Engage NY Eureka Math Algebra 2 Module 1 Lesson 29 Answer Key
Eureka Math Algebra 2 Module 1 Lesson 29 Example Answer Key
Example 1.
Solve the equation 6 = x + √x.
Answer:
6 – x = √x
(6 – x)2 = √x2
36 – 12x + x2 = x
x2 – 13x + 36 = 0
(x – 9) (x – 4) = 0
The solutions are 9 and 4.
Check x = 9:
9 + √9 = 9 + 3 = 12
6 ≠ 12
Check x = 4:
4 + √4 = 4 + 2 = 6
So, 9 is an extraneous solution.
The only valid solution is 4.
Example 2.
Solve the equation \(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x+3}\) = 3.
Answer:
\(\sqrt{x+3}\) = 3 – √x
\((\sqrt{x+3})^{2}\) = \((3-\sqrt{x})^{2}\)
x + 3 = 9 – 6√x + x
1 = √x
1 = x
Check:
√1 + \(\sqrt{1+3}\) = 1 + 2 = 3
So the solution is 1.
Eureka Math Algebra 2 Module 1 Lesson 29 Exercise Answer Key
Solve:
Exercise 1.
3x = 1 + 2√x
Answer:
The only solution is 1.
Note that \(\frac{1}{9}\) is an extraneous solution.
Exercise 2.
3 = 4√x – x
Answer:
The two solutions are 9 and 1.
Exercise 3.
\(\sqrt{x+5}\) = x – 1
Answer:
The only solution is 4.
Note that – 1 is an extraneous solution.
Exercise 4.
\(\sqrt{3 x+7}\) + \(2 \sqrt{x-8}\) = 0
Answer:
There are no solutions.
Exercises 5 – 6
Solve the following equations.
Exercise 5.
\(\sqrt{x-3}\) + \(\sqrt{x+5}\) = 4
Answer:
4
Exercise 6.
3 + √x = \(\sqrt{x+81}\)
Answer:
144
Eureka Math Algebra 2 Module 1 Lesson 29 Problem Set Answer Key
Solve.
Question 1.
\(\sqrt{2 x-5}-\sqrt{x+6}\) = 0
Answer:
11
Question 2.
\(\sqrt{2 x-5}+\sqrt{x+6}\) = 0
Answer:
No solution
Question 3.
\(\sqrt{x-5}-\sqrt{x+6}\) = 2
Answer:
No solution
Question 4.
\(\sqrt{2 x-5}-\sqrt{x+6}\) = 2
Answer:
43
Question 5.
\(\sqrt{x+4}\) = 3 – \(\sqrt{x}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{25}{36}\)
Question 6.
\(\sqrt{x+4}\) = 3 + \(\sqrt{x}\)
Answer:
No solution
Question 7.
\(\sqrt{x+3}\) = \(\sqrt{5 x+6}\) – 3
Answer:
6
Question 8.
\(\sqrt{2 x+1}\) = x – 1
Answer:
4
Question 9.
\(\sqrt{x+12}+\sqrt{x}\) = 6
Answer:
4
Question 10.
2√x = 1 – \(\sqrt{4 x-1}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 11.
2x = \(\sqrt{4 x-1}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 12.
\(\sqrt{4 x-1}\) = 2 – 2x
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 13.
x + 2 = 4\(\sqrt{x-2}\)
Answer:
6
Question 14.
\(\sqrt{2 x-8}+\sqrt{3 x-12}\) = 0
Answer:
4
Question 15.
x = 2\(\sqrt{x-4}\) + 4
Answer:
4, 8
Question 16.
x – 2 = \(\sqrt{9x – 36}\)
Answer:
5, 8
Question 17.
Consider the right triangle ABC shown to the right, with AB = 8 and BC = x.
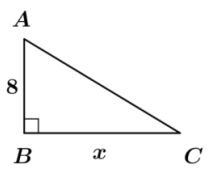
a. Write an expression for the length of the hypotenuse in terms of x.
Answer:
AC = \(\sqrt{64+x^{2}}\)
b. Find the value of x for which AC – AB = 9.
Answer:
The solutions to the mathematical equation \(\sqrt{64+x^{2}}\) – 8 = 9 are – 15 B and 15. Since lengths must be positive, – 15 is an extraneous solution, and x = 15.
Question 18.
Consider the triangle ABC shown to the right where AD = DC, and \(\overline{B D}\) is the altitude of the triangle.
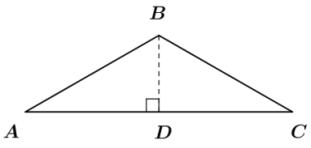
a. If the length of is x cm, and the length of \(\overline{A C}\) is 18 cm, write an expression for the lengths of \(\overline{A B}\) and \(\overline{B C}\) in terms of x.
Answer:
AB = BC = \(\sqrt{81+x^{2}}\) cm
b. Write an expression for the perimeter of ∆ABC in terms of x.
Answer:
(2\(\sqrt{81+x^{2}}\) + 18)cm
c. Find the value of x for which the perimeter of ∆ABC is equal to 38 cm.
Answer:
\(\sqrt{19}\)cm
Eureka Math Algebra 2 Module 1 Lesson 29 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Solve \(\) = x + 6. Verify the solution(s).
Answer:
2x+ 15 = x2 + 12x + 36
0 = x2 + 10x + 21
0 = (x + 3) (x + 7)
The solutions are – 3 and – 7.
Check x = – 3:
\(\sqrt{2(-3)+15}\) = \(\sqrt{9}\) = 3
– 3 + 6 = 3
So, – 3 is a valid solution.
Therefore, the only solution to the original equation is – 3.
Check x = – 7:
\(\sqrt{2(-7)+15}\) = \(\sqrt{1}\) = 1
– 7 + 6 = – 1
Since – 1 ≠ 1, we see that – 1 is an extraneous solution.
Question 2.
Explain why it is necessary to check the solutions to a radical equation.
Answer:
Raising both sides of an equation to a power can produce an equation whose solution set is not equivalent to that of the original equation. In the problem above, x = – 7 does not satisfy the equation.