Engage NY Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 Lesson 11 Answer Key
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 Lesson 11 Exercise Answer Key
Exercise 1.
Triangle ABC has been dilated with scale factor \(\frac{1}{2}\) from centers O1 and O2 What can you say about line segments A1A2, B1B2, and C1C2?
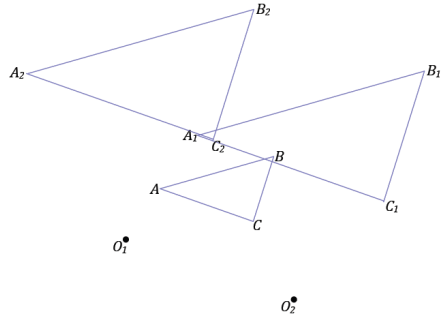
Answer:
They are all parallel to the line that passes through O1O2.
Exercise 2.
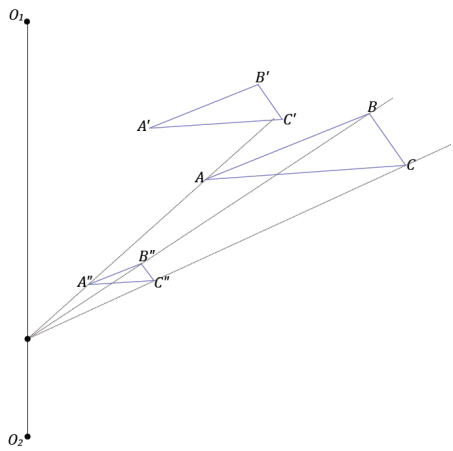
Triangle ABC has been dilated with scale factor \(\frac{2}{3}\) from center O1 to get triangle A’B’C’, and then triangle A’B’C’ is dilated from center O2 with scale factor \(\frac{1}{2}\) to get triangle A”B”C”. Describe the dilation that maps triangle ABC to triangle A”B”C”. Find the center and scale factor for that dilation.
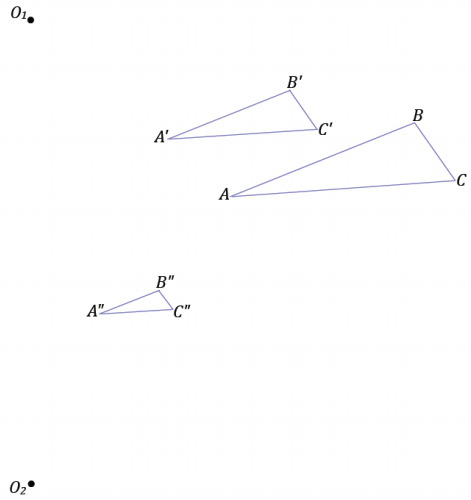
Answer:
The dilation center is a point on the line segment O1O2, and the scale factor is = \(\frac{2}{3} \cdot \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{3}\).
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 Lesson 11 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
In Lesson 7, the dilation theorem for line segments said that if two different-length line segments in the plane were parallel to each other, then a dilation exists mapping one segment onto the other. Explain why the line segments must be different lengths for a dilation to exist.
Answer:
If the line segments were of equal length, then it would have ro be true that the scale factor of the supposed dilation would be r = 1; however, we found that any dilation with a scale factor of r = 1 maps any figure to itself, which implies that the line segment would have to be mapped to itself. Two different line segments that are parallel to one another implies that the line segments are not one and the same,which means that the supposed dilation does not exist.
Question 2.
