Everyday Mathematics 6th Grade Answer Key Unit 6 Equivalent Expressions and Solving Equations
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.1 Answers
Approximating Solutions
For each equation, try to get as close as possible to the exact solution. Use the suggested test numbers to get started. Round numbers to the nearest thousandth.
Question 1.
Equation: r2 + r = 15
My closest number: ___________
Answer:
The given equation is:
r² + r = 15
So,
The completed table of the values of r, r², and r² + r is:
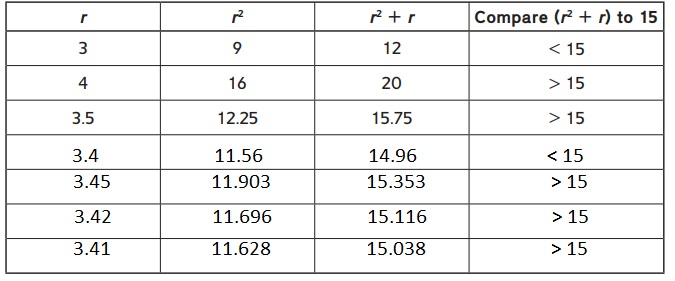
Hence, from the above table,
We can conclude that the closest exact number for the given equation is: 3.41
Question 2.
Equation: x2 – 2x = 23
My closest number: __________
Answer:
The given equation is:
x² – 2x = 23
So,
The completed table of the values of x, x², 2x, and x² – 2x is:
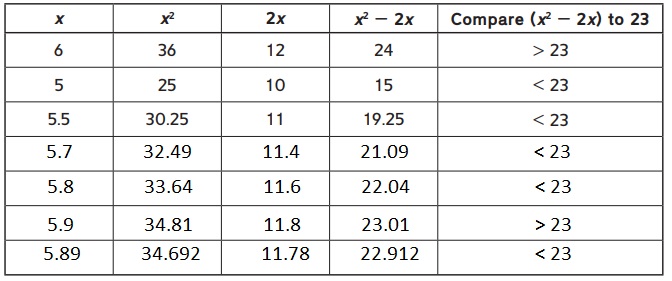
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the closest exact number for the given equation is: 5.9
Practice
Rewrite each expression in exponential notation.
Question 3.
9 × 9 × 9 __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
9 × 9 × 9
Hence,
The representation of the given expression in the exponential form is: 93
Question 4.
7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7 _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
7 × 7 × 7 × 7 × 7
Hence,
The representation of the given expression in the exponential form is: 75
Question 5.
6.2 × 6.2 ________
Answer:
The given expression is:
6.2 × 6.2
Hence,
The representation of the given expression in the exponential form is: 6.22
Everyday Math Grade 6 Home Link 6.2 Answer Key
Solution Sets
Question 1.
The solution set is {all numbers less than 7}. Circle inequalities with this solution set.
j > 4
7 < j
7 > j
j < 7
Answer:
The given inequalities are:
j > 4
7 < j
7 > j
j < 7
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the solution sets for all the numbers less than 7 are:
j < 7, and 7 > j
Question 2.
a. The solution set is {all numbers greater than 10}. Circle inequalities with this solution set.
m + 10 < 11
11 < m + 1
6 > 5 + m
6 > 5m
Answer:
The given inequalities are:
a) m + 10 < 11
b) 11 < m + 1
c) 6 > 5 + m
d) 6 > 5m
So,
a)
Subtract with 10 on both sides
So,
m + 10 – 10 < 11 – 10
m < 1
b)
Subtract with 1 on both sides
So,
11 – 1 < m + 1 – 1
10 < m
m > 10
c)
Subtract with 5 on both sides
So,
6 – 5 > 5 + m – 5
1 > m
m < 1
d)
6 > 5m
So,
5m < 6
m < \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the solution set for all numbers greater than 10 is: m > 10
b. Explain how you found your answer for Problem 2a.
Answer:
We have to solve the given inequalities so that only variable will be present either it is given on the left side or the right side
So,
We will get the inequality in the form of
Variable < constant or Variable > constant or Variable = constant
Hence, in the above way,
We can conclude that we have found the answer to problem 2a.
Question 3.
Record the solution sets for the equations below.
a. 3x = 45
Solution set: __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
3x = 45
Divide with 3 on both sides
So,
\(\frac{3}{3}\)x = \(\frac{45}{3}\)
x = 15
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the solution set for the given expression is: {15}
b. x + 138 = 204
Solution set: ____________
Answer:
The given expression is:
x + 138 = 204
Subtract with 138 on both sides
So,
x + 138 – 138 = 204 – 138
x = 66
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the solution set for the given expression is: {66}
Question 4.
Write the letter of the solution set that matches each number sentence.
x ÷ 4 = 8 ________ A. {All numbers}
\(\frac{4}{x}\) = 8 _________ B. {0}
10 – x = 7 __________ C. { }
3x + x = 16 _________ D. {\(\frac{1}{2}\)}
5x = 0 __________ E. {- \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\)}
12 ∗ x = x ∗ 12 ________ F. {3}
0.5 = |x| _________ G. {32}
x – 5 = x __________ H. {4}
Answer:
The given expressions are:
a)
x ÷ 4 = 8
So,
x = 8 × 4
x = 32
So,
The solution set is: {32}
b)
\(\frac{4}{x}\) = 8
So,
x = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
The solution set is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
c)
10 – x = 7
So,
x = 10 – 7
x = 3
So,
The solution set is: {3}
d)
3x + x = 16
4x = 16
x = \(\frac{16}{4}\)
x = 4
So,
The solution set is: {4}
e)
5x = 0
x = \(\frac{0}{5}\)
x = 0
So,
The solution set is: {0}
f)
12 * x = x * 12
12x = 12x
So,
The solution set is: {All numbers}
g)
0.5 = |x|
We know that,
|x| = x for x > 0
|x| = -x for x < 0
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = |x|
x = \(\frac{1}{2}\) or x = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
The solution set is: {\(\frac{1}{2}\), –\(\frac{1}{2}\)}
h)
x – 5 = x
x – x = 5
0 = 5
So,
The solution set is: No solution or {}
Hence, from the above,
The letter of the solution set that matches each number sentence is:

Practice
Divide.
