times.

A. How many trials did you conduct? Do the outcomes appear to be equally likely based on your results? Explain.
Answer:
B. Use the number of times each event occurs compared to the number of trials to approximate the probability of each event.
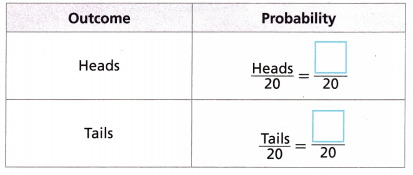
Answer:
C. If you flip the coin only four times, do you think it is possible that you might record only tails and no heads’,? What if you flip a coin 100 times? Compare the chances of the two possibilities.
Answer:
D. What happens to the number of times each outcome occurs as you perform more trials?
Answer:
E. What is the sum of the probabilities in Part B?
Answer:
Turn and Talk Are there any outcomes that did not occur in your set of trials? Why is this so?
Answer:
Step It Out
The experimental probability of an event is found by comparing the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials.
![]()
Question 2.
Muriel has a spinner with red, blue, and green sections. She spins the spinner 50 times and records the results in a table.

A. Find the experimental probability of each outcome.
Answer:
B. What conclusions can you make about the spinner using the experimental probabilities?
Answer:
C. How would you find the experimental probability of the spinner landing on a color that is not red, and what is that experimental probability in this example?
Answer:
D. How is the experimental probability of the spinner landing on a color that is not red related to the experimental probability of the spinner landing on red?
Answer:
Connect to Vocabulary
The complement of an event is the set of all outcomes in the sample space that are not included in the event. The sum of the probability of an event and the probability of its complement is 1.
E. Muriel spins the spinner another 50 times and records the outcomes. Do you think the experimental probabilities based on the results will be the same as the ones in Part A? Explain.
Answer:
A simulation is a model of an experiment that would be difficult to actually perform. A simulation can be used to find an experimental probability and make a prediction.
Question 3.
A softball player hits the ball and reaches base safely about 30% of the time. The player hits the ball but is called “out” about 50% of the time. The player strikes out about 20% of the time.
A. How could you use a random number generator to simulate the next 25 times the player comes up to hit the ball?
Answer:
B. Perform the simulation. Record your results.
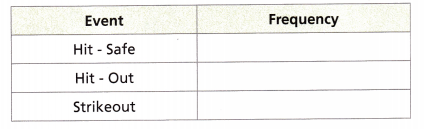
Answer:
C. Make a prediction based on your simulation.
Answer:
D. Combine the results of your simulation with the results of all the simulations. How do the total results of the class compare to your simulation?
Answer:
Check Understanding
Question 1.
Allison rolls a standard number cube 30 times and records her results. The number of times she rolled a 4 is 6. What is the experimental probability of rolling a 4? What is the experimental probability of not rolling a 4?
Answer:
Question 2.
Kelly averages 90% correct on her math assignments. She wants to perform a simulation to predict the number of questions she will answer correctly out of her next 70 questions. What is a simulation she could use to make this prediction?
Answer:
On Your Own
Question 3.
Andreas is performing an experiment involving rolling a number cube. “He rolls the number cube bD times and records the results in the table.
A. Construct Arguments Do you think the outcomes are equally likely? Explain.
Answer:
B. Find the experimental probabilities to complete the table.
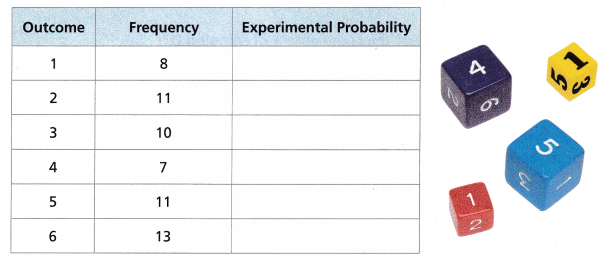
Answer:
Total = 8 + 11 + 10 + 7 + 11 + 13 = 60
Experimental probability = number of times event occur/total number of trials
Question 4.