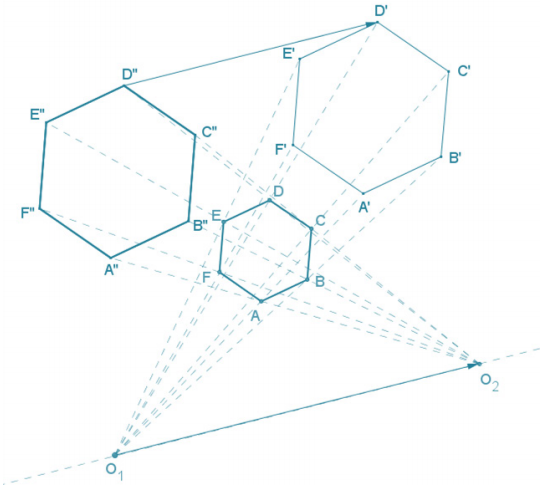
Regular hexagon A’B’C’D’E’F’ is the image of regular hexagon ABCDEF under a dilation from center O1, and regular hexagon A”B”C”D”E”F” is the image of regular hexagon ABCDEF under a dilation from center O2. Points A’, B’, C’, D’, E’, and F’ are also the images of points A”, B”, C”, D”, E”, and F”, respectively, under a
translation along vector \(\overrightarrow{D^{\prime \prime} D^{\prime}}\). Find a possible regular hexagon ABCDEF.
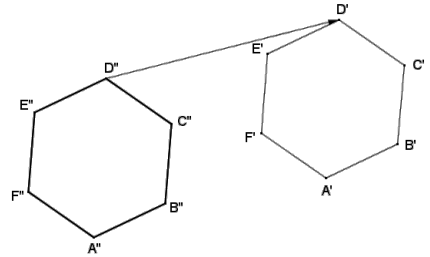
Answer:
Student diagrams will vary; however, the centers of dilation O1 and O2 must lie on a line parallel to vector \(\overrightarrow{D^{\prime \prime} D^{\prime}}\).
Question 3.
A dilation with center O1 and scale factor \(\frac{1}{2}\) maps figure F to figure F’. A dilation with center O2 and scale factor \(\frac{3}{2}\) maps figure F’ to figure F”. Draw figures F’ and F”, and then find the center O and scale factor r of the dilation that takes F to F”.

Answer:
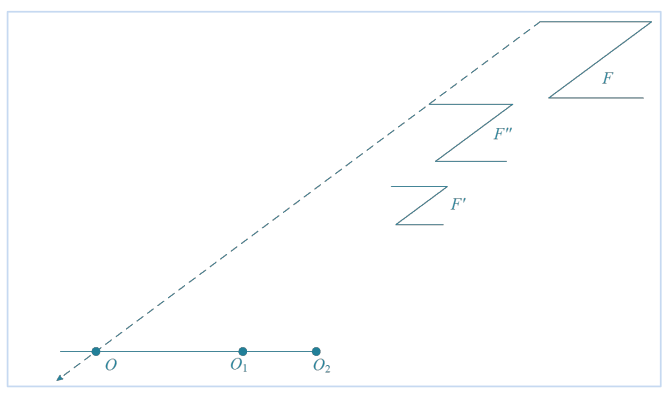
r = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 4.
A figure T is dilated from center O1 with a scale factor r1 = \(\frac{3}{4}\) to yield image T’, and figure T’ is then dilated from center O2 with a scale factor r2 = \(\frac{4}{3}\) to yield figure T”. Explain why T ≅ T”.
Answer:
For any distance, a, between two points in figure T, the distance between corresponding points in figure T’ is \(\frac{3}{4}\)a.
For the said distance between points in T’, \(\frac{3}{4}\)a, the distance between corresponding points in figure T” is \(\frac{4}{3}\)(\(\frac{3}{4}\)a) = 1a. This implies that all distances between two points in figure T” are equal to the distances between corresponding points in figure T. Furthermore, since dilations preserve angle measures, angles formed by any three noncollinear points in figure T” are congruent to the angles formed by the corresponding three noncollinear points in figure T. There is then a correspondence between T and T” in which distance is preserved and angle measures are preserved, implying that a sequence of rigid motions maps T onto T”; hence, a congruence exists between figures T and T”.
Question 5.
