Engage NY Eureka Math 7th Grade Module 6 Lesson 21 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 21 Example Answer Key
Example 1.
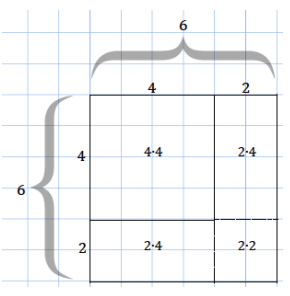
Examine the change in dimension and area of the following square as it increases by 2 units from a side length of 4 units to a new side length of 6 units. Observe the way the area is calculated for the new square. The lengths are given in units, and the areas of the rectangles and squares are given in units squared.
a. Based on the example above, draw a diagram for a square with a side length of 3 units that is increasing by 2 units. Show the area calculation for the larger square in the same way as in the example.
b. Draw a diagram for a square with a side length of 5 units that is increased by 3 units. Show the area calculation for the larger square in the same way as in the example.
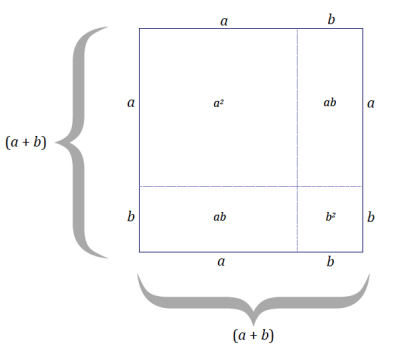
c. Generalize the pattern for the area calculation of a square that has an increase in dimension. Let the length of the original square be a units and the increase in length be b units. Use the diagram below to guide your work.
Answer:
Area of the 6 by 6 square = (4 + 2)2 units2 = 42 units2 + 2(2 ∙ 4) units2 + 22 units2 = 36 units2
The area of the 6 by 6 square can be calculated either by multiplying its sides represented by (4 + 2)(4 + 2) or by adding the areas of the subsections, represented by (4 ∙ 4), 2(2 ∙ 4), and (2 ∙ 2).
a.
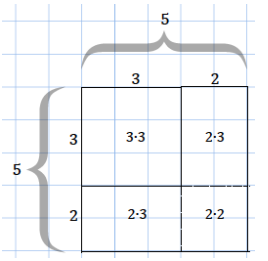
Area of the 5 by 5 square = (3 + 2)2 units2 = 32 units2 + 2(2 ∙ 3) units2 + 22 units2 = 25 units2
The area of the 5 by 5 square can be calculated either by multiplying its sides represented by (3 + 2)(3 + 2) or by adding the areas of the subsections, represented by (3 ∙ 3), 2(2 ∙ 3), and (2 ∙ 2).
b.
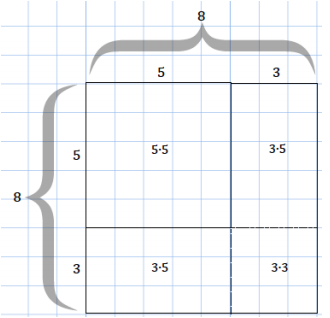
Area of the 8 by 8 square = (5 + 3)2 units2 = 52 units2 + 2(3 ∙ 5) units2 + 32 units2 = 64 units2
The area of the 8 by 8 square can be calculated either by multiplying its sides represented by (5 + 3)(5 + 3) or by adding the areas of the subsections, represented by (5 ∙ 5), 2(3 ∙ 5), and (3 ∙ 3).
c.
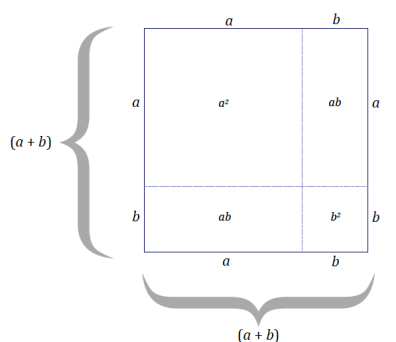
Area of the (a + b) by (a + b) square = (a + b)2 units2 = (a2 + 2ab + b2 ) units2
The area of the square with side length (a + b) is equal to the sum of the areas of the subsections. Describing the area as (a + b)2 units2 is a way to state the area in terms of the dimensions of the figure; whereas describing the area as (a2 + 2ab + b2 ) units2 is a way to state the area in terms of the sum of the areas of the sections formed by the extension of b units in each dimension.
Show how the distributive property can be used to rewrite the expression (a + b)2:
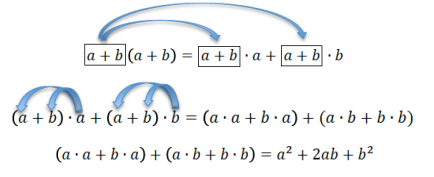
Example 2.
