Students looking for the Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Answer Key Unit 2 Module 3 can find a better approach to solve the problems.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Answer Key Unit 2 Module 3
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 1 Answer Key
Buying Granola
Granola costs $6 for 5 pounds.
Use the ratio tables to find the prices for different amounts of granola: \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\), 1, 2, 3, 8, 13, 15, 28, 31, 50, 60, and 80 pounds. You can find the prices in any order.
ex
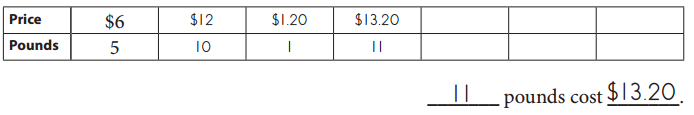

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

1 pound cost 1.20 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

2 pounds cost 2.40 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 2 pounds = 2 x 1.20 = $2.40

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:
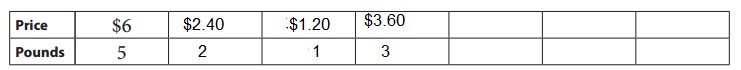
3 pounds cost 3.60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 3 pounds = 3 x 1.20 = $3.60

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

8 pounds cost 9.60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 8 pounds = 8 x 1.20 = $9.600

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

13 pounds cost 15.60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 13 pounds = 13 x 1.20 = $15.60

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

15 pounds cost 18 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 15 pounds = 15 x 1.20 = $18

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:
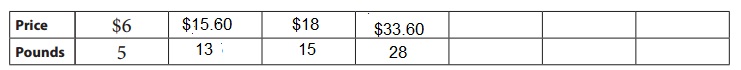
28 pounds cost 33.60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 28 pounds = 28 x 1.20 = $33.60

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

1/2 or half pound cost 0.60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of half pound = 0.5 x 1.20 = $0.60

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

1/4 pounds cost 0.30 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 1/4 pounds = 1/4 x 1.20 = $0.30

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

3/4 pounds cost 0.90 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 3/4 pounds = 3/4 x 1.20 = $0.90

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

31 pounds cost 37.20 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 31 pounds = 31 x 1.20 = $37.20

___ pounds cost _____
Answer:

50 pounds cost 60 dollars.
Explanation:
Given, to find the prices for different amounts of granola.
Based on the given example, cost of one pound a dollar twenty.
Cost of 50 pounds = 50 x 1.20 = $60
Buying Apples
Question 1.
Color in the geoboards to show the fractions below. Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
a. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
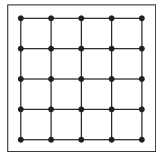
Answer:
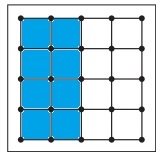
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{1}{2}\) x16 = 8
So, color 8 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
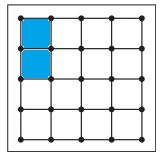
b. \(\frac{1}{4}\)

Answer:
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{1}{4}\) x16 = 4
So, color 4 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
c. \(\frac{3}{4}\)

Answer:
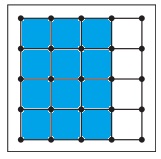
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{3}{4}\) x16 = 3 x 4 = 12
So, color 12 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
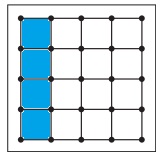
d. \(\frac{1}{8}\)

Answer:
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{1}{8}\) x16 = 2
So, color 2 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
e. \(\frac{2}{8}\)

Answer:
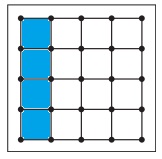
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{2}{8}\) x16 = 2 x 2=4
So, color 4 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
f. \(\frac{5}{8}\)