A dilation with center O1 and scale factor \(\frac{3}{2}\) maps figure H to figure H’. A dilation with center O2 and scale factor 2 maps figure H’ to figure H”. Draw figures H’ and H”. Find a vector for a translation that maps H to H”.
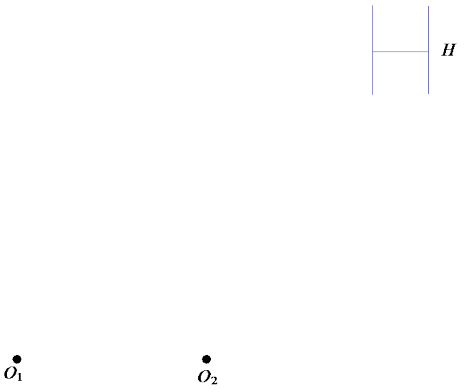
Answer:
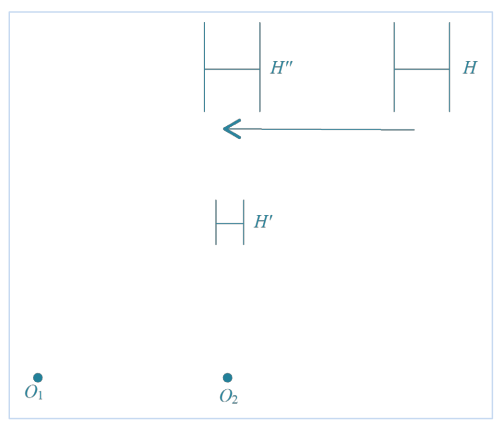
Question 6.
Figure W is dilated from 01 with a scale factor r1 = 2 to yield W’. Figure W’ is then dilated from center O2 with a scale factor r2 = \(\frac{1}{4}\) to yield W”.
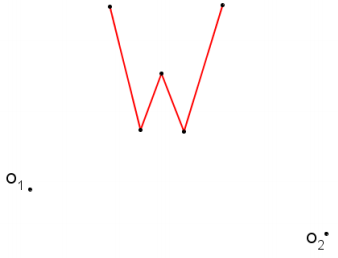
a. Construct the composition of dilations of figure W described above.
Answer:
b. If you were to dilate figure w”, what scale factor would be required to yield an image that is congruent to figure W?
Answer:
In a composition of dilations, for the resulting ima ge to be congruent to the original pre-image, the product of the scale factors of the dilations must be 1.
r1 ∙ r2 ∙ r3 = 1
2 ∙ \(\frac{1}{4}\) ∙ r3 = 1
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ∙ r3 = 1
r3 = 2
The scale factor necessary to yield an image congruent to the original pre-image is r3 = 2.
c. Locate the center of dilation that maps W” to W using the scale factor that you identified in part (b).
Answer:
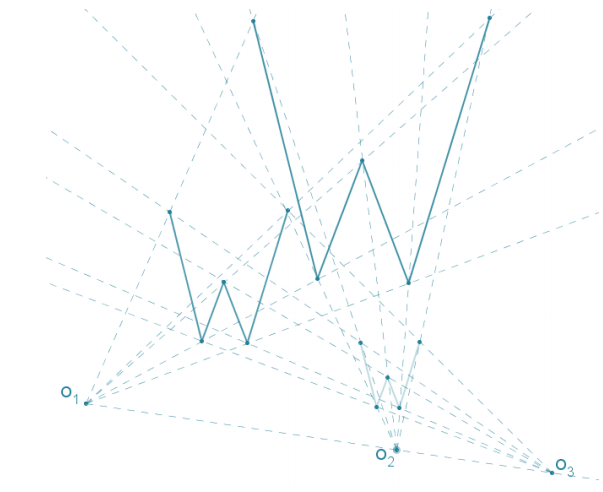
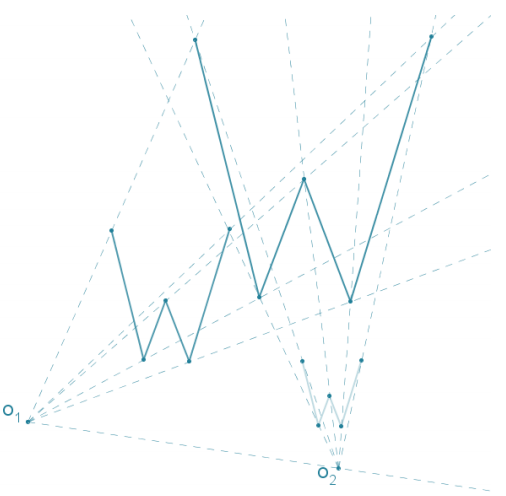
Question 7.