Question 5.
8.8 ÷ 2 = _______
Answer:
The given expression is:
8.8 ÷ 2
So,
8.8 ÷ 2 = (8 + 0.8) ÷ 2
= (8 ÷ 2) + (0.8 ÷ 2)
= 4 + 0.4
= 4.4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 4.4
Question 6.
0.95 ÷ 5 = _______
Answer:
The given expression is:
0.95 ÷ 5
So,
0.95 ÷ 5 = (0.90 + 0.5) ÷ 5
= (0.90 ÷ 5) + (0.5 ÷ 5)
= 0.18 + 0.1
= 0.19
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 0.19
Question 7.
98 ÷ 0.2 = _____
Answer:
The given expression is:
98 ÷ 0.2
So,
98 ÷ 0.2
= 980 ÷ 2
= (1,000 – 20) ÷ 2
= (1,000 ÷ 2) – (20 ÷ 2)
= 500 – 10
= 490
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 490
Question 8.
198 ÷ 0.2 = ________
Answer:
The given expression is:
198 ÷ 0.2
So,
198 ÷ 0.2
= 1980 ÷ 2
= (2,000 – 20) ÷ 2
= (2,000 ÷ 2) – (20 ÷ 2)
= 1,000 – 10
= 990
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 990
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.3 Answers
Modeling and Solving Number Stories
Use bar models to solve these equations. Check your answers.
Question 1.
4a + 12 = 96
Solution: _______
Check: _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
4a + 12 = 96
We know that,
A bar model is a pictorial representation of a problem or concept where bars or boxes are used to represent the known and unknown quantities.
So,
Subtract with 12 on both sides
4a + 12 – 12 = 96 – 12
4a = 84
a = \(\frac{84}{4}\)
a = 21
Now,
The representation of the given expression as a bar model is:
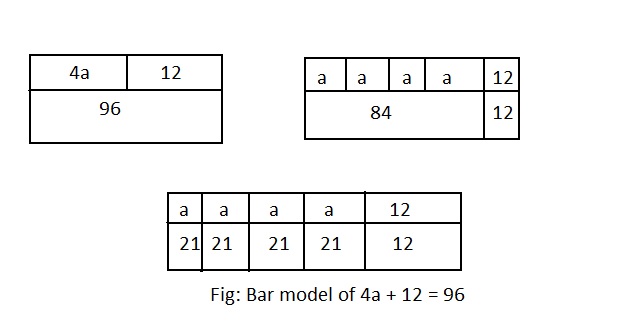
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of a is: 21
Question 2.
6d + 7 = d + 22
Solution: _______
Check: _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
6d + 7 = d + 22
We know that,
A bar model is a pictorial representation of a problem or concept where bars or boxes are used to represent the known and unknown quantities.
So,
Subtract with 7 on both sides
6d + 7 – 7 = d + 22 – 7
6d = d + 15
6d – d = 15
5d = 15
d = \(\frac{15}{5}\)
d = 3
Now,
The representation of the given expression as a bar model is:
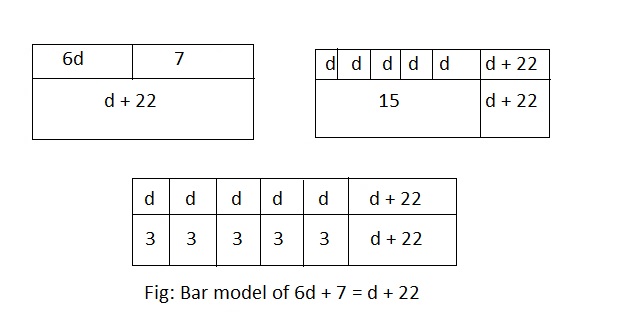
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of d is: 3
Use bar models to solve the problems.
Question 3.
Jane is 6 years older than twice Martin’s age.
Let s be Martin’s age.
The sum of Jane’s and Martin’s ages is 39.
a)
Write an expression to represent Jane’s age ________________
b)
Write an equation to represent the situation. _____________
c)
How old are Jane and Martin?
Jane: __________
Martin: __________
Answer:
a)
It is given that
Jane is 6 years older than twice Martin’s age
It is also given that s is Martin’s age
So,
The expression to represent Jane’s age is: 2s + 6
b)
It is also given that
The sum of Jane’s and Martin’s age is 39
So,
Jane’s age + Martin’s age = 39
From part (a),
Jane’s age = 2s + 6
So,
2s + 6 +s = 39
3s + 6 = 39
Subtract with 6 on both sides
So,
3s + 6 – 6 = 39 – 6
3s = 33
s = \(\frac{33}{3}\)
s = 11 years
So,
Jane’s age = 2s + 6
= 2 (11) + 6
= 22 + 6
= 28 years
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
The age of Jane is: 28 years
The age of Martin is: 11 years
Try This
Question 4.