Answer:
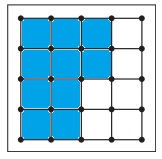
Explanation:
Given, Each geoboard represents 1 whole.
\(\frac{5}{8}\) x16 = 5 x 2 = 10
So, color 10 units in the geoboard to shown the fraction.
Add the following fractions. If the sum is greater than 1, write the answer as both an improper fraction and a mixed number.
Question 2.
Find equivalent fractions and then add or subtract.
ex \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{9}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{8}\)
a. 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = ___ + ___ = ___ = ____
Answer:
1\(\frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation:
Given,
1\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{12}{8}\) + \(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{15}{8}\) = 1\(\frac{7}{8}\)
If the sum is greater than 1, write the answer as both an improper fraction and a mixed number.
b. 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) = ___ + ___ = ___ = ____
Answer:
2\(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation:
Given,
2\(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{9}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{18}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{20}{8}\) = 2\(\frac{4}{8}\)
If the sum is greater than 1, write the answer as both an improper fraction and a mixed number.
c. \(\frac{3}{4}\) – \(\frac{2}{8}\) = ___ + ___ = ___ = ____
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{8}\) or \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation:
Given,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) – \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\) – \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Question 3.
Five pounds of apples cost $8. Use the ratio table to find the cost for 9 pounds and 11 pounds. You do not need to use all of the table cells.

a. Cost of 9 pounds of apples: ____
Answer:

Explanation:
Given,
Five pounds of apples cost $8.
So, cost of one pound = 8/5 = $1.60
Therefore, the cost for 9 pounds = 9 x 1.60 = $14.58
b. Cost of 11 pounds of apples: _____
Answer:

Explanation:
Given,
Five pounds of apples cost $8.
So, cost of one pound = 8/5 = $1.60
Therefore, the cost for 11 pounds = 11 x 1.60 = $17.60
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 2 Answer Key
Rewrite & Calculate
Question 1.
Complete the tables to show equivalent fractions of an hour. Use the clocks to show each equivalent fraction.
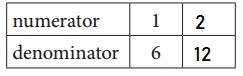
a. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{1}{6}\)
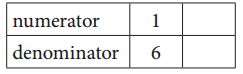
Answer:
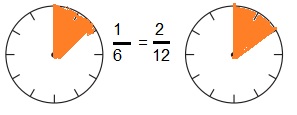
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{1}{6}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
b. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{1}{3}\)
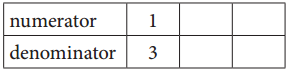
Answer:
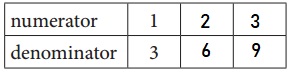
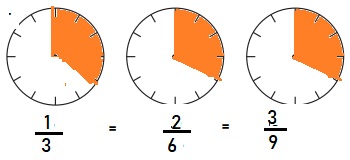
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{3}{9}\)
c. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{3}{4}\)
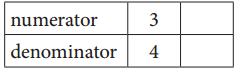
Answer:
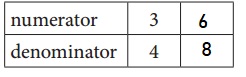
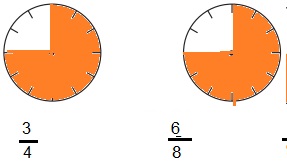
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{3}{4}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Question 2.
Use the tables of equivalent fractions above to help you solve these problems.
a. Dylan spent \(\frac{1}{6}\) of an hour sweeping the floor and \(\frac{1}{3}\) of an hour picking weeds to help his parents. What fraction of an hour did Dylan spend helping his parents?
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{2}\) hours.
Explanation:
Given that,