Figures F1 and F2 in the diagram below are dilations of F from centers O1 and O2, respectively.
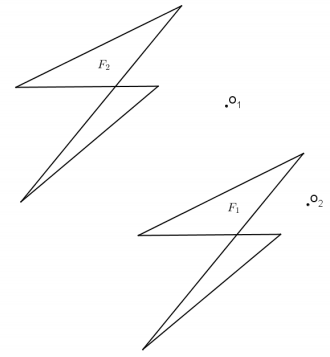
a. Find F.
Answer:
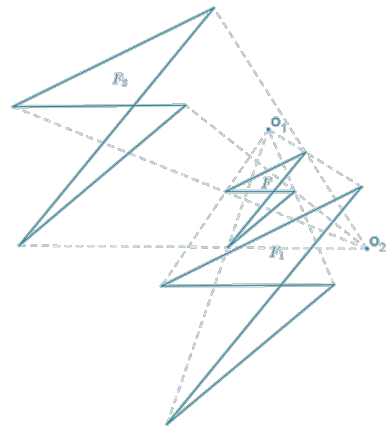
b. If F1 ≅ F2, what must be true of the scale factors r1 and r2 of each dilation?
Answer:
The scale factors nust be equal.
c. Use direct measurement to determine each scale factor for D01,r1 and D02,r2.
Answer:
By direct measurement, the scale factor used for each dilation is r1 = r2 = 2\(\frac{1}{2}\).
Question 8.
Use a coordinate plane to complete each part below using U(2, 3), V(6,6), and W(6, – 1).
Answer:
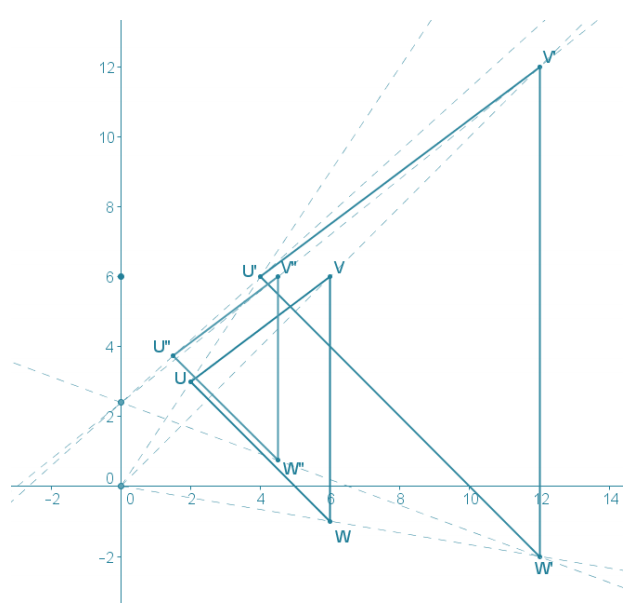
a. Dilate ∆ UVW from the origin with a scale factor r1 = 2. List the coordinates of image points U’, V’, and W’.
Answer:
U'(4, 6) V(12, 12), and W'(12, – 12)
b. Dilate ∆ UVW from (0, 6) with a scale factor of r2 = \(\frac{3}{4}\) . List the coordinates of image points U”, V”, and W”.
