The solutions to Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Answer Key Unit 6 Module 4 can help students to clear their doubts quickly.
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Answer Key Unit 6 Module 4
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Unit 6 Module 4 Session 1 Answer Key
Geoboard Halves
How many different ways can you find to divide the square geoboard into halves? Record them here. Put a star by the boards that show halves that are not the same shape and size, but take up the same amount of area.
Answer:
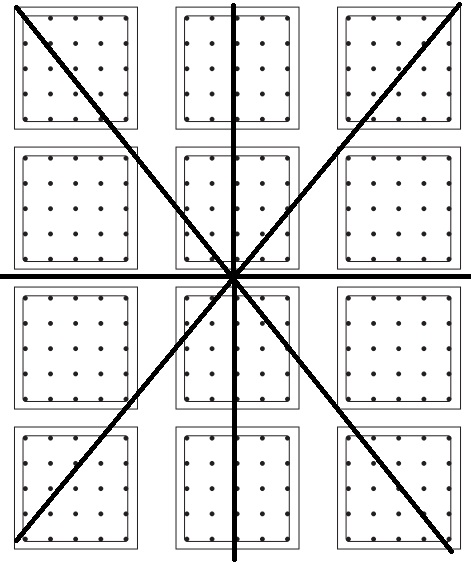
The geoboard can be divided into 6 parts,
Explanation:
We can divide the geoboard into parts by drawing 1 horizontal and 2 diagonals then we obtain 6 different parts out of which the parts obtained by drawing a horizontal line are of equal areas while the parts obtained by drawing diagonal lines divide the geoboard into parts of equal area but they are not the correct halves.
How many different ways can you find to divide the square geoboard into halves? Record them here. Put a star by the boards that show halves that are not the same shape and size, but take up the same amount of area.
Answer:

The geoboard can be divided into 6 parts,
Explanation:
We can divide the geoboard into parts by drawing 1 horizontal and 2 diagonals then we obtain 6 different parts out of which the parts obtained by drawing a horizontal line are of equal areas while the parts obtained by drawing diagonal lines divide the geoboard into parts of equal area but they are not the correct halves.
Fractions of a Circle
Question 1.
Fill in the circle to show each fraction.
ex: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
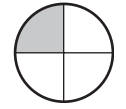
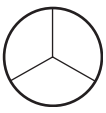
a. \(\frac{1}{3}\)

Answer:
Explanation:
Divide a circle into three equal parts.
Shade one part out of the three equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{1}{3}\).
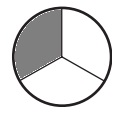
b. \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer:
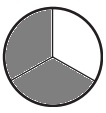
Explanation:
Divide a circle into three equal parts.
Shade two parts out of the three equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{2}{3}\).
c. \(\frac{1}{5}\)
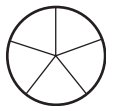
Answer:
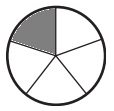
Explanation:
Divide a circle into five equal parts.
Shade one part out of the five equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{1}{5}\).
d. \(\frac{2}{10}\)
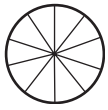
Answer:
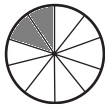
Explanation:
Divide a circle into ten equal parts.
Shade two parts out of the ten equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{2}{10}\).
e. \(\frac{2}{5}\)
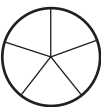
Answer:
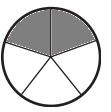
Explanation:
Divide a circle into five equal parts.
Shade two parts out of the five equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{2}{5}\).
Question 2.
Look at the fractions you shaded in above. Use them to help complete each number sentence by writing <, >, or =.
ex: \(\frac{1}{3}\) > \(\frac{1}{5}\)
a. \(\frac{2}{5}\) ______________ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{5}\) < \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 3 is less than 5.
So \(\frac{2}{5}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{3}\).
b. \(\frac{2}{3}\) ______________ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{3}\) > \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 3 is less than 5.
So \(\frac{2}{5}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{3}\).
c. \(\frac{2}{10}\) ______________ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{10}\) which is equivalent to \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{10}\)= \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Now,
Since the both fractions are same.
So \(\frac{2}{10}\) is equal to \(\frac{1}{5}\).
d. \(\frac{2}{5}\) ______________ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{5}\) > \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 5 is less than 10.
So \(\frac{2}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{10}\)
e. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ______________ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\) > \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{10}\) which is equivalent to \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Now,
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 4 is less than 5.
So \(\frac{1}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{10}\)
CHALLENGE
f. \(\frac{1}{19}\) ______________ \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{19}\) < \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 9 is less than 19.
So \(\frac{1}{19}\) is less than \(\frac{1}{9}\)
g. \(\frac{2}{18}\) ______________ \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{18}\) = \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{18}\) is equivalent to \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Since the fractions are same..
So\(\frac{2}{18}\) is equal to \(\frac{1}{9}\)
h. \(\frac{1}{9}\) ______________ \(\frac{2}{20}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{9}\) > \(\frac{2}{20}\)
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{20}\) is equivalent to \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 9 is less than 10.
So \(\frac{1}{9}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{20}\)
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Unit 6 Module 4 Session 2 Answer Key
Geoboard Fractions
Fraction Draw & Compare
Question 1.
Divide each square into the number of pieces you need to model the fraction. Then shade in the correct amount.
ex: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
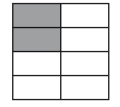
a. \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer:
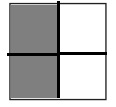
Explanation:
Divide a square into four equal parts.
Shade two parts out of the four equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{2}{4}\).
b. \(\frac{3}{4}\)

