Students looking for the Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Answer Key Unit 6 Module 2 can find a better approach to solve the problems.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Answer Key Unit 6 Module 2
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 6 Module 2 Session 1 Answer Key
Triangles Record Sheet
Answer:
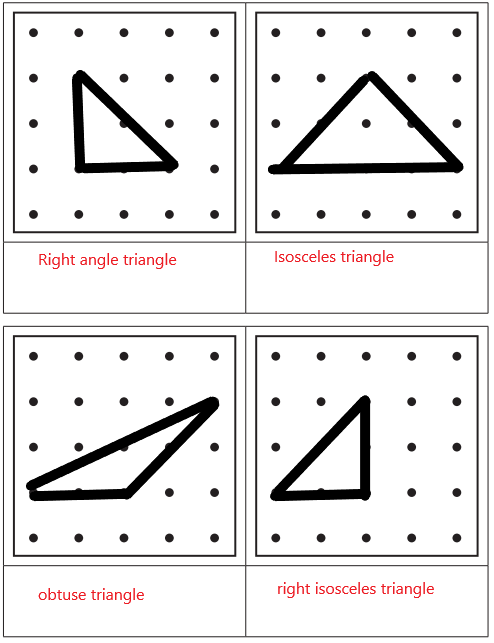
More Geoboard Triangles
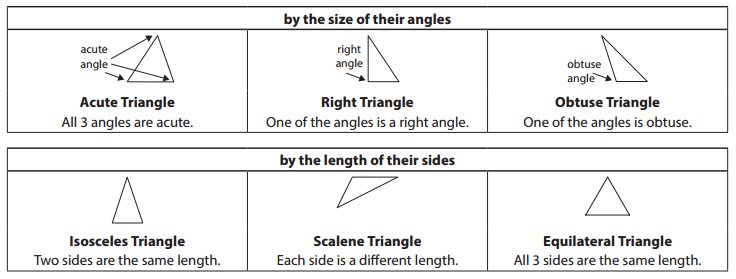
Remember that you can classify and describe triangles in two different ways:
Question 1.
Follow the instructions below each geoboard to draw some different triangles. Hint Build your triangles on a geoboard first. Then copy them onto the paper.
Answer:
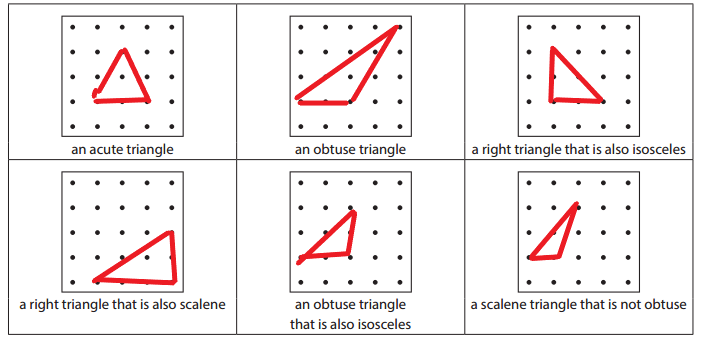
Question 2.
CHALLENGE Dana says it is impossible to draw a right triangle that is also acute. Do you agree with her? Why or why not? Use the geoboards below to test your ideas. Explain your ideas in writing.
Answer: yes Dana said correct. It is impossible to draw the right triangle which is acute. Because acute triangle means all the 3 angles are less than 90 degrees. But in right triangle one angle is 90.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 6 Module 2 Session 2 Answer Key
Thinking About Quadrilaterals
Question 1.
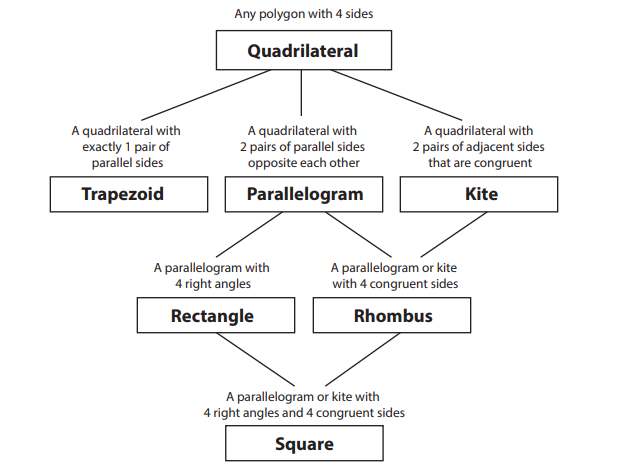
Fill in the hierarchy of quadrilaterals below.
a. Sketch an example of each shape beside or below its box on the chart.