Open-Ended Ask 8 students how many letters are in their first name. Record the number of letters for each answer. Describe one event from your experiment and find the experimental probability of this event.
Answer:
Question 5.
Use Tools A football quarterback completes 60% of attempted passes. Describe a simulation that you can perform in order to predict how many passes out of 40 this quarterback will complete.
Answer:
Question 6.
Jean estimates that her friend completes a new level of a video game on the first try 20% of the time. She conducts a simulation to predict how many times out of 80 her friend would complete a new level on the first try. Jean uses a random number generator. Every digit that is 8 or 9 represents completing the level. What is the probability that her friend completes a new level on the first try, written as a percent?
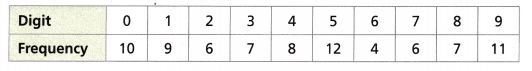
Answer:
Given,
Jean estimates that her friend completes a new level of a video game on the first try 20% of the time.
Total = 80
The probability is (7 + 11) ÷ (10 + 9 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 12 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 11)
= 18/80
= 9/40
= 22.5
Question 7.
Diego has a spinner that is divided into four sections labeled A, B, C, and D as shown. He spins the spinner many times and records the results. The results are shown in the table.
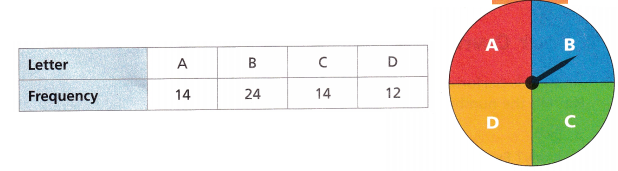
A. Add the frequency of each event to find the total number of times that he spun the spinner. Then find the experimental probability of spinning each letter.
Answer:
Number of possible outcomes of getting A = 14
Number of possible outcomes of getting B = 7
Number of possible outcomes of getting C = 11
Number of possible outcomes of getting D = 8
Total number of possible outcomes = 14 + 7 + 11 + 8 = 40
Probability of getting A = 14/40 = 7/20 = 0.35
Probability of getting B = 7/40 = 0.175
Probability of getting C = 11/40 = 0.275
Probability of getting D = 8/40 = 0.5
B. What is the probability of the complement of spinning D?
Answer:
Probability of getting D = 8/40 = 1/5
The probability of the complement of spinning D = 5
C. Construct Arguments What conclusion can Diego make about the bias of the spinner he used, based on the experimental probabilities? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 8.
Dustin buys packs of trading cards. He reads that half of the packs contain a bonus card. Dustin uses a coin to perform a simulation to estimate how many packs will contain a bonus card if he buys 20 packs. He uses heads to represent a pack with a bonus card. The results of his simulation are shown.
H, H, T, H, T, T, T, H, T, H, H, T, T, H, T, H, H, T, H, H
How many packs in this simulation did not contain a bonus card?
Answer:
I’m in a Learning Mindset!
Am I willing to accept new challenges while learning about probability?
Answer:
Lesson 14.2 More Practice/Homework
Question 1.
Luther is performing an experiment involving a triangular pyramid with faces labeled 1—4. He shakes it in a jar and empties the jar without looking 80 times. He records the number of the face it lands on in a table. Find the experimental probabilities to complete the table.
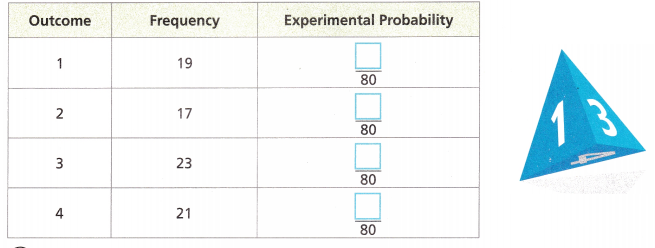
Answer:
Experimental probability = number of times event occur/total number of trials
Experimental probability of outcome 1 = 19/80
Experimental probability of outcome 2 = 17/80
Experimental probability of outcome 3 = 23/80
Experimental probability of outcome 4 = 21/80
Question 2.