Dan is thinking of a number. He doubles his number and adds 15. He multiplies his number by 5 and gets the same answer. Let n be Dan’s number.
a)
Write an equation to represent the situation. ____________
b)
Dan’s number: __________
Answer:
a)
It is given that
Dan doubles his number and adds 15.
It is also given that he multiplies his number by 5 and gets the same answer
Now,
Let n be Dan’s number
So,
So,
The representation of “Dan doubles his number and adds 15” is: 2n + 15
The representation of “He multiplies his number by and gets the same answer” is: 5n = 2n + 15
Hence,
The equation to represent the above situation is: 5n = 2n + 15
b)
From part (a),
The equation that represents the given siyuation is:
5n = 2n + 15
Subtract with 2n on both sides
So,
5n – 2n = 2n + 15 – 2n
3n = 15
n = \(\frac{15}{3}\)
n = 5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that Dan’s number is: 5
Practice
Solve.
Question 5.
5 × (6.8 – 2) = ________
Answer:
The given expression is:
5 × (6.8 – 2)
= 5 × 4.8
= 24.0
= 24
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 24
Question 6.
8 ÷ 2 × 3.5 = ________
Answer:
The given expression is:
8 ÷ 2 × 3.5
According to the BODMAS rule,
We have to first make the division and then multiplication (D – Division, M – Multiplication in the BODMAS)
So,
\(\frac{8}{2}\) × 3.5
= 4 × 3.5
= 14.0
= 14
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 14
Question 7.
9.43 – 4.5 + 1.7 = _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
9.43 – 4.5 + 1.7
According to the BODMAS rule,
We have to first make the addition and then subtraction (A – Addition, S – Subtraction in the BODMAS)
So,
(9.43 + 1.7) – 4.5
= 11.13 – 4.5
= 6.63
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 6.63
Everyday Math Grade 6 Home Link 6.4 Answer Key
Pan-Balance Problems
In each figure, the two pans are balanced. Solve these pan-balance problems.
Question 1.
One triangle weighs as much as __________ squares.
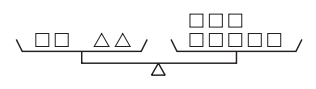
Answer:
In the given figure,
Let each triangle be x
Let each square be y
It is given that the two pans are balanced
So,
LHS = RHS
Now,
2x + 2y = 8y
Subtract with 2y on both sides
2x + 2y – 2y = 8y – 2y
2x = 6y
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = ]latex]\frac{6}{2}[/latex]
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{3}{1}\)
x = 3y
1 Triangle = 3 squares
So,
From the above expression,
We can say that one triangle weighs as much as 3 squares
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that 1 Triangle weighs as much as 3 Squares
Question 2.
One ball weighs as much as _______ coin(s).
Note: Remember that 2 ![]() means
means ![]()
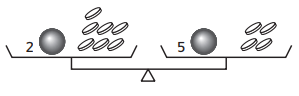
Answer:
In the given figure,
Let each circle be x
Let each coin be y
It is given that the two pans are balanced
So,
LHS = RHS
Now,
2x + 7y = 4y + 5x
Rearrange the like terms at one side
So,
5x – 2x = 7y – 4y
3x = 3y
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{3}{3}\)
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{1}{1}\)
x = y
So,
1 Circle = 1 Coin
So,
From the above expression,
We can say that one circle weighs as much as 1 coin
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that 1 Circle weighs as much as 1 Coin
Question 3.
Two cantaloupes weigh as much as _________ apples.
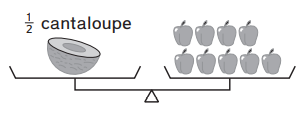
Answer:
In the given figure,
Let each cantaloupe be x
Let each apple be y
It is given that the two pans are balanced
So,
LHS = RHS
Now,
\(\frac{1}{2}\)x = 9y
Multiply with 2 on both sides
So,
\(\frac{2}{2}\)x = 9 (2)y
x = 18y
Multiply with 2 again on both sides
So,
2x = 18 (2)y
2x = 36y
So,
2 Cantaloupes = 36 Apples
So,
From the above expression,
We can say that two cantaloupes weigh as much as 36 apples
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that 2 Cantaloupes weigh as much as 36 Apples
Question 4.
One cube weighs as much as _________ coin(s).
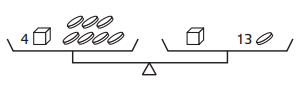
Answer:
In the given figure,
Let each cube be x
Let each coin be y
It is given that the two pans are balanced
So,
LHS = RHS
Now,
4x + 7y = 13y + x
Rearrange the like terms at one side
So,
4x – x = 13y – 7y
3x = 6y
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{6}{3}\)
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{2}{1}\)
x = 2y
So,
1 Cube = 2 Coins
So,
From the above expression,
We can say that one cube weighs as much as 2 coins
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that 1 Cube weighs as much as 2 Coins
Question 5.
One cube weighs as much as _______ marbles.
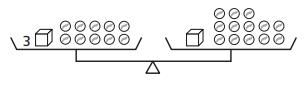
Answer:
In the given figure,
Let each cube be x
Let each marble be y
It is given that the two pans are balanced
So,
LHS = RHS
Now,
3x + 10y = 13y + x
Rearrange the like terms at one side
So,
3x – x = 13y – 10y
2x = 3y
\(\frac{x}{y}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
x = \(\frac{3}{2}\)y
So,
1 Cube = \(\frac{3}{2}\) Marbles
So,
From the above expression,
We can say that one cube weighs as much as \(\frac{3}{2}\) marbles
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that 1 Cube weighs as much as \(\frac{3}{2}\) Marbles
Practice
Solve.