Bobby draws a square that is 10 units by 10 units. He increases the length by x units and the width by 2 units.
a. Draw a diagram that models this scenario.
b. Assume the area of the large rectangle is 156 unit2. Find the value of x.
Answer:
a.
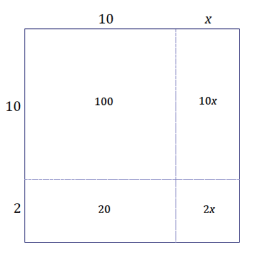
b. 156 = 100 + 20 + 10x + 2x
156 = 120 + 12x
156 – 120 = 120 + 12x – 120
36 = 12x
(\(\frac{1}{12}\))36 = (\(\frac{1}{12}\))12x
x = 3
Example 3.
The dimensions of a square with a side length of x units are increased. In this figure, the indicated lengths are given in units, and the indicated areas are given in units2.
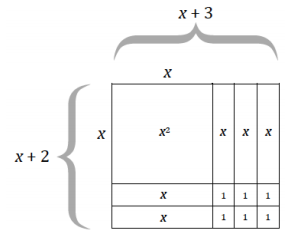
a. What are the dimensions of the large rectangle in the figure?
b. Use the expressions in your response from part (a) to write an equation for the area of the large rectangle, where A represents area.
c. Use the areas of the sections within the diagram to express the area of the large rectangle.
d. What can be concluded from parts (b) and (c)?
e. Explain how the expressions (x + 2)(x + 3) and x2 + 3x + 2x + 6 differ within the context of the area of the figure.
Answer:
a. The length (or width) is (x + 3) units, and the width (or length) is (x + 2) units.
b. A = (x + 3)(x + 2) units2
c. A = (x2 + 3x + 2x + 6) units2
d. (x + 2)(x + 3) = x2 + 3x + 2x + 6
e. The expression (x + 2)(x + 3) shows the area is equal to the quantity of the width increased by 2 units times the quantity of the length increased by 3 units. The expression x2 + 3x + 2x + 6 shows the area as the sum of four sections of the expanded rectangle.
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 21 Exercise Answer Key
Opening Exercise
Patty is interested in expanding her backyard garden. Currently, the garden plot has a length of 4 ft. and a width of 3 ft.
a. What is the current area of the garden?
Patty plans on extending the length of the plot by 3 ft. and the width by 2 ft.
b. What will the new dimensions of the garden be? What will the new area of the garden be?
c. Draw a diagram that shows the change in dimension and area of Patty’s garden as she expands it. The diagram should show the original garden as well as the expanded garden.
d. Based on your diagram, can the area of the garden be found in a way other than by multiplying the length by the width?
e. Based on your diagram, how would the area of the original garden change if only the length increased by 3 ft.? By how much would the area increase?
f. How would the area of the original garden change if only the width increased by 2 ft.? By how much would the area increase?
g. Complete the following table with the numeric expression, area, and increase in area for each change in the dimensions of the garden.
h. Will the increase in both the length and width by 3 ft. and 2 ft., respectively, mean that the original area will increase strictly by the areas found in parts (e) and (f)? If the area is increasing by more than the areas found in parts (e) and (f), explain what accounts for the additional increase.
Answer:
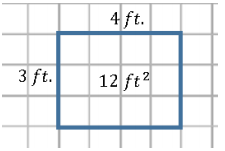
a. The garden has an area of 12 ft2.
b. The new dimensions of the garden will be 7 ft. by 5 ft., and it will have an area of 35 ft2.
Part (c) asks students to draw a plan of the expanded garden and quantify how the area increases. Allow students time to find a way to show this. Share out student responses; if none are able to produce a valid response, share the diagram shown on the next page.
c.
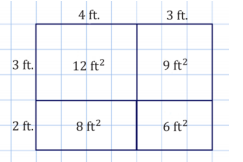
d. The area can be found by taking the sum of the smaller sections of areas.
e. The area of the garden would increase by 9 ft2.
f. The area of the garden would increase by 8 ft2.
g.
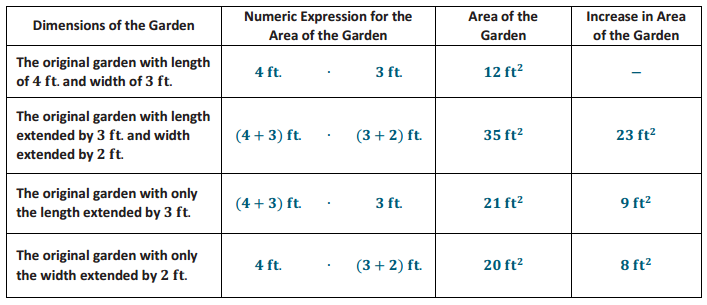
h. The area of the garden increases not only by 9 ft2 and 8 ft2, but also by an additional 6 ft2. This additional 6 ft2 is the corresponding area formed by the 3 ft. and 2 ft. extensions in both dimensions (length and width); that is, this area results from not just an extension in the length or just in the width but because the extensions occurred in both length and width.