Use Tools Marcela gets to school later than her friend Kim about half the time. Describe a way to simulate this event for 10 school days. Then perform the simulation. How many times does it show Marcela arriving later than Kim? What is the experimental probability of this event?
Answer:
Question 3.
Math on the Spot For one month, Terry recorded the time at which her school bus arrived. She organized her results in a frequency table. Find the experimental probability that the bus will arrive between 8:20 and 8:24. Find the experimental probability that the bus will arrive after 8:19.
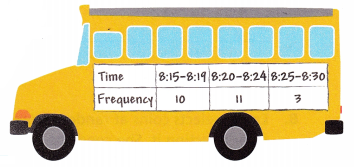
Answer:
Question 4.
Model with Mathematics Wei has two different routes he takes to a park. He labels the routes A and B. He takes route B about 33% of the time. Describe a simulation Wei could perform using a number cube to estimate the number of times he will take route B to get to the park if he goes to the park 60 times.
Answer:
Given,
Wei has two different routes he takes to a park.
He labels routes A and B. He takes route B about 33% of the time.
33% of 60
33/100 × 60 = 19.8
Test Prep
Question 5.
Asia has a jar of marbles. She randomly selects a marble from the jar, records its color, and returns it to the jar. She repeats this 74 times. Her results are shown in the table.
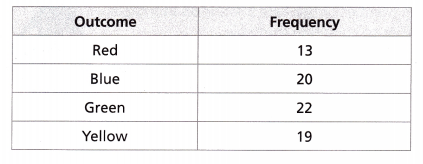
What is the experimental probability of Asia choosing a green marble?
Answer:
Total = 74
Number of green marbles = 22
Experimental probability = number of times event occur/total number of trials
P = 22/74 = 0.297
Thus the experimental probability of choosing green marble = 0.297
Question 6.
Jordan performed an experiment using a number cube. He rolled a number cube 50 times. He found that he rolled a 6 a total of 8 times. What is the experimental probability that he did not roll a 6?
(A) \(\frac{3}{25}\)
(B) \(\frac{4}{25}\)
(C) \(\frac{21}{25}\)
(D) \(\frac{22}{25}\)
Answer: (C) \(\frac{21}{25}\)
Explanation:
Given,
Jordan performed an experiment using a number cube.
He rolled a number cube 50 times.
He found that he rolled a 6 a total of 8 times.
Number of times not rolling a 6 = 50 – 8 = 42
p(~6) = \(\frac{42}{50}\) = \(\frac{21}{25}\)
Option C is the correct answer.
Question 7.
Juan rolls a number cube 40 times. He rolls a 3 on the number cube 6 times. What is the experimental probability that he rolls a 3?
Answer:
Given,
Juan rolls a number cube 40 times. He rolls a 3 on the number cube 6 times.
Experimental probability = Time the event occurs/ Total number of trials
In this case, the event we are looking for is rolling a 3 on the number cube. The total number of trials is: 40
P = 6/40
P = 3/20
Spiral Review
Question 8.
Emma selects coins at random from a jar, putting the coin back each time after selecting it. She conducts 28 trials and selects 7 pennies, 12 nickels, and 9 dimes. Based on the results, describe in words the likelihood that she selects a penny.
Answer:
Question 9.
Claire wants to start a stamp collection. She spends $15 on an album to hold her stamps and $1.25 for each stamp. If she has $40, what is the maximum number of. stamps she can buy?
Answer:
Given,
Claire wants to start a stamp collection.
She spends $15 on an album to hold her stamps and $1.25 for each stamp.
40 – 15 = 25
25 ÷ 1.25 = 20