Answer:
The center of this dilation is not the origin. The x-coordinate of the center is O, so the x-coordinates of the image points can be calculated in the same manner as in part (a). However, the y-coordinates of the pre-image must be considered as their distance from the y-coordinate of the center, 6.
Point U is 3 units below the center of dilation, point V is at the same vertical level as the center of dilation, and point W is7 units below the center of dilation.
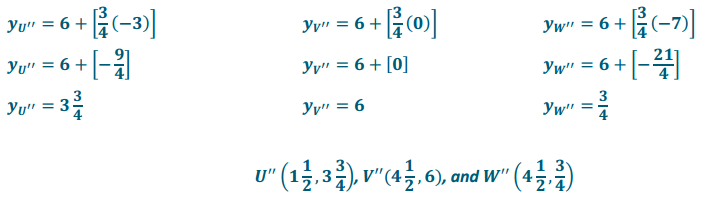
c. Find the scale factor, r3, from ∆ U’V’W’ to ∆ U”V”W”.
Answer:
∆ U’V’W’ is the image of ∆ UVW with a scale factor r1 = 2, so it follows that ∆ UVW can be considered the image of ∆ U’V’W’ with a scale factor of r4 = \(\frac{1}{2}\). Therefore, ∆ U”V”W” can be considered the image of the composition of dilations \(D_{(0,6), \frac{3}{4}}\left(D_{(0,0) \frac{1}{2}}\right)\) of ∆ U’V’W’. This means that the scale factor r3 = r4 ∙ r2.
r3 = r4 ∙ r2
r3 = \(\frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{3}{4}\)
r3 = \(\frac{1}{8}\)
d. Find the coordinates of the center of dilation that maps ∆ U’V’W’ to ∆ U”V”W”.
Answer:
The center of dilation O3 must lie on the y-axis with centers (0, 0) and (0, 6). Therefore, the x-coordinate O3 is 0. Using the graph, it appears that the y-coordinate of O3 is a little more than 2.
Considering the points V’ and V”:
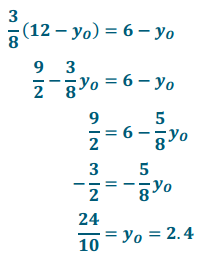
The center of dilation O3 is (0, 2.4).
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 Lesson 11 Exit Ticket Answer Key
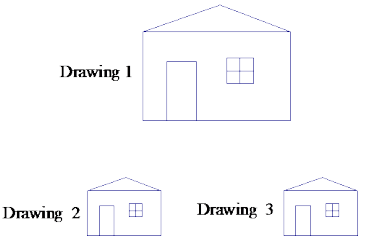
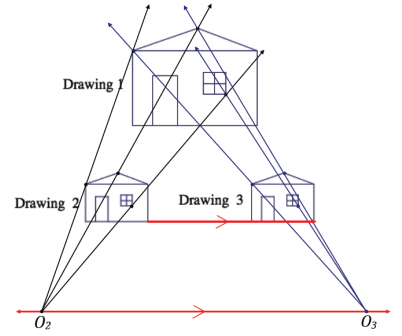
Marcos constructed the composition of dilations shown below. Drawing 2 is \(\frac{3}{2}\) the size of Drawing 1, and Drawing 3 is twice the size of Drawing 2.
Answer:
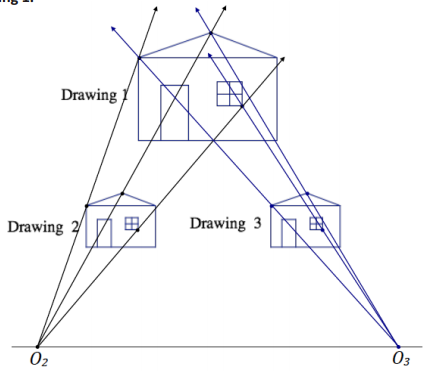
Question 1.