Question 6.
1 = \(\frac{3}{5}\) × ________
Answer:
Let the missing term be x in the given expression
So,
1 = \(\frac{3}{5}\) × x
Multiply by \(\frac{5}{3}\) on both sides
So,
x = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing term in the given expression is: \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Question 7.
\(\frac{1}{6}\) × ______ = 1
Answer:
Let the missing term in the given expreesion be x
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) × x = 1
Multiply with 6 on both sides
\(\frac{6}{6}\)x = 1 (6)
So,
x = 6
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing term in the given expression is: 6
Question 8.
________ × 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 1
Answer:
Let the missing term in the given expression be x
So,
x × 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) = 1
We know that,
1\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
So,
x × \(\frac{3}{2}\) = 1
Multiply with \(\frac{2}{3}\) on both sides
So,
x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing term in the given expression is: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 9.
1 = 1 \(\frac{5}{6}\) × _________
Answer:
Let the missing term in the given expression be x
So,
1 = 1\(\frac{5}{6}\) × x
We know that,
1\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{11}{6}\)
So,
1 = \(\frac{11}{6}\) × x
Multiply with \(\frac{6}{11}\) on both sides
So,
x = \(\frac{6}{11}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing term in the given expression is: \(\frac{6}{11}\)
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.5 Answers
Solving Pan-Balance Problems
Question 1.
These two pan balances are in perfect balance.
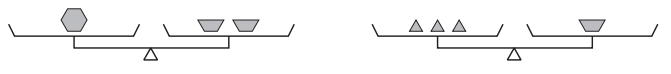
a. Use the relationships in the pan balances shown above to determine which of the pan balances below are balanced. Circle the ones that are in balance.
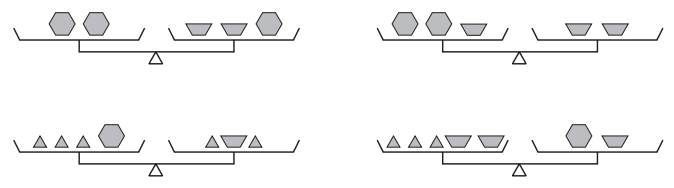
Answer:
b. For any pan balance above that you did not a circle, add, or cross out objects to balance the pans.
Answer:
Let each hexagon be x
Let each semicircle be y
Let each triangle be z
Now,
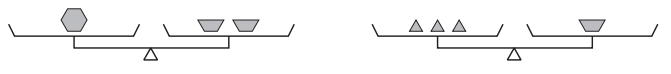
It is given that these 2 pan balances are in perfect balance
So,
x = 2y —–> From pan 1 ———> (1)
3z = y ——> From Pan 2 ———> (2)
a)
The given pan balances are:

Now,
From Pan 1,
2x = 2y + x
Subtract with x on both sides
2x – x = 2y + x – x
x = 2y
From Pan 2,
2x + y = 2y
Subtract with y on both sides
2x + y – y = 2y – y
2x = y
From Pan 3,
3z + x = 2z + y
Rearrange the terms at both sides
So,
3z – 2z = y – x
z = y – x
From Pan 4,
3z + 2y = x + y
Rearrange the terms at both sides
So,
x – 3z = 2y – y
x – 3z = y
2y – 3z = y (From eq (2))
3z = 2y – y
y = 3z
Now,
When we compare eq (1) and eq (2) with the equations of 4 pans,
We can observe that Pan 1 and Pan 4 are the balanced
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the pans that are in balance are:
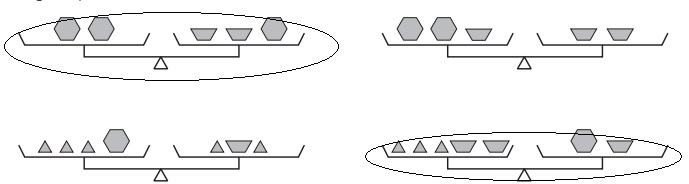
b)
From part (a),
We can observe that Pan 2 and Pan 4 are not balanced as of eq (1) and eq (2)
Now,
The pan equations of Pan2 and Pan 3 are:
2x = y —–> Pan 2’s equation
z = y – x —–> Pan 3’s equation
Now,
To balance the Pan 2’s equation,
We have to add x and y at the right side of the Pan 2’s equation to compare with eq (1)
So,
2x = y + x + y
Hence,
For Pan 2 to be balanced,
We have to add a hexagon and a semicircle at the right side of the pan 2
Now,
To balance the Pan 3’s equation,
We have to add 2z at the left side and x at the right side of the Pan 3’s equation to compare with eq (2)
So,
2z + z = y – x + x
Hence,
For Pan 3 to be balanced,
We have to add 2 triangles at the left side and 1 hexagon at the right side of the pan 3
Question 2.
Find the value of the missing number that will balance each set of pans below. The same number is missing from both sides of a pan balance.