Dylan spent \(\frac{1}{6}\) of an hour sweeping the floor.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) of an hour picking weeds to help his parents.
Total fraction of an hour did Dylan spend helping his parents,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
b. Lisa spent \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour reading her book and 3 of an hour drawing. What fraction of an hour did Lisa spend reading and drawing?
Answer:
2\(\frac{1}{4}\) hours.
Explanation:
Given that,
Lisa spent \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour reading her book.
3 of an hour drawing.
The fraction of an hour did Lisa spend reading and drawing = \(\frac{3}{4}\) + 3
= \(\frac{3 × 3}{4}\) = \(\frac{9}{4}\) = 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)
c. Rory spent 1\(\frac{1}{6}\) of an hour swimming and then \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour playing basketball. What fraction of an hour did Rory spend swimming and playing basketball?
Answer:
1\(\frac{11}{12}\) hours.
Explanation:
Rory spent 1\(\frac{1}{6}\) of an hour swimming.
\(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour playing basketball.
The fraction of an hour did Rory spend swimming and playing basketball,
1\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{7}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{(2 × 7)+(3 × 3)}{12}\) = \(\frac{14 + 9}{12}\) = \(\frac{23}{12}\) = 1\(\frac{11}{12}\) hours.
d. Lisa spent \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour doing chores on Friday, and her sister Eva spent \(\frac{1}{3}\) of an hour doing chores. How much more time (as a fraction of an hour) did Lisa spend on chores than Eva?
Answer:
1\(\frac{1}{12}\) hours more than her sister.
Explanation:
Given that,
Lisa spent \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour doing chores on Friday,
her sister Eva spent \(\frac{1}{3}\) of an hour doing chores.
more time (as a fraction of an hour) did Lisa spend on chores than Eva,
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{(3 × 3)+(1×4)}{12}\) = \(\frac{9 + 4}{12}\) = \(\frac{13}{12}\)
= 1\(\frac{1}{12}\)
Question 3.
Rewrite each problem using equivalent fractions with a common denominator. Then find the sum.
ex \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
\(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
a. \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{1 × 2}{3 × 2}\) + \(\frac{1 × 3}{2 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{6}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{2+3}{6}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\)
b. \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{3 × 3}{4 × 3}\) + \(\frac{1 × 2}{6 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{9}{12}\) + \(\frac{2}{12}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{9+2}{12}\) = \(\frac{11}{12}\)
More Equivalent Fractions
Question 1.
Fill in the tables to show equivalent fractions. You can use the clocks to help if you want to.
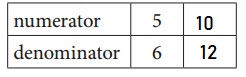
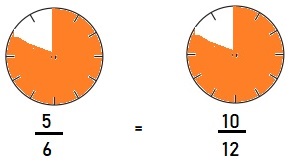
a. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{5}{6}\)
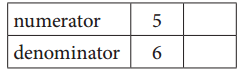
Answer:
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{5}{6}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\)
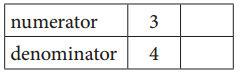
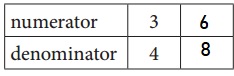
b. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
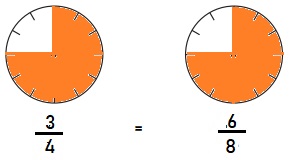
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{3}{4}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
c. Equivalent Fractions for \(\frac{1}{3}\)
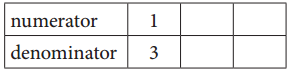
Answer:


Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
Equivalent fractions are the fractions that have different numerators and denominators but are equal to the same value.
So, the numerator and denominator of a fraction are multiplied by the and the result is a fraction that is equivalent to the original fraction.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Question 2.
Rewrite each problem using equivalent fractions with a common denominator. Then find the sum.
ex \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\)
\(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
a. \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{1 × 4}{3 × 4}\) + \(\frac{1 × 3}{4 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{4}{12}\) + \(\frac{3}{12}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{4+3}{12}\) = \(\frac{7}{12}\)
b. \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer:
1\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{3 × 3}{4 × 3}\) + \(\frac{5 × 2}{6 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{9}{12}\) + \(\frac{10}{12}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{9+10}{12}\) = \(\frac{19}{12}\) = 1\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 3 & 4 Answer Key
Fraction Story Problems
Question 1.
Zack and Noah jogged \(\frac{2}{5}\) of a mile and walked another \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a mile. How far did they go in all?
Answer:
\(\frac{13}{20}\) miles.
Explanation:
Given that,
Zack and Noah jogged \(\frac{2}{5}\) of a mile.
walked another \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a mile.
Number of miles he go in all = \(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{2 × 4}{5 × 4}\) + \(\frac{1 × 5}{4 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{8}{20}\) + \(\frac{5}{20}\)
when denominators are same add the numerators.
\(\frac{8+5}{20}\) = \(\frac{13}{20}\)
Question 2.
Mrs. Brown bought a dozen eggs at the store, but when she got home she discovered that \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the eggs were broken so she threw them away. She used \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the dozen in a recipe. How many eggs were left? What fraction of the dozen was left?
Answer:
Left over eggs = 8
fraction of the dozen was left \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
Mrs. Brown bought a dozen eggs at the store = 12 eggs.
But, when she got home she discovered that \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the eggs were broken.
12 x \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 4 eggs.
Left over eggs = 12 – 4 = 8
She used \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the dozen in a recipe.
8 x \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Question 3.
Erin had 3\(\frac{1}{9}\) boxes of granola bars. She gave 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) of the boxes of granola bars to her friends. How much did Erin have left for herself?
Answer:
1\(\frac{13}{36}\) boxes.
Explanation:
Given that,
Erin had 3\(\frac{1}{9}\) boxes of granola bars.
She gave 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) of the boxes of granola bars to her friends.
3\(\frac{1}{9}\) – 1\(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{28}{9}\) – \(\frac{7}{4}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{28 × 4}{9 × 4}\) – \(\frac{7 × 9}{4 × 9}\)
= \(\frac{112}{36}\) – \(\frac{63}{36}\)
when denominators are same subtract the numerators.
\(\frac{112-63}{36}\) = \(\frac{49}{36}\)
= 1\(\frac{13}{36}\) boxes.
Question 4.
Jada had 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) pieces of red licorice. Her cousin gave her 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) more pieces of red licorice. Then Jada gave 1\(\frac{1}{8}\) of the pieces to her dad. How many pieces did Jada have left?
Answer:
2\(\frac{5}{8}\) pieces.
Explanation:
Given that,
Jada had 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) pieces of red licorice.
Her cousin gave her 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) more pieces of red licorice.
1\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2\(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{3}{2}\) + \(\frac{9}{4}\)
Take the L.C.M of the denominators 2 and 4 as 4.
= \(\frac{(3×2) + (9×1)}{4}\) = \(\frac{6+9}{4}\) = \(\frac{15}{4}\)
Simplify, 3\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Then Jada gave 1\(\frac{1}{8}\) of the pieces to her dad.
Total pieces left with Jada = 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) – 1\(\frac{1}{8}\)
= \(\frac{15}{4}\) – \(\frac{9}{8}\)
Take the L.C.M of the denominators 4 and 8 as 8.
= \(\frac{(15×2) – (9×1)}{8}\) = \(\frac{30-9}{8}\) = \(\frac{21}{8}\)
Simplify, 2\(\frac{5}{8}\) pieces.
Question 5.
Last Saturday, Michael spent \(\frac{2}{6}\) of an hour cleaning the hamster cage, \(\frac{3}{12}\) of an hour walking the dog around the block, and \(\frac{5}{60}\) of an hour feeding the bird. What part of an hour did Michael spend taking care of his pets?
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{3}\) hours.
Explanation:
Given that,
Last Saturday, Michael spent \(\frac{2}{6}\) of an hour cleaning the hamster cage,
\(\frac{3}{12}\) of an hour walking the dog around the block,
\(\frac{5}{60}\) of an hour feeding the bird.
Number of hours did Michael spend taking care of his pets,
\(\frac{2}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{12}\) + \(\frac{5}{60}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{(2 × 10)}{(6 × 10)}\) + \(\frac{(3 × 5)}{(12 × 5)}\) + \(\frac{5}{60}\)