Determine the scale factor from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3.
Answer:
Drawing 2 is a 3:8 scale drawing of Drawing 1, and Drawing 3 is a 2: 1 scale drawing of Drawing 2, so Drawing 3 is a 2: 1 scale drawing of a 3: 8 scale drawing:
Drawing 3 = 2 (\(\frac{3}{8}\) Drawing 1)
Drawing 3 = \(\frac{3}{4}\) (Drawing 1)
The scale factor from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 is \(\frac{3}{4}\).
Question 2.
Find the center of dilation mapping Drawing 1 to Drawing 3.
Answer:
See diagram: The center of dilation is O3.
Eureka Math Geometry Module 2 Lesson 11 Exploratory Challenge Answer Key
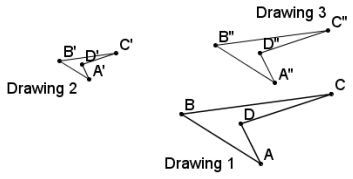
Question 1.
Drawing 2 and Drawing 3 are both scale drawings of Drawing 1.
Answer:
a. Determine the scale factor and center for each scale drawing. Take measurements as needed.
Answer:
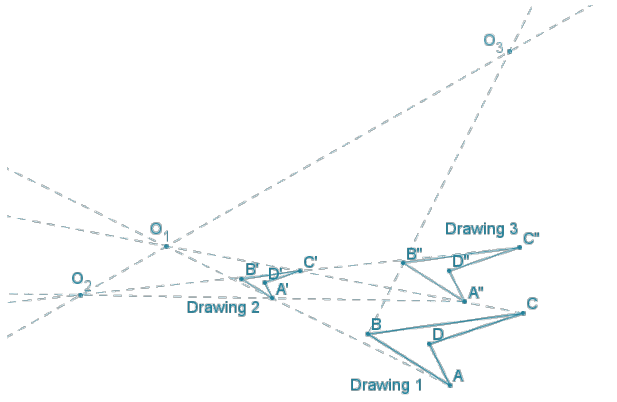
The scale factor for each drawing is the same; the scale factor for both is r = \(\frac{1}{2}\). Each scale drawing has a different center.
b. Is there a way to map Drawing 2 onto Drawing 3 or map Drawing 3 onto Drawing 2?
Answer:
Since the two drawings are identical, a translation maps either Drawing 2 onto Drawing 3 or Drawing 3 onto Drawing 2.
→ What do you notice about a translation vector that maps either scale drawing onto the other and the line that passes through the centers of the dilations?
A translation vector that maps either scale drawing onto the other is parallel to the line that passes through the centers of the dilations.
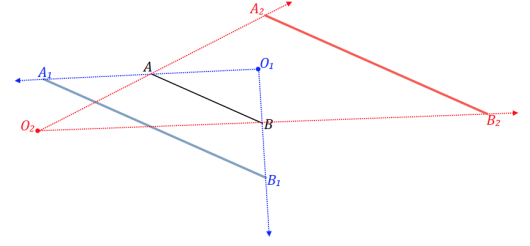
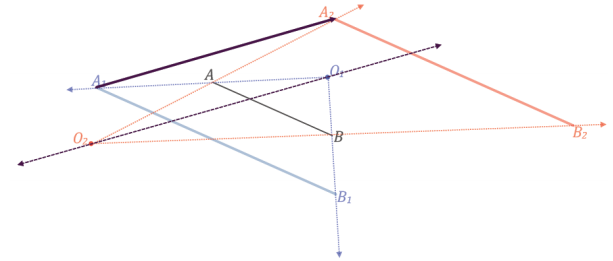
→ We are not going to generally prove this, but let’s experimentally verify this by dilating a simple figure (e.g., a segment) by the same scale factor from two different centers, O1 and O2.
→ Do this twice, in two separate cases, to observe what happens.