Answer:
Square:

Kite:
Parralelogram:
Trapezoid:
b. Then use the information to help answer the questions on this page and the next.
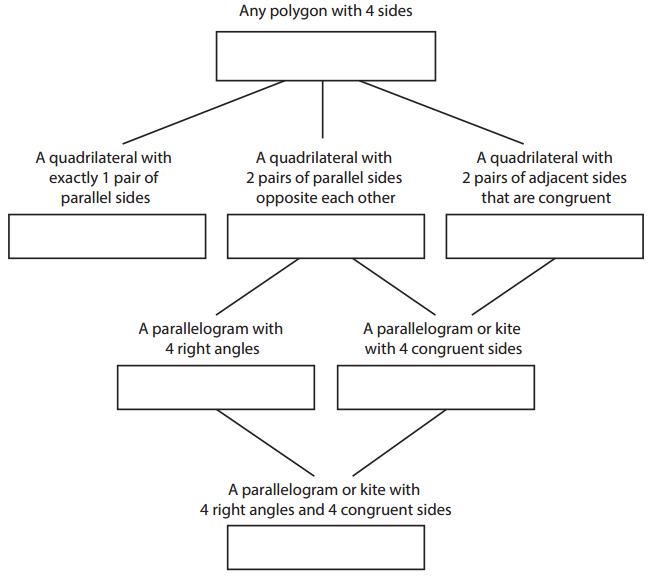
Answer:
Question 2.
Compare a rhombus and a square. List two ways in which they are alike, and two ways in which they are different.
Answer:
Alike:
1) Both are having 4 sides
2) both rhombus and square are closed figures.
different:
1) In square the angles between two sides is 90 degrees. But in rhombus the angle is not 90 degrees.
2) A square has four lines of symmetry and a rhombus has two lines of symmetry.
Question 3.
Why do people say that a square is a special kind of rectangle?
Answer: Because both square and rectangle is having some similar properties.
Both are closed figures with 4 sides. And the angle between two sides is 90 degrees.
Question 4.
Lily says that a square is a special kind of rhombus. Do you agree with her? Explain your answer.
Answer: Yes Lily is correct.
Square is a special kind of rhombus. The main two features of a square are that it has all sides of equal lengths and all its angles are right angles. Now, a rhombus does have all its sides equal.
Question 5.
Jared says that a trapezoid has 2 sides parallel so it must be a parallelogram. Do you agree with him? Explain your answer.
Answer: No Jared is not correct.
trapezoid has 1 side parallel where as parallelogram has 2 sides parallel.
Question 6.
Square is the most specific name for a quadrilateral with 4 right angles and 4 congruent sides. List all the other names for a square (there are at least 4 of them).
Answer: Square, Rectangle, Rhombus, Trapezoid, Parallelogram.
Because all these properties are same. Hence the names of the square are Square, Rectangle, Rhombus, Trapezoid, Parallelogram.
Question 7.
CHALLENGE. Is a rhombus also a kite? Why or why not?
Answer: Yes rhombus is a kite.
We can conclude from the solution that all rhombuses are kites but all kites are not rhombus because diagonals of rhombus bisect each other but diagonals of kites do not. Also, all sides of rhombus are equal to each other but kites have two consecutive pairs of congruent sides.
Perimeters & Trapezoids
This graph represents the perimeters of regular polygons (triangles, squares, pentagons, and hexagons) that have the same side lengths.