Answer:
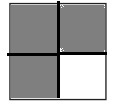
Explanation:
Divide a square into four equal parts.
Shade three parts out of the four equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{3}{4}\).
c. \(\frac{2}{3}\)

Answer:
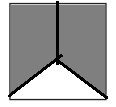
Explanation:
Divide a square into three equal parts.
Shade two parts out of the three equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{2}{3}\).
d. \(\frac{4}{8}\)

Answer:
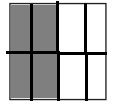
Explanation:
Divide a square into eight equal parts.
Shade four parts out of the eight equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{4}{8}\).
e. \(\frac{6}{8}\)

Answer:
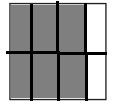
Explanation:
Divide a square into eight equal parts.
Shade six parts out of the eight equal parts.
This gives us the fraction \(\frac{6}{8}\).
Question 2.
Look at the fractions you shaded in above. Use them to help complete each equation by writing <, >, or =.
ex: \(\frac{4}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{8}\)
a. \(\frac{2}{4}\) ________________ \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{4}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
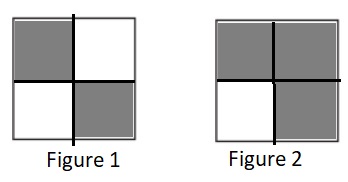
Figure 1 represents the fraction \(\frac{2}{4}\).
Figure 2 represents the fraction \(\frac{3}{4}\).
Since figure 2 is more shaded than figure 1 so \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{4}\).
b. \(\frac{6}{8}\) ________________ \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
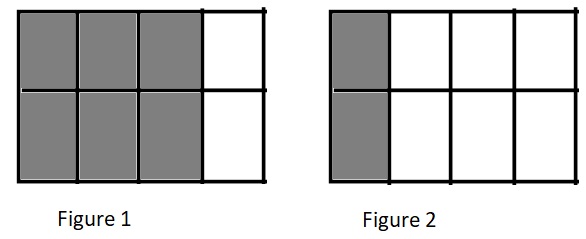
Figure 1 represents the fraction \(\frac{6}{8}\).
Figure 2 represents the fraction \(\frac{2}{8}\).
Since figure 1 is more shaded than figure 2 so \(\frac{6}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{8}\).
c. \(\frac{2}{4}\) ________________ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation:
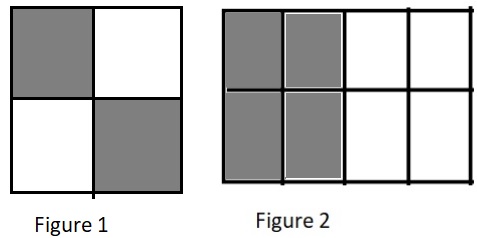
Figure 1 represents the fraction \(\frac{2}{4}\).
Figure 2 represents the fraction \(\frac{4}{8}\).
Since figure 2 is more shaded than figure 1 so \(\frac{6}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{8}\).
d. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ________________ \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{4}\) > \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 4 is less than 8.
So \(\frac{1}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{8}\).
e. \(\frac{2}{4}\) ________________ \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{4}\) > \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 4 is less than 8.
So \(\frac{2}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{8}\).
Question 3.
CHALLENGE Use what you know about fractions to complete each equation by writing <, >, or =.
a. \(\frac{1}{8}\) ________________ \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{8}\) > \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Explanation:
Since the numerators are same we need to check the denominators.
Since 8 is less than 16.
So \(\frac{1}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{16}\).
b. \(\frac{3}{16}\) ________________ \(\frac{5}{16}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{16}\) < \(\frac{5}{16}\)
Explanation:
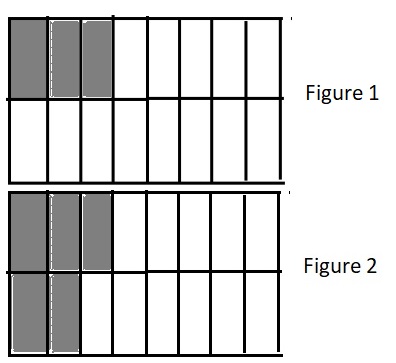
Figure 1 represents the fraction \(\frac{3}{16}\).
Figure 2 represents the fraction \(\frac{5}{16}\).
Since figure 2 is more shaded than figure 1 so \(\frac{5}{16}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{16}\).
c. \(\frac{2}{4}\) ________________ \(\frac{8}{16}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{8}{16}\)
Explanation:
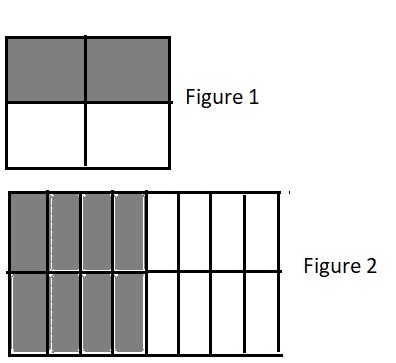
Figure 1 represents the fraction \(\frac{2}{4}\).
Figure 2 represents the fraction \(\frac{8}{16}\).
Since figure 2 is more shaded than figure 1 so \(\frac{8}{16}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{4}\).
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Unit 6 Module 4 Session 3 Answer Key
Geoboard Quilt Blocks
1. Build each quilt block design on your geoboard.
2. Write as many equivalent fractions as you can that describe how much area of the geoboard is shaded in each quilt block. Remember that the geoboard is 1 whole unit.
3. Then design your own quilt blocks on your geoboard and record your designs.
4. Write equivalent fractions for the shaded areas on your quilt block designs.
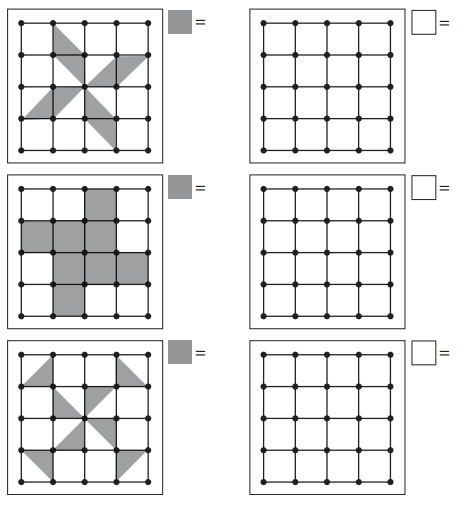
Answer:

Answer:
The fractions are:
1) \(\frac{4}{16}\), Equivalent fractions are: \(\frac{8}{32}\), \(\frac{12}{48}\)
2) \(\frac{8}{16}\), Equivalent fractions are: \(\frac{16}{32}\), \(\frac{24}{48}\)
3) \(\frac{4}{16}\), Equivalent fractions are: \(\frac{8}{32}\), \(\frac{12}{48}\)
Explanation:
The fractions are written by using the shaded portions and the total number of portions,
The fraction is written as \(\frac{Number of Shaded portions }{Total number of fractions}\),
The fractions are 1) \(\frac{4}{16}\) 2) \(\frac{8}{16}\) 3) \(\frac{4}{16}\),
Equivalent fractions:
1) \(\frac{4}{16}\) × \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{8}{32}\),
\(\frac{4}{16}\) × \(\frac{3}{3}\) = \(\frac{12}{48}\),
2) \(\frac{8}{16}\) × \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{16}{32}\),
\(\frac{8}{16}\) × \(\frac{3}{3}\) = \(\frac{24}{48}\),
3) \(\frac{4}{16}\) × \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{8}{32}\),
\(\frac{4}{16}\) × \(\frac{3}{3}\) = \(\frac{12}{48}\),
Patchwork Fractions
Question 1.
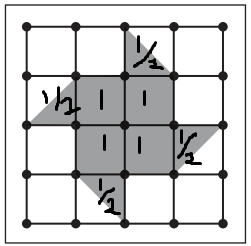
Circle all the fractions that describe the shaded part of each geoboard patchwork quilt block, if the geoboard is 1 whole unit.
a.
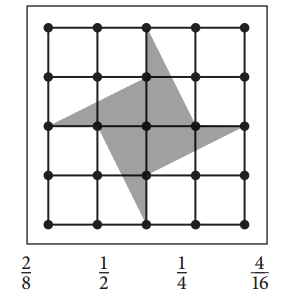
Answer:
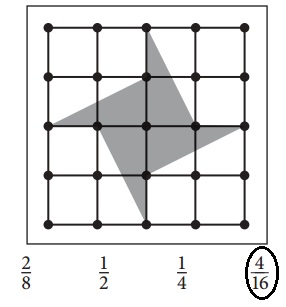
Explanation:
\(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4
Total number of squares = 16
Number of squares that are shaded = 4
Fraction = \(\frac{4}{16}\).
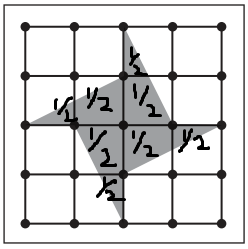
b.
Answer:
Explanation:
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6
Total number of squares = 16
Number of squares that are shaded = 6
Fraction = \(\frac{6}{16}\).
Question 2.
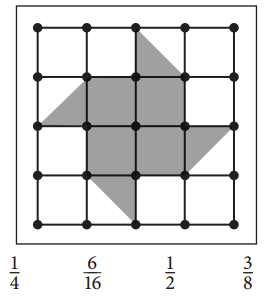
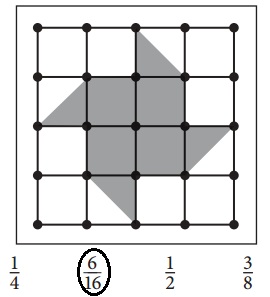
Choose two fractions that you marked in part a above, and explain why they are equivalent.
Answer:
The above equations are equivalent.
Explanation:
\(\frac{2}{8}\) × \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{16}\)
\(\frac{3}{8}\) × \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{6}{16}\).
Question 3.
Fill in the bubble next to the equation that will help you solve each word problem. Then solve the problem. Show all your work.
a. Rosa wants to buy a T-shirt for each of her 4 cousins. The T-shirts cost $12 each.
![]() 4 + 12 = d
4 + 12 = d
![]() 4 × 12 = d
4 × 12 = d
![]() 12 – 4 = d
12 – 4 = d
![]() 12 ÷ 4 = d
12 ÷ 4 = d
Rosa will spend $ _____________ on T-shirts for her cousins.
Answer:
Rosa will spend $48 on T-shirts for her cousins.
Explanation:
Number of cousins Rosa have = 4
Cost of each T-shirt = 12
Cost of 4 T-shirts = 4 × 12 = 48
b. Marco has some boxes of cookies. Each box has 6 cookies. There are 24 cookies in all. How many boxes of cookies does Marco have?
![]() 6 + 24 = b
6 + 24 = b
![]() 6 × 24 = b
6 × 24 = b
![]() 24 – 6 = b
24 – 6 = b
![]() 24 ÷ 6 = b
24 ÷ 6 = b
Marco has ______________ boxes of cookies.
Answer:
Marco has 4 boxes of cookies.
Explanation:
Number of cookies in each box = 6
Total number of cookies = 24
Number of needed = 24 ÷ 6 =4
Bridges in Mathematics Grade 3 Student Book Unit 6 Module 4 Session 4 Answer Key
The 18¢ Problem
Question 1.
What are all the different ways you can make 184 with pennies, nickels, and dimes?
a. Choose the strategy you will use to solve this problem.
![]() Draw a picture
Draw a picture
![]() Guess and check
Guess and check
![]() Make an organized list
Make an organized list
Answer:
Make an organized list,
Explanation:
When different pennies, nickels and dimes are given we can find the total amount by organizing the coins in different groups and then add the values, hence we can find the value.
b. Why does this strategy make the most sense to you?
Answer:
Yes, the method of organized list can make more sense,
Explanation:
We can segregate the coins as pennies, nickels and dimes and then add the values of each group to figure out the total amount.
c. Solve the problem with the strategy you picked. Show all your work.
Answer:
The value of the given coins is 16 cents,
Explanation:
There are 3 coins given consisting of pennies, nickels and dimes
The value of 1 penny = 1 cent,
The value of 1 nickel = 5 cents,
The value of 1 dime = 10 cents,
Total value of the coins given = The value of 1 penny + The value of 1 nickel + The value of 1 dime = 1 + 5 + 10 = 16 cents.