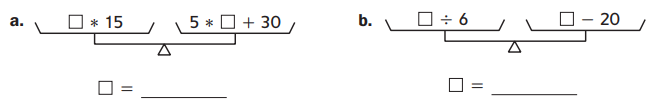
Answer:
The given pan balances are:
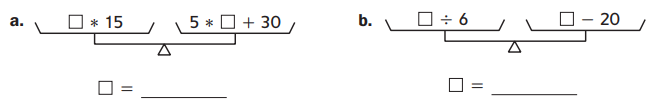
a)
Let the missing numer be x
Since the pans are balanced,
LHS = RHS
So,
15 × x = 5 × x + 30
15x = 5x + 30
15x – 5x = 30
10x = 30
x = \(\frac{30}{10}\)
x = 3
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing number is: 3
b)
Let the missing number be x
Since the pans are balanced,
LHS = RHS
So,
x ÷ 6 = x – 20
Multiply with 6 on both sides
x = 6(x – 20)
x = 6x – 120
6x – x = 120
5x = 120
x = \(\frac{120}{5}\)
x = 24
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing number is: 24
Question 3.
Makeup two of your own missing-number pan balances.
Fill in the missing numbers for the pan-balance problems you made.
Answer:
a)
Let the missing number be y
Since the pan is balanced,
LHS = RHS
So,
The equation is:
5y = 20
y = \(\frac{20}{5}\)
y = 4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing number is: 4
b)
Let the missing number be x
Since the pan is balanced,
LHS = RHS
So,
The equation is:
x + 3 = 5
Subtract with 3 on both sides
x + 3 – 3 = 5 – 3
x = 2
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the missing number is: 2
Practice
Solve.
Question 4.
4.3 × 7 = _____
Answer:
The given expression is:
4.3 × 7
= (4 + 0.3) × 7
= (4 × 7 ) + (0.3 × 7)
= 28 + 2.1
= 30.1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 30.1
Question 5.
0.2 × 1.5 = ______
Answer:
The given expression is:
0.2 × 1.5
= 0.2 × (1 + 0.5)
= (0.2 × 1) + (0.2 × 0.5)
= 0.2 + 0.1
= 0.3
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 0.3
Question 6.
1.9 × 2.3 = ________
Answer:
The given expression is:
1.9 × 2.3
= (2 – 0.1) × (2 + 0.3)
= (2 × 2) + (2 × 0.3) – (0.1 × 2) – (0.1 × 0.3)
= 4 + 0.6 – 0.2 – 0.03
= 4 + 0.37
= 4.37
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 4.37
Everyday Math Grade 6 Home Link 6.6 Answer Key
Simplifying Expressions
Question 1.
Simplify each expression by combining the like terms.
a. 42x + 12x __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
42x + 12x
= x (42 + 12)
= x(54)
= 54x
Hence,
42x + 12x = 54x
b. 17w – 8w __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
17w – 8w
= w (17 – 8)
= w (9)
= 9w
Hence,
17w – 8w = 9w
c. 25.42e – 23.3e __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
25.42e – 23.3e
= e (25.42 – 23.3)
= e (2.12)
= 2.12e
Hence,
25.42e – 23.3e = 2.12e
d. 88h + 30.5h __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
88h + 30.5h
= h (88 + 30.5)
= h (118.5)
= 118.5h
Hence,
88h + 30.5h = 118.5h
Question 2.
Simplify. Check that your expressions are equivalent.
a. 12m + 24m
Answer:
The given expression is:
12m + 24m
= m (12 + 24)
= m (36)
= 36m
Hence,
12m + 24m = 36m
b. 90a – 30a
Answer:
The given expression is:
90a – 30a
= a (90 – 30)
= a (60)
= 60a
Hence,
90a – 30a = 60a
c. 14b + 15b + 8
Answer:
The given expression is:
14b + 15b + 8
= b (14 + 15) + 8
= b (29) + 8
= 29b + 8
Hence,
14b + 15b + 8 = 29b + 8
d. 58d + 25 – 22d
Answer:
The given expression is:
58d + 25 – 22d
= d ( 58 – 22) + 25
= d (36) + 25
= 36d + 25
Hence,
58d + 25 – 22d = 36d + 25
e. 3(14 + 15f) + 79
Answer:
The given expression is:
3 (14 + 15f) + 79
= 3 (14) + 3 (15f) + 79
= 45f + 42 + 79
= 45f + 121
Hence,
3 (14 + 15f) + 79 = 45f + 121
f. 20(18 + 5t) – 47 + 28t
Answer:
The given expression is:
20 (18 + 5t) – 47 + 28t
= 20 (18) + 20 (5t) – 47 + 28t
= 360 + 100t – 47 + 28t
= t (100 + 28) + 360 – 47
= t (128) + 313
= 128t + 313
Hence,
20 (18 + 5t) – 47 + 28t = 128t + 313
Practice
Insert =, <, or >.
Question 3.
-5 _____ -10
Answer:
The given expression is:
-5 ______ -10
We know that,
5 is less than 10
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
-5 > -10
Question 4.
0.23 _____ 0.009
Answer:
The given expression is:
0.23 _____ 0.009
We know that,
0.23 is greater than 0.009
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
0.23 > 0.009
Question 5.
-11 ______ 1
Answer:
The given expression is:
-11 _____ 1
We know that,
-11 is less than 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
-11 < 1
Question 6.
0.092 ______ 0.0920
Answer:
The given expression is:
0.092 _____ 0.0920
We know that,
0.92 is equal to 0.0920 (Since if the last digit is 0, then it does not have any value after the decimal point)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
0.092 = 0.0920
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.7 Answers
Exploring Equivalent Equations
Question 1.
Use the Commutative Property (turn-around rule) to create an equivalent expression in which like terms are next to each other.
a. 12k + 2 × 3 + 3k + 1 __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
12k + 2 × 3 + 3k + 1
Using the Commutative property (Turn -around rule),
The representation of the given expression is:
12k + 3k + 3 × 2 + 1
b. Combine like terms from Problem 1a and write a simplified equivalent expression.