= \(\frac{20}{60}\) + \(\frac{15}{60}\) + \(\frac{5}{60}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{20+15+5}{60}\) = \(\frac{40}{60}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 6.
Leah was planning to spend 2\(\frac{1}{3}\) hours with a friend on Saturday, but her mom said she had to finish her chores first. If it took her \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour to do her chores, how much time did Leah have left to spend with her friend?
Answer:
1\(\frac{7}{12}\) hours left.
Explanation:
Given that,
Leah was planning to spend 2\(\frac{1}{3}\) hours with a friend on Saturday,
If it took her \(\frac{3}{4}\) of an hour to do her chores.
Total time did Leah have left to spend with her friend = 2\(\frac{1}{3}\) – \(\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\frac{7}{3}\) – \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{(7 × 4)}{(3 × 4)}\) + \(\frac{(3 × 3)}{(4 × 3)}\)
= \(\frac{28}{12}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\)
When denominators are same subtract the numerators.
= \(\frac{28 – 9}{12}\) = \(\frac{19}{12}\) = 1\(\frac{7}{12}\)
Question 7.
Josie walked \(\frac{3}{10}\) of a mile to the park. Then she walked \(\frac{2}{5}\) of a mile to Angie’s house. Then she walked \(\frac{1}{20}\) of a mile home. How far did Josie walk in all?
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{4}\) miles.
Explanation:
Given that,
Josie walked \(\frac{3}{10}\) of a mile to the park.
Then she walked \(\frac{2}{5}\) of a mile to Angie’s house.
Then she walked \(\frac{1}{20}\) of a mile home.
Total miles did Josie walk in all = \(\frac{3}{10}\) + \(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{3 × 2}{10 × 2}\) + \(\frac{2 × 4}{5 × 4}\) + \(\frac{1}{20}\)
= \(\frac{6}{20}\) + \(\frac{8}{20}\) + \(\frac{1}{20}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{6+8+1}{20}\) = \(\frac{15}{20}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) miles.
Question 8.
The class was celebrating reading week with cupcakes. The red and blue table groups ate \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the cupcakes, and the green and purple table groups ate \(\frac{3}{7}\) of the cupcakes. What fraction of the cupcakes was left? How many cupcakes might there have been?
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{35}\) cup cakes
The number of cup cakes 35.
Explanation:
Given that,
The red and blue table groups ate \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the cupcakes.
The green and purple table groups ate \(\frac{3}{7}\) of the cupcakes.
\(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{3}{7}\)
= \(\frac{2×7}{5×7}\) + \(\frac{3×5}{7×5}\)
= \(\frac{14}{35}\) + \(\frac{15}{35}\)
= \(\frac{14 + 15}{35}\)
= \(\frac{29}{35}\)
The fraction of the cupcakes was left
\(\frac{35 – 29}{35}\)
= \(\frac{6}{35}\) cup cakes
The number of cup cakes 35.
Question 9.
CHALLENGE Pablo found part of a carton of eggs in the refrigerator. He used \(\frac{1}{3}\) of a dozen for baking a cake and \(\frac{1}{6}\) of a dozen to make brownies. Then he had 2 eggs left over. How many eggs were in the carton when Pablo started?
Answer:
8 eggs.
Explanation:
Given that,
Pablo used \(\frac{1}{3}\) of a dozen for baking a cake.1
12 x \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 4 eggs.
12 – 4 = 8 eggs left.
\(\frac{1}{6}\) of a dozen to make brownies.
12 x \(\frac{1}{6}\) = 2 eggs.
Then he had 2 eggs left over.
Total eggs were in the carton when Pablo started = 4 + 2 + 2 = 8 eggs.
Question 10.
CHALLENGE Morgan had \(\frac{1}{2}\) a box of candy left after the movie. She ate \(\frac{1}{2}\) of that on the way home and still had 8 pieces left to give to her little brother. How many pieces of candy were in the box when Morgan bought it?
Answer:
32 candies.
Explanation:
Given that,
Morgan had \(\frac{1}{2}\) a box of candy left after the movie.
let the candies in the box be x.
x – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
She ate \(\frac{1}{2}\) of that on the way home.
Still had 8 pieces left to give to her little brother.
Total pieces of candy were in the box when Morgan bought it = 8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 16
16 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 32 candies.
or 32 x \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 16
16 x \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 8 left over candies.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 3 Answer Key
Ratio Tables to the Rescue!
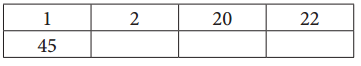
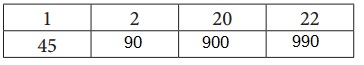
Question 1.
Use the ratio table to multiply 22 × 45.
Answer:
Explanation:
A ratio is a relationship between two things when it is expressed in numbers or amounts.
Given, the ratio table to multiply 22 × 45.
1 x 45 = 45
2 x 45 = 90
20 x 45 = 900
22 x 45 = 990
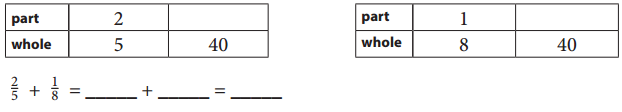
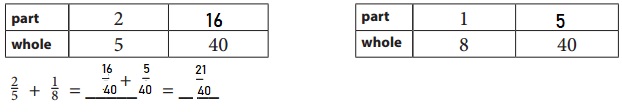
Question 2.
Use a ratio tables to find equivalent fractions so that you can add \(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Answer:
Explanation:
Given,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{2 × 8}{5 × 8}\) + \(\frac{1 × 5}{8 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{16}{40}\) + \(\frac{5}{40}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{16+5}{40}\) = \(\frac{21}{40}\)
Question 3.
Use a ratio table to simplify a fraction. You might not need all of the columns.
ex Use the ratio table to simplify \(\frac{35}{100}\).
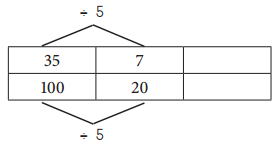
a. Use the ratio table to simplify \(\frac{6}{24}\).