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 21 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
A square with a side length of a units is decreased by b units in both length and width.
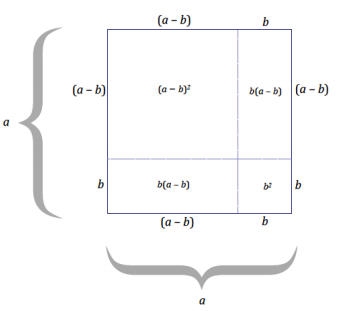
Use the diagram to express(a – b)2 in terms of the other a2, ab, and b2 by filling in the blanks below:
(a – b)2 = a2 – b(a – b) – b(a – b) – b2
= a2 – _____ + _____ – _____ + _____ – b2
= a2 – 2ab + _____ – b2
= _____________________________________
Answer:
(a – b)2 = a2 – b(a – b) – b(a – b) – b2
= a2 – ba + b2 – ba + b2 – b2
= a2 – 2ab + 2b2 – b2
= a2 – 2ab + b2
Question 2.
In Example 3, part (c), we generalized that (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2. Use these results to evaluate the following expressions by writing 1,001 = 1,000 + 1.
a. Evaluate 1012.
b. Evaluate 1,0012.
c. Evaluate 212.
Answer:
a. (100 + 1)2 = 1002 + 2(100 ∙ 1) + 12
= 10,000 + 200 + 1
= 10,201
b. (1,000 + 1)2 = 1,0002 + 2(1,000 ∙ 1) + 12
= 1,000,000 + 2,000 + 1
= 1,002,001
c. (20 + 1)2 = 202 + 2(20 ∙ 1) + 12
= 400 + 40 + 1
= 441
Question 3.
Use the results of Problem 1 to evaluate 9992. by writing 999 = 1,000 – 1.
Answer:
(1,000 – 1)2 = 1,0002 – 2(1,000 ∙ 1) + 12
= 1,000,000 – 2,000 + 1
= 998,001
Question 4.
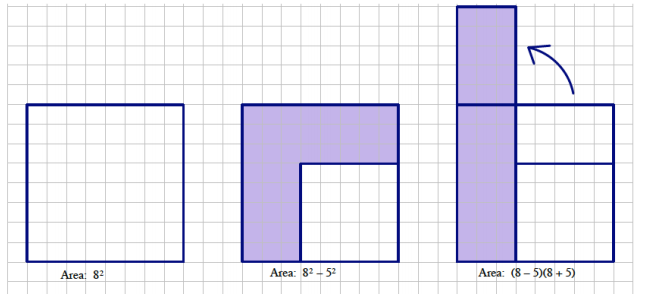
The figures below show that 82 – 52 is equal to (8 – 5)(8 + 5).
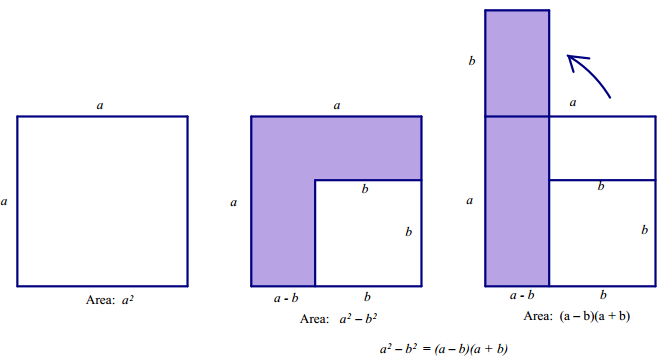
a. Create a drawing to show that a2 – b2 = (a – b)(a + b).
b. Use the result in part (a), a2 – b2 = (a – b)(a + b), to explain why:
i) 352 – 52 = (30)(40).
ii) 212 – 182 = (3)(39).
iii) 1042 – 632 = (41)(167).
c. Use the fact that 352 = (30)(40) + 52 = 1,225 to create a way to mentally square any two – digit number ending in 5.
Answer:
a.
b. i) 352 – 52 = (35 – 5)(35 + 5) = (30)(40)
ii) 212 – 182 = (21 – 18)(21 + 18) = (3)(39)
iii) 1042 – 632 = (104 – 63)(104 + 63) = (41)(167)
c. 152 = (10)(20) + 25 = 225
252 = (20)(30) + 25 = 625
352 = (30)(40) + 25 = 1,225
In general, if the first digit is n, then the first digit(s) are n(n + 1), and the last two digits are 25.
Question 5.