Answer:
From paroblem 1a,
The given expression is:
12k + 2 × 3 + 3k + 1
= 12k + 6 + 3k + 1
= k (12 + 3) + 6 + 1
= k (15) + 7
= 15k + 7
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the simplified expression for the expression mentioned in problem 1a is: 15k + 7
Write the expressions in the simplest form.
Question 2.
4a + 5 – a + 10 __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
4a + 5 – a + 10
= a (4 – 1) + 5 + 10
= a (3) + 15
= 3a + 15
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the simplified expression for the given expression is: 3a + 15
Question 3.
10(b + 5) + 15 + w _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
10 (b + 5) + 15 + w
= 10 (b) + 10 (5) + 15 + w
= 10b + 50 + 15 + w
= 10b + w + 65
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the simplified expression for the given expression is: 10b + w + 65
For Problems 4–5, identify the equations that are equivalent to the given equation. Circle ALL that apply.
Question 4.
6x + (7 – 2) × x = 8 + 3x – 4
A. 6x + 5x = 8 + 3x – 4
B. 6x + (7 – 2) × x = 3x + 12
C. 11x = 3x + 4
Answer:
The given expression is:
6x + (7 – 2) × x = 8 + 3x – 4
6x + 5 × x = 8 + 3x – 4
6x + 5x = 8 + 3x – 4
11x = 3x + 4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the equations that are equivalent to the given equation are: A and C
Question 5.
b + 2b – 10 = 10(b + 5) + 15 + b
A. 3b – 10 = 10(b + 5) + 15 + b
B. b + 2b – 10 = 10b + 50 + 15b
C. b(1 + 2) – 10 = 10b + 50 + 15 + b
Answer:
The given expression is:
b + 2b – 10 = 10 (b + 5) + 15 + b
3b – 10 = 10 (b + 5) + 15 + b
3b – 10 = 10 (b) + 10 (5) + 15 + b
3b – 10 = 10b + 50 + 15 + b
b (1 + 2) – 10 = 10b + 50 + 15 + b
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the equivalent equations for the given equation are: A and C
Question 6.
Use a bar model or pan-balance model to solve one of the equations you circled in Problem 4.
x = _________
Answer:
One of the quations that is circled in problem 4 is:
11x = 3x + 4
Now,
Subtract with 3x on both sides
11x – 3x = 3x + 4 – 3x
8x = 4
x = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence,
The representation of bar model for the equation we have taken is:
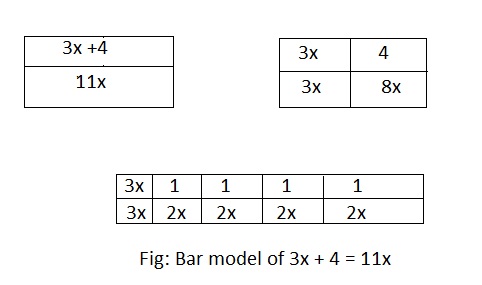
Practice
Multiply
Question 7.
2\(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{3}{7}\) = _________
Answer:
The given expression is:
2\(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{3}{7}\)
= \(\frac{7}{3}\) × \(\frac{3}{7}\)
= \(\frac{7 × 3}{3 × 7}\)
= \(\frac{1}{1}\)
= 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 1
Question 8:
1\(\frac{2}{3}\) × 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) = __________
Answer:
The given expression is:
1\(\frac{2}{3}\) × 2\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{5}{3}\) × \(\frac{5}{2}\)
= \(\frac{5 × 5}{3 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{25}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We acn conclude that the value of the given expression is: \(\frac{25}{6}\)
Question 9.
_______ = 3\(\frac{7}{10}\) × 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
The given expression is:
3\(\frac{7}{10}\) × 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{37}{10}\) × \(\frac{9}{4}\)
= \(\frac{37 × 9}{10 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{333}{40}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: \(\frac{333}{40}\)
Question 10:
5\(\frac{3}{4}\) × 4\(\frac{2}{5}\) = ______
Answer:
The given expression is:
5\(\frac{3}{4}\) × 4\(\frac{2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{23}{4}\) × \(\frac{22}{5}\)
= \(\frac{23 × 22}{4 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{506}{20}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: \(\frac{506}{20}\)
Everyday Math Grade 6 Home Link 6.8 Answer Key
Comparing Racing Times
Katya runs at a rate of 6.25 meters per second. Her younger cousin, Liova, runs 2.5 meters per second. Because Katya runs faster than Liova, she gives Liova a 100-meter head start in a 200-meter race.
Question 1.
Using the variable t to represent the number of seconds, write two expressions—one for Katya and one for Liova—that model how far from the start line they will be after t seconds.
Expression for Katya: _______________
Expression for Liova: _________________
Answer:
a)
It is given that Katya runs at a rate of 6.25 meters per second and her younger cousin, Liova, runs 2.5 meters per second.
We know that,
Speed = \(\frac{Distance}{Time}\)
It is given that use the variable t for time
So,
The expression that represents how far Katya is from the start line is:
Distance (d) = Speed (Time)
d = 6.25t
Hence,
The expression of how far Katya traveled from the start line is:
d = 6.25t
b)
It is also given that Katya runs faster than Liova, and she gives Liova a 100-meter head start in a 200-meter race.
So,
The expression that represents how far Liova is from the start line is:
Distance (d) = Speed (Time)
d = 100 + 2.5t
Hence,
The expression of how far Liova is from the start line is:
d = 100 + 2.5t
Question 2.
Use your expressions from Problem 1 to figure out who will win the race.