Answer:
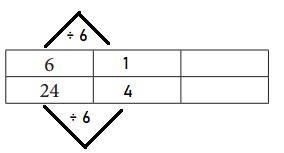
Explanation:
Given to simplify \(\frac{6}{24}\).
Divide by 6 both numerator and denominator to get equivalent fraction.
\(\frac{6}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\).
Question 4.
Use the ratio tables to find the better buy. You might not need all of the columns.
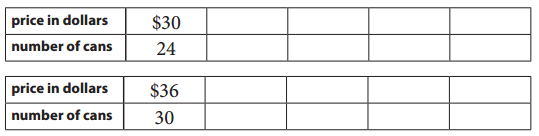
Which is the better buy? Explain.
Answer:
Better buy is 30 cans at the rate $1.2
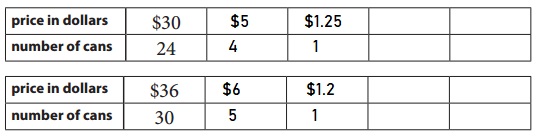
Explanation:
Given,
24 cans = $30
the cost of one can = \(\frac{30}{24}\) = $1.25
30 cans = $36
the cost of one can = \(\frac{36}{30}\) = $1.2
So, Better buy is 30 cans at the rate $1.2
Question 5.
Regina used a ratio table incorrectly to add \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\). Explain her error.
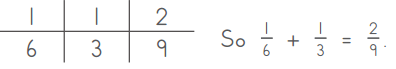
Answer:
Regina added the denominators instead of rewriting each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
Explanation:
Given to add,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1 × 2}{3 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{2}{6}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{1+2}{6}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 4 Answer Key
Adding Fractions & Mixed Numbers
Question 1.
Rewrite each pair of fractions so they have the same denominator. Then find their sum. Simplify the sum if you can.
ex
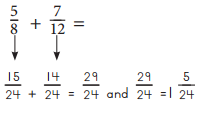
Explanation:
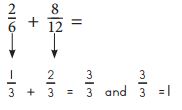
a. \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) =
Answer:
1
Explanation:
\(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\)
= \(\frac{3 × 8}{4 × 8}\) + \(\frac{2 × 4}{8 ×4}\)
=\(\frac{24}{32}\) + \(\frac{8}{32}\)
= \(\frac{24 + 8}{32}\)
= \(\frac{32}{32}\)
= 1
b. \(\frac{6}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\) =
Answer:
1\(\frac{48}{96}\)
Explanation:
\(\frac{6}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{12}\)
= \(\frac{6 × 12}{8 × 12}\) + \(\frac{9 × 8}{12 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{72}{96}\) + \(\frac{72}{96}\)
= \(\frac{72 + 72}{96}\)
= \(\frac{144}{96}\)
= 1\(\frac{48}{96}\)
c. 3\(\frac{6}{12}\) + 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) =
Answer:
8
Explanation:
3\(\frac{6}{12}\) + 4\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 3\(\frac{6}{12}\) + 4\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{42}{12}\) + \(\frac{9}{2}\)
= \(\frac{42×2}{12×2}\) + \(\frac{9×12}{2×12}\)
= \(\frac{84}{24}\) + \(\frac{108}{24}\)
= \(\frac{84 + 108}{24}\)
= \(\frac{192}{24}\)
= 8
d. 1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{3}{4}\) =
Answer:
4 \(\frac{12}{32}\)
Explanation:
1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{3}{4}\)
= 1\(\frac{5}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{13}{8}\) + \(\frac{11}{4}\)
= \(\frac{13×4}{8×4}\) + \(\frac{11×8}{4×8}\)
= \(\frac{52}{32}\) + \(\frac{88}{32}\)
= \(\frac{52 + 88}{32}\)
= \(\frac{140}{32}\)
= 4 \(\frac{12}{32}\)
Question 2.
Randy solved the following problem: \(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{15}\). He said, “I can add 7 and 9 to get 16 and add 8 and 15 to get 23. The answer is \(\frac{16}{23}\)” Is Randy correct? Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, he is wrong.
We can not add the unlike fractions directly.
Correct answer is 1\(\frac{57}{120}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
Randy solved the following problem:
\(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{15}\).
He said, “I can add 7 and 9 to get 16 and add 8 and 15 to get 23.
The answer is \(\frac{16}{23}\)”
can not be added directly as the fractions are unlike.