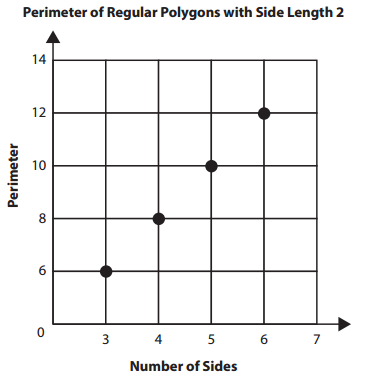
Question 1.
What does the 4 in the point (4, 8) represent?
Answer: The 4 tells how many sides the shape has.
Because from the graph x coordinate describes the shape. As 4 is the x coordinate hence it describes the sides.
Question 2.
What does the 8 in the point (4, 8) represent?
Answer: The 8 (eight) tells the perimeter of the shape.
Because y coordinates describes the perimeter. As 8 is the y coordinate hence it describes the perimeter.
Question 3.
What does the point (6, 12) represent?
Answer: A polygon with 6 sides with the perimeter of 12.
Because from the graph x coordinate describes the shape. As 6 is the x coordinate hence it describes the sides.
Because y coordinates describes the perimeter. As 12 is the y coordinate hence it describes the perimeter.
Question 4.
Kevin says, “A trapezoid is a special quadrilateral, so a quadrilateral has all of the properties of a trapezoid.” Do you agree with Kevin? Explain your answer.
Answer: Kevin is incorrect.
Explanation: Not all quadrilaterals have exactly 1 pair of parallel sides opposite each other. Some quadrilaterals have 0 pairs of parallel sides, while others have 2 pairs of parallel sides.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 6 Module 2 Session 3 Answer Key
The Logic of Quadrilaterals Challenge
Question 1.
Label each shape in this diagram with the name that describes it most exactly.
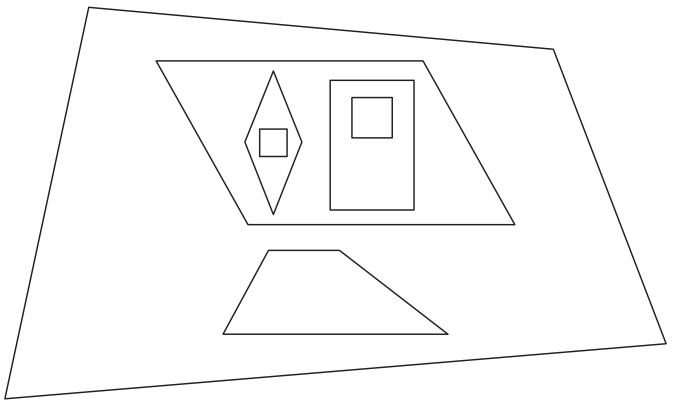
Answer:
square, rhombus, rectangle, Parallelogram, trapezoid
Question 2.
Why is the trapezoid inside the quadrilateral but outside the parallelogram?
Answer: Because trapezoid is the quadrilateral that’s why trapezoid is inside the quadrilateral but whereas it is not a parallelogram hence it is kept outside of the parallelogram.
Question 3.
Why are there a rhombus and a rectangle inside the parallelogram?
Answer: Because both rhombus and Kite are parallelogram. Hence they arranged inside of the parallelogram.
Question 4.
Why are there two squares, one inside the rhombus and one inside the rectangle?
Answer: Because square properties are similar to both rhombus and rectangle. Therefore, one square is placed inside of the rhombus and the other is placed inside of the rectangle.
Question 5.
Write at least two other observations to explain why the shapes in this diagram have been placed where they are in relation to each other.
Answer:
1) trapezoid inside the quadrilateral but outside the parallelogram. Because trapezoid is the quadrilateral that’s why trapezoid is inside the quadrilateral but whereas it is not a parallelogram hence it is kept outside of the parallelogram.
2) Rhombus and a rectangle inside the parallelogram. Because both rhombus and Kite are parallelogram. Hence they arranged inside of the parallelogram.
Quad Construction
Use a ruler marked in inches and the grid lines below to draw the following figures.
Question 1.
A trapezoid with at least one right angle, one side length of 1\(\frac{7}{8}\) inches and one side length of 2\(\frac{5}{8}\) inches.