Show your work and explain your answer.
Winner: _____________
Answer:
From problem 1,
We know that,
Katya runs 200 meters and she gives Liova a 100 meters headstart
Now,
The expression of how far Katya is from the start line is:
d = 6.25t
Now,
t = \(\frac{d}{6.25}\)
t = \(\frac{200}{6.25}\)
t = 32 seconds
The expression of how far Liona is from the start line is:
d = 100 + 2.5t
Now,
200 = 100 + 2.5t
2.5t = 200 – 100
2.5t = 100
t = \(\frac{100}{2.5}\)
t = 40 seconds
When we compare the time taken by Katya and Liova to complete the race,
We can observe that
The time took by Katya < The time took by Liova
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that Katya wins the race
Practice
Solve.
Question 3.
5% of 66 is _______.
Answer:
The given expression is:
5% of 66
So,
5% of 66
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) × 66
= 0.05 × 66
= 3.30
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 3.30
Question 4.
18% of 50 is ___________ .
Answer:
The given expression is:
18% of 50
So,
18% of 50
= \(\frac{18}{100}\) × 50
= 0.18 × 50
= 9
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 9
Question 5.
45% of 120 is _______.
Answer:
The given expression is:
45% of 120
So,
45% of 120
= \(\frac{45}{100}\) × 120
= \(\frac{45}{10}\) × 12
= \(\frac{45 × 12}{10}\)
= 54
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 54
Question 6.
90% of 8,000 is _________.
Answer:
The given expression is:
90% of 8,000
So,
90% of 8,000
= \(\frac{90}{100}\) × 8,000
= 90 × 80
= 7,200
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of the given expression is: 7,200
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.9 Answers
Using Inverse Operations
Question 1.
Linda has a secret number. She doubles the number, adds 5, and then subtracts 7. Her result is 8. What was her original secret number? Explain what you did to find her secret number.
Answer:
It is given that Linda has a secret number.
It is also given that she doubles the number, adds 5, and then subtracts 7. Her result is 8.
Now,
Let the secret number of Linda be x
So,
Double of Linda’s secret number is: 2x
So,
2x + 5 – 7 = 8
2x – 2 = 8
Add with 2 on both sides
2x – 2 + 2 = 8 + 2
2x = 10
x = \(\frac{10}{2}\)
x = 5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the secret number of Linda is: 5
The process of how I find Linda’s secret number:
I subtracted 5 from -7 to get -2 and added 2 on both sides to make 0 on the left side and make 10 on the right side and I make half of the value of 10 to get the result i.e., 5
For Problems 2–5, solve the equations using the inverse-operations strategy. Show all of your steps and check your work.
Question 2.
257 = a – 105
Check:
Answer:
The given expression is:
257 = a – 105
Add with 105 on both sides
So,
257 + 105 = a – 105 + 105
362 = a
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of ‘a’ from the given expression is: 362
Question 3.
12 = \(\frac{r}{4}\)
Check:
Answer:
The given expression is:
12 = \(\frac{r}{4}\)
Multiply with 4 on both sides
So,
12 (4) = \(\frac{4r}{4}\)
r = 48
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of r from the given expression is: 48
Question 4.
j + 3 \(\frac{3}{4}\) = 8
Check:
Answer:
The given expression is:
j + 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = 8
We know that,
3\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{15}{4}\)
So,
j + \(\frac{15}{4}\) = 8
Subtract with \(\frac{15}{4}\) on both sides
So,
j + \(\frac{15}{4}\) – \(\frac{15}{4}\) = 8 – \(\frac{15}{4}\)
j = \(\frac{17}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of j from the given expression is: \(\frac{17}{4}\)
Question 5.
6.72 = 4u
Check:
Answer:
The given expression is:
6.72 = 4u
Divide by 4 on both sides
So,
\(\frac{6.72}{4}\) = \(\frac{4u}{4}\)
1.68 = u
u = 1.68
Hence,f rom the above,
We can conclude that the value of u from the given expression is: 1.68
Practice
Write a unit rate for each rate below.
Question 6.
55 pages in 10 minutes _________
Answer:
The given rate is:
55 pages in 10 minutes
So,
The number of pages in 1 minute (Unit rate) = \(\frac{55}{10}\)
= 5.5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the unit rate is: 5.5 pages per minute
Question 7.
$46.50 for 6 hours _______
Answer:
The given rate is:
$46.50 for 6 hours
So,
The number of dollars per hour (Unit rate) = \(\frac{46.50}{6}\)
= 7.75
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the unit rate is: $7.75 per hour
Everyday Math Grade 6 Home Link 6.10 Answer Key
Solving Pan-Balance Equations
Question 1.
Build an equation with two operations that are equivalent to the equation k = 19. Record the operations that you use to create each equation below.
Original equation:
Operation (in words)
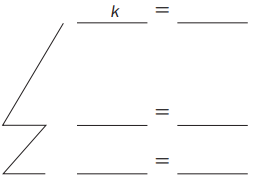
Answer:
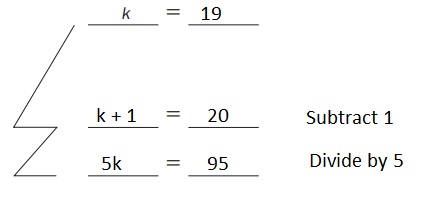
Question 2.
Check that 19 is a solution to your equations.