→ In the first case, dilate \(\overline{A B}\) by a factor of 2, and be sure to give each dilation a different center. Label the dilation about O1 as \(\overline{A_{1} B_{1}}\) and the dilation about O2 as \(\overline{A_{2} B_{2}}\).
→ Repeat the experiment, and create a segment, \(\overline{C D}\), different from \(\overline{A B}\). Dilate \(\overline{C D}\) by a factor of 2, and be sure
to give each dilation a different center. Label the dilation about O1 as \(\overline{C_{1} D_{1}}\) and the dilation about O2 as \(\overline{C_{2} D_{2}}\).
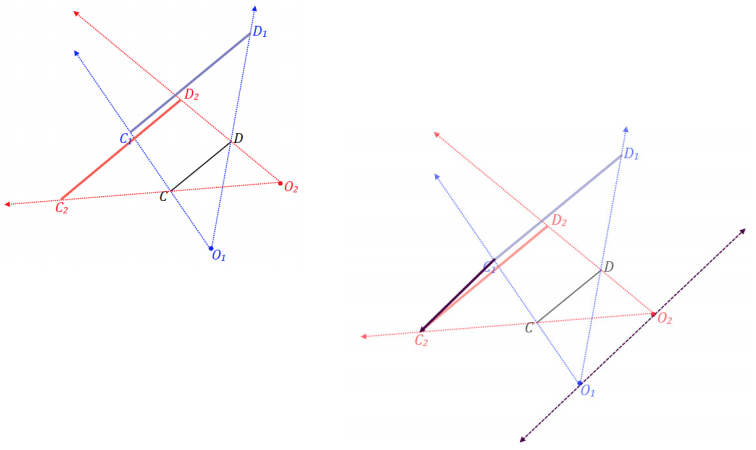
The translation vector is always parallel to the line that passes through the centers of the dilations.
c. Generalize the parameters of this example and its results.
Answer:
The dilation of a figure from two different centers by the same scale factor yields congruent figures that are congruent by a translation along a vector that is parallel to the line through the centers.
Question 2.
If Drawing 2 is a scale drawing of Drawing 1 with scale factor r1 and Drawing 3 is a scale drawing of Drawing 2 with scale factor r2, what is the relationship between Drawing 3 and Drawing 1?
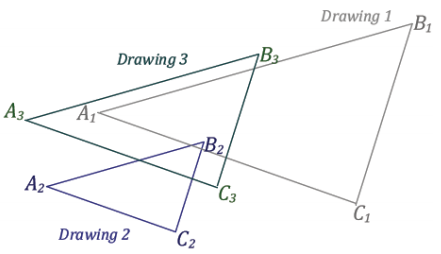
a. Determine the scale factor and center for each scale drawing. Take measurements as needed.
Answer:
The scale factor for Drawing 2 relative to Drawing 1 is r1 = \(\frac{1}{2}\), and the scale factor for Drawing 3 relative to Drawing 2 is r2 = \(\frac{3}{2}\).
b. What is the scale factor going from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3? Take measurements as needed.
Answer:
The scale factor to go from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 is r3 = \(\frac{3}{4}\).
→ Do you see a relationship between the value of the scale factor going from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 and the scale factors determined going from Drawing 1 to Drawing 2 and Drawing 2 to Drawing 3?
Allow students a moment to discuss before taking responses.
The scale factor to go from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 is the same as the product of the scale factors to go from Drawing 1 to Drawing 2 and then Drawing 2 to Drawing 3. So the scale factor to go from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 is r1 r2 = \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)=\frac{3}{4}\).
→ To go from Drawing 1 to Drawing 3 is the same as taking a composition of the two dilations: \(D_{O_{2}, \frac{3}{2}}\left(D_{O_{1}, \frac{1}{2}}\right)\).
→ So, with respect to scale factor, a composition of dilations D02,r2 (D01,r1) results in a dilation whose scale factor is r1r2.