Create an area model for each product. Use the area model to write an equivalent expression that represents the area.
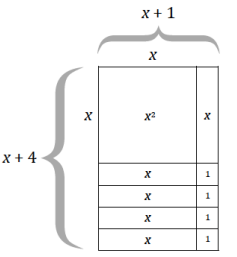
a. (x + 1)(x + 4) =
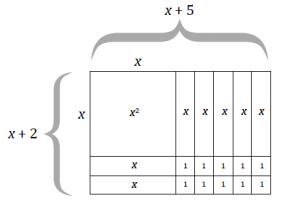
b. (x + 5)(x + 2) =
c. Based on the context of the area model, how do the expressions provided in parts (a) and (b) differ from the equivalent expression answers you found for each?
Answer:
a. (x + 1)(x + 4) = x2 + x + 4x + 4
b. (x + 5)(x + 2) = x2 + 5x + 2x + 10
c. The expression provided in each question shows the area as a length times width product or as the product of two expanded lengths. Each equivalent expression shows the area as the sum of the sections of the expanded rectangle.
Question 6.
Use the distributive property to multiply the following expressions.
a. (2 + 6)(2 + 4)
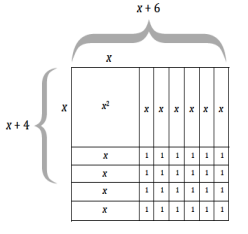
b. (x + 6)(x + 4); draw a figure that models this multiplication problem.
c. (10 + 7)(10 + 7)
d. (a + 7)(a + 7)
e. (5 – 3)(5 + 3)
f. (x – 3)(x + 3)
Answer:
a. (2 + 6)(2 + 4)
(2 + 6)(2 + 4) = (2 + 6) ∙ 2 + (2 + 6) ∙ 4
= (2 ∙ 2 + 6 ∙ 2) + (2 ∙ 4 + 6 ∙ 4)
= 22 + 10(2) + 24
= 48
b. (x + 6)(x + 4) = (x + 6) ∙ x + (x + 6) ∙ 4
= (x ∙ x + 6 ∙ x) + (x ∙ 4 + 6 ∙ 4)
= x2 + 10x + 24
c. (10 + 7)(10 + 7) = (10 + 7) ∙ 10 + (10 + 7) ∙ 7
= (10 ∙ 10 + 7 ∙ 10) + (7 ∙ 10 + 7 ∙ 7)
= 102 + 2(7 ∙ 10) + 49
= 102 + 140 + 49
= 289
d. (a + 7)(a + 7) = (a + 7) ∙ a + (a + 7) ∙ 7
= (a ∙ a + 7 ∙ a) + (a ∙ 7 + 7 ∙ 7)
= a2 + 2(7 ∙ a) + 49
= a2 + 14a + 49
e. (5 – 3)(5 + 3) = (5 – 3) ∙ 5 + (5 – 3) ∙ 3
= (5 ∙ 5 – 3 ∙ 5) + (5 ∙ 3 – 3 ∙ 3)
= 52 – (3 ∙ 5) + (5 ∙ 3) – 32
= 52 – 32
= 16
f. (x – 3)(x + 3) = (x – 3) ∙ x + (x – 3) ∙ 3
= (x ∙ x – 3 ∙ x) + (x ∙ 3 – 3 ∙ 3)
= x2 – (3 ∙ x) + (x ∙ 3) – 32
= x2 – 9
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 21 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Create an area model to represent this product: (x + 4)(x + 2).
Answer:
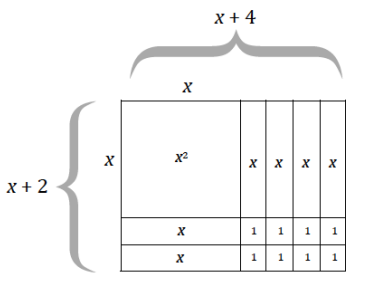
Question 2.
Write two different expressions that represent the area.
Answer:
(x + 2)(x + 4) and x2 + 6x + 8
Question 3.
Explain how each expression represents different information about the situation.
Answer:
The expression (x + 2)(x + 4) shows the area is equal to the quantity of the length increased by 4 times the quantity of the width increased by 2. The expression x2 + 4x + 2x + 8 shows the area as the sum of four sections of the expanded rectangle.
Question 4.
Show that the two expressions are equal using the distributive property.
Answer:
(x + 4)(x + 2) = (x + 4) ∙ x + (x + 2) ∙ 2
(x + 4) ∙ x + (x + 4) ∙ 2 = (x ∙ x + 4 ∙ x) + (x ∙ 2 + 4 ∙ 2)
(x ∙ x + 4 ∙ x) + (x ∙ 2 + 4 ∙ 2) = x2 + 6x + 8