Answer:
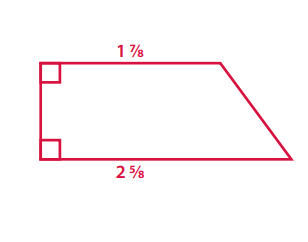
Question 2.
A parallelogram that is not a rectangle, with an area of 18 square units. (The smallest square on the grid has an area of 1 square unit.) Label your drawing to prove that the area is 18 square units.
Answer:
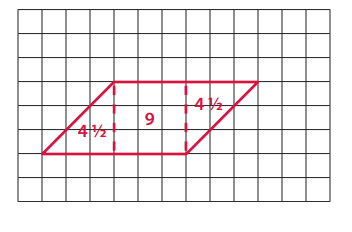
Question 3.
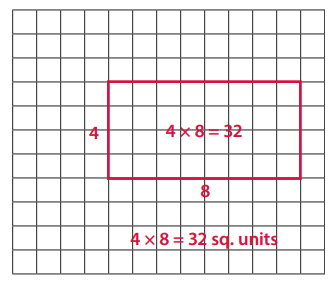
A parallelogram with 4 right angles and an area of 32 square units. Label your drawing to prove that the area is 32 square units.

Answer:
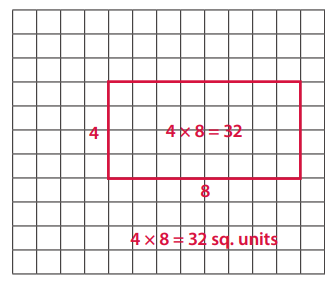
Question 4.
A parallelogram that is not a rectangle, with an area of 32 square units. Label your drawing to prove that the area is 32 square units.

Answer:
Properties of Parallelograms
Use the diagrams below to answer the following questions.
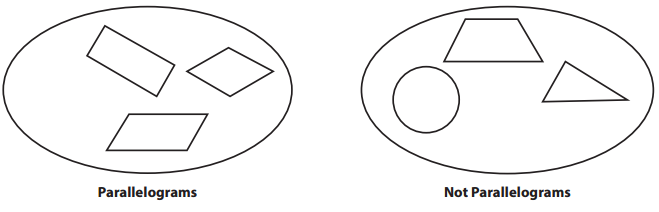
Question 1.
List three properties of a parallelogram.
Answer:
1) parallelogram is a closed figure
2) 2 pairs of parallel sides opposite to each other
3) straight sides it contains
4) 4 right angles or 2 obtuse and 2 acute angles
Question 2.
Fill in the bubbles beside the other names that fit all parallelograms.
![]() rectangles
rectangles
![]() quadrilaterals
quadrilaterals
![]() polygons
polygons
![]() rhombuses
rhombuses
Answer:
quadrilaterals, polygons
Because all quadrilaterals, polygons properties are similar to parallelograms.
Question 3.
Add one shape to each of the diagrams at the top of the page.
Answer:
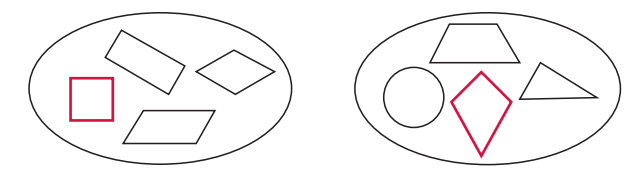
Question 4.
Why can’t trapezoids be classified as parallelograms?
Answer: A trapezoid must have exactly one pair of parallel sides, but a parallelogram always has two pairs of parallel sides.
Question 5.
Circle the word to tell if each statement below is true or false.
a. If the opposite sides on a parallelogram are parallel and congruent, then rectangles are parallelograms.
True
False
Answer: True
because, if the opposite sides parallelogram are parallel and congruent then it is rectangle.
b. If rectangles have 4 right angles, then all parallelograms must be rectangles.
True
False
Answer: false
Because one of the property of rectangle is having right triangle between two sides.
c. If parallelograms have 4 sides, then all quadrilaterals must be parallelograms.
True
False
Answer: False
parallelogram is the one which is having 4 sides. If parallelograms have 4 sides, then all quadrilaterals must be parallelograms.