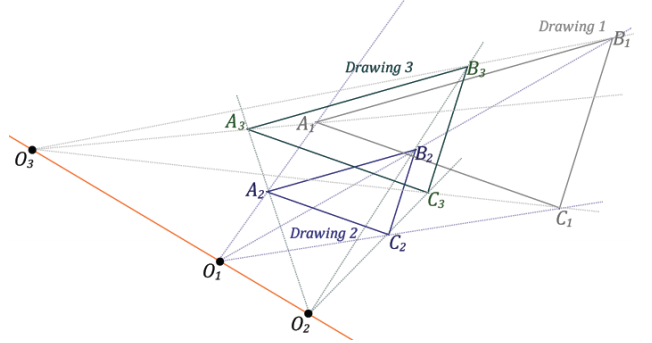
c. Compare the centers of dilations of Drawing 1 (to Drawing 2) and of Drawing 2 (to Drawing 3). What do you notice about these centers relative to the center of the composition of dilations O3?
Answer:
The centers of each for Drawing 1 and Drawing 2 are collinear with the center of dilation of the composition of dilations.
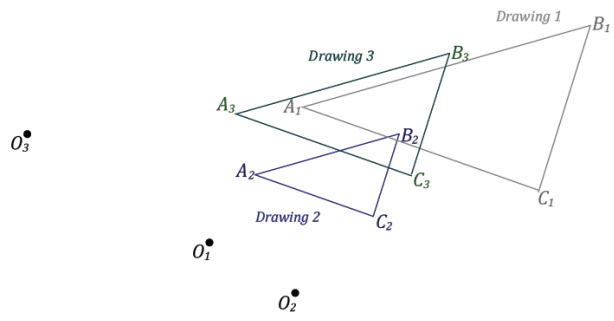
→ From this example, it is tempting to generalize and say that with respect to the centers of the dilations, the center of the composition of dilations D02,r2 (D01,r1) is collinear with the centers O1 and O2, but there is one situation where this is not the case.
→ To observe this one case, draw a segment AB that serves as the figure of a series of dilations.
→ For the first dilation D1, select a center of dilation O1 and scale factor r1 = \(\frac{1}{2}\). Dilate AB and label the result as A’B’.
→ For the second dilation D2, select a new center O2 and scale factor r2 = 2. Determine why the centers of each of these dilations cannot be collinear with the center of dilation of the composition of dilations D2(D1).
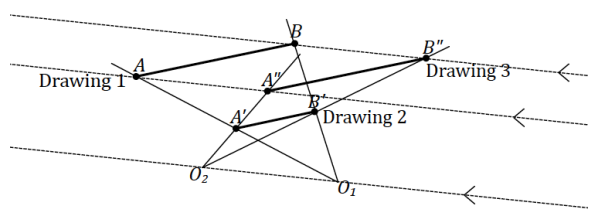
Since Drawing 1 and Drawing 3 are identical figures, the lines that pass through the corresponding endpoints of the segments are parallel; a translation will map Drawing 1 to Drawing 3.
→ Notice that this occurs only when r1r2 = 1.
→ Also, notice that the translation that maps \(\overline{A B}\) to \(\overline{A^{\prime \prime} B^{\prime \prime}}\) must be parallel to the line that passes through the centers of the two given dilations.
d. Generalize the parameters of this example and its results.
Answer:
A composition of dilations, D01,r1 and D02,r2, is a dilation with scale factor r1r2 and center on ![]() unless r1r2 = 1. If r1r2 = 1, then there is no dilation that maps a figure onto the image of the composition of dilations; there is a translation parallel to the line passing through the centers of the individual dilations that maps the figure onto its image.
unless r1r2 = 1. If r1r2 = 1, then there is no dilation that maps a figure onto the image of the composition of dilations; there is a translation parallel to the line passing through the centers of the individual dilations that maps the figure onto its image.