to add the fraction, the denominators to be equalized as below.
\(\frac{7}{8}\) + \(\frac{9}{15}\)
= \(\frac{7 ×15}{8 ×15}\) + \(\frac{9 × 8}{15 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{105}{120}\) + \(\frac{72}{120}\)
= \(\frac{105 + 72}{120}\)
= \(\frac{177}{120}\)
= 1\(\frac{57}{120}\)
Question 3.
Bobby used a ratio table to find an equivalent fraction to add \(\frac{4}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\). He thought he would simplify \(\frac{4}{6}\) first, and wrote down \(\frac{8}{3}\). Kelly said she didn’t think \(\frac{4}{6}\) was equivalent to \(\frac{8}{3}\). Who is correct? Explain your answer.
Answer:
1\(\frac{4}{15}\)
Explanation:
With reference to the above information,
\(\frac{4}{6}\) is not equivalent to \(\frac{8}{3}\)
the addition can be done as follows,
\(\frac{4}{6}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{2}{3}\) + \(\frac{3}{5}\)
= \(\frac{2×5}{3×5}\) + \(\frac{3×3}{5×3}\)
= \(\frac{10}{15}\) + \(\frac{9}{15}\)
= \(\frac{10 + 9}{15}\)
= \(\frac{19}{15}\)
=1\(\frac{4}{15}\)
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 5 Answer Key
Question 1.
Find the sum or the difference for each pair of fractions.
a. \(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\) =
Answer:
= \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\)
= \(\frac{5×6}{6×5}\) – \(\frac{2×6}{5×6}\)
= \(\frac{30}{30}\) – \(\frac{12}{30}\)
= \(\frac{30 – 12}{30}\)
= \(\frac{18}{30}\)
= \(\frac{6}{10}\)
= \(\frac{3}{5}\)
b. \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{6}{7}\) =
Answer:
1\(\frac{4}{21}\)
Explanation:
Given, \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{6}{7}\)
= \(\frac{1×7}{3×7}\) + \(\frac{6×3}{7×3}\)
= \(\frac{7}{21}\) + \(\frac{18}{21}\)
= \(\frac{7 + 18}{21}\)
= \(\frac{25}{21}\)
= 1\(\frac{4}{21}\)
Question 2.
Annie ran \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a mile. Lexi ran \(\frac{7}{10}\) of a mile. Who ran farther and by exactly how much? Show all your work.
Answer:
Lexi ran \(\frac{3}{40}\) of a mile.
\(\frac{3}{40}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
Annie ran \(\frac{5}{8}\) of a mile.
Lexi ran \(\frac{7}{10}\) of a mile.
So, \(\frac{5}{8}\) – \(\frac{7}{10}\)
= \(\frac{5×10}{8×10}\) – \(\frac{7×8}{10×8}\)
= \(\frac{50}{80}\) – \(\frac{56}{80}\)
= \(\frac{50 – 56}{80}\)
= –\(\frac{6}{80}\)
= –\(\frac{3}{40}\)
Question 3.
Juan and his mother hiked \(\frac{3}{8}\) of a mile this morning and \(\frac{4}{5}\) of a mile this afternoon. How far did they hike today? Show all your work.
Answer:
1\(\frac{7}{40}\) hike today.
Explanation:
Given that,
Juan and his mother hiked \(\frac{3}{8}\) of a mile this morning.
\(\frac{4}{5}\) of a mile this afternoon.
So, \(\frac{3}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{5}\)
= \(\frac{3 × 5}{8 × 5}\) + \(\frac{4 × 8}{5 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{15}{40}\) + \(\frac{32}{40}\)
= \(\frac{15 + 32}{40}\)
= \(\frac{47}{40}\)
= 1\(\frac{7}{40}\)
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 5 Student Book Unit 2 Module 3 Session 6 Answer Key
More Fraction Problems
Question 1.
Fill in the missing fraction or mixed number in each equation.
ex 1\(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) = 2
a. 1 = \(\frac{6}{10}\) + ____
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
1 = \(\frac{6}{10}\) +
let the unknown number be x.
1 – \(\frac{6}{10}\) = x
x = \(\frac{10-6}{10}\)
x = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
x = \(\frac{2}{5}\)
b. 2 = 1\(\frac{4}{12}\) + ____
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
2 = 1\(\frac{4}{12}\)
let the unknown number be x.