Answer:
From Question 1,
The equations are:
k + 1 = 20 —— (1)
5k = 95 ——— (2)
Now,
Put k = 19
So,
In eq (1),
19 + 1 = 20
20 = 20
In eq (2),
5 (19) = 95
95 = 95
Hence, from the baove,
We can conclude that 19 is a solution to your equations
Question 3.
Find the mistake in the work below.
Original pan-balance equation:
Operation (in words)
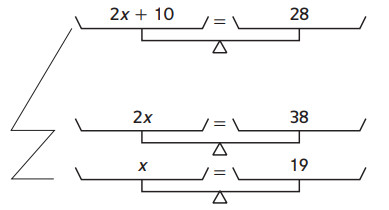
Subtract 10.
Divide by 2.
Describe the mistake and how to correct it.
Answer:
The mistake is:
In the original Pan-Balance equation,
We have to subtract with 10 on both sides
But, it is added on the right side of the Pan-Balance equation
Nw,
The given original Pan-Balance equation is:
2x + 10 = 28
Subtract with 10 on both sides
So,
2x + 10 – 10 = 28 – 10
2x = 18
x = \(\frac{18}{2}[/altex]
x = 9
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that after correcting the mistake in the original Pan-Balance equation,
The value of x is: 9
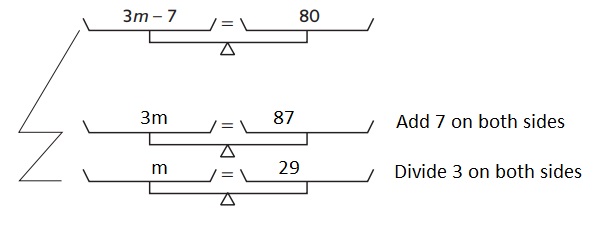
Question 4.
Record the operations you use to create equivalent equations and solve the equation.
Original equation:
Operation (in words)
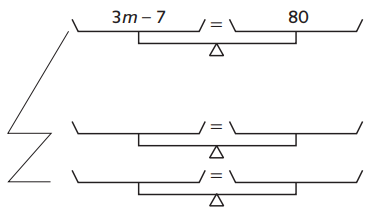
Answer:
Everyday Mathematics Grade 6 Home Link 6.11 Answers
Solving Multistep Home Equations
Solve the equations below. Use each of these strategies once:
A. Trial and Error
B. Bar Model
C. Pan-Balance Model
D. Inverse-Operations Strategy
Plan ahead to make sure you use the strategy or model that you think works better for each equation.
Question 1.
54 = 4m + 2
Strategy: _________
Solution: ________
Answer:
The given equation is:
54 = 4m + 2
Now,
The strategy that is used to solve the given equation is: Bar Model
So,
The Bar Model representation for the given equation is:
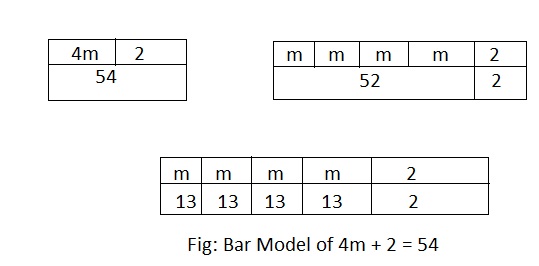
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of m for the given equation is: 13
Question 2.
6n + 8 = 10n + 4
Strategy: _________
Solution: ________
Answer:
The given equation is:
6n + 8 = 10n + 4
Now,
The strategy that is used to solve the given equation is: Inverse Operations Strategy
So,
Now,
Subtract with 8 on both sides
6n + 8 – 8 = 10n + 4 – 8
6n = 10n – 4
Rearrange the like terms on both sides
So,
10n – 6n = 4
4n = 4
n = [latex]\frac{4}{4}\)
n = 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of n for the given equation is: 1
Question 3.
3p + 3 = 2p + 4.5
Strategy: _________
Solution: ________
Answer:
The given equation is:
3p + 4 = 2p + 4.5
Now,
The strategy that is used to solvethe given equation is Pan-Balance Model
So,
Now,
The representation of the Pan-Balance Model for the given equation is;
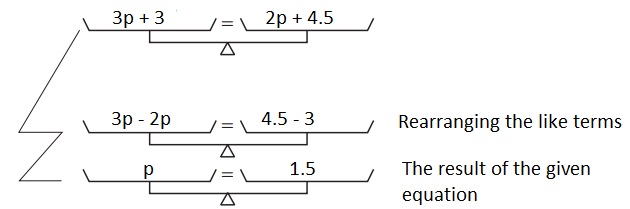
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of p is: 1.5
Question 4.
\(\frac{2}{3}\)q + 8 = q – 10
Strategy: _________
Solution: ________
Answer:
The given equation is:
\(\frac{2}{3}\)q + 8 = q – 10
Now,
The strategy that is used to solve the given equation is Trial -error method
So,
Now,
By using trial and error method,
Let the value of q be: 54
So,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) (54) + 8 = 54 – 10
\(\frac{2 × 54}{3}\) + 8 = 44
36 + 8 = 44
44 = 44
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the value of q from the given equation is: 54
Practice
List the numbers in order from least to greatest.
Question 5.
\(\frac{9}{4}\), 2.35, \(\frac{1}{8}\), 1.5, \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Answer:
The given numbers are:
\(\frac{9}{4}\), 2.35, \(\frac{1}{8}\), 1.5, \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Now,
The representation of all the numbers in the decimal form is:
2.25, 2.35, 0.125, 1.5, 0.375
Hence, from the above,
The list of numbers in order from the least to the greatest is:
0.125, 0.375, 1.5, 2.25, 2.35