Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 9 Right Triangles and Trigonometry
Right Triangles and Trigonometry Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Simplify the expression.
Question 1.
√75
Answer:
square root of 75 = 5,625.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
√75.
square root of 75 = 75 x 75.
75 x 75 = 5,625.
√75 = 5,625.
Question 2.
√270
Answer:
square root of 270 = 72,900.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
√270.
square root of 270 = 270 x 270.
270 x 270 = 72900.
√270 = 72900.
Question 3.
√135
Answer:
square root of 135 = 18225.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
√135.
square root of 135 = 135 x 135.
135 x 135 = 18225.
√135 = 18,225.
Question 4.
\(\frac{2}{\sqrt{7}}\)
Answer:
2/49 = 0.04.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
square root of 7 = 7 x 7.
7 x 7 = 49.
\(\frac{2}{\sqrt{7}}\).
2/49 = 0.04.
Question 5.
\(\frac{5}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Answer:
5/4 = 1.25.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
square root of 2 = 2 x 2.
2 x 2 = 4.
\(\frac{5}{\sqrt{2}}