2 – \(\frac{16}{12}\) = x
x = \(\frac{24-16}{12}\)
x = \(\frac{8}{12}\)
x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
c. 3 = + 1\(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer:
1\(\frac{1}{8}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
3 = + 1\(\frac{7}{8}\)
let the unknown number be x.
x = 3 – \(\frac{15}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{24-15}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{9}{8}\)
x = 1\(\frac{1}{8}\)
d. 2 = \(\frac{10}{12}\) + _____
Answer:
1\(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
2 = \(\frac{10}{12}\)
let the unknown number be x.
2 – \(\frac{10}{12}\) = x
x = \(\frac{24-10}{12}\)
x = \(\frac{14}{12}\)
x = 1\(\frac{2}{12}\)
e. 2\(\frac{6}{8}\) + ____ = 4
Answer:
1\(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
2\(\frac{6}{8}\) + ___ = 4
let the unknown number be x.
x = 4 – 2\(\frac{6}{8}\)
x = 4 – \(\frac{22}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{32-22}{8}\)
x = \(\frac{10}{8}\)
x = 1\(\frac{2}{8}\)
Question 2.
Calvin and his family were going on a walk. They wanted to walk to the park, then go to the ice cream parlor, and finally walk home. The map below shows their path and the distances between each stop. How many kilometers will they walk in all? Show all your work.
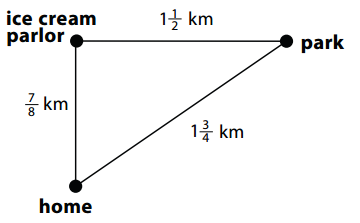
Answer:
4\(\frac{1}{8}\) miles.
Explanation:
With reference to the above given map,
The distance between home to park = 1\(\frac{3}{4}\)
The distance between park to ice-cream parlor = 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
The distance between ice-cream parlor to home = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Total kilometers they walk all together = 1\(\frac{3}{4}\) + 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
convert the mixed fraction to improper fraction.
\(\frac{7}{4}\) + \(\frac{3}{2}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{7 × 2}{4 × 2}\) + \(\frac{3 × 4}{2 × 4}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
= \(\frac{14}{8}\) + \(\frac{12}{8}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{14+12+7}{8}\) = \(\frac{33}{8}\) = 4\(\frac{1}{8}\)
Question 3.
Add or subtract to solve each equation. Show all your work.
a. 3\(\frac{7}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{9}{10}\) =
Answer:
6\(\frac{31}{40}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
3\(\frac{7}{8}\) + 2\(\frac{9}{10}\)
= \(\frac{31}{8}\) + \(\frac{29}{10}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{31 × 5}{8 × 5}\) + \(\frac{29 × 4}{10 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{155}{40}\) + \(\frac{116}{40}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{155+116}{40}\) = \(\frac{271}{40}\) = 6\(\frac{31}{40}\)
b. \(\frac{7}{16}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\) =
Answer:
1\(\frac{3}{16}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
\(\frac{7}{16}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{7}{16}\) + \(\frac{3 × 4}{4 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{7}{16}\) + \(\frac{12}{16}\)
When denominators are same add the numerators.
= \(\frac{7+12}{16}\) = \(\frac{19}{16}\) = 1\(\frac{3}{16}\)
c. 1\(\frac{4}{5}\) – \(\frac{6}{7}\) =
Answer:
\(\frac{33}{35}\)
Explanation:
Given that,
1\(\frac{4}{5}\) – \(\frac{6}{7}\)
= \(\frac{9}{5}\) – \(\frac{6}{7}\)
Rewrite each fraction using equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
\(\frac{9 × 7}{5 × 7}\) – \(\frac{6 × 5}{7 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{63}{35}\) – \(\frac{30}{35}\)
When denominators are same subtract the numerators.
= \(\frac{63 – 30}{35}\) = \(\frac{33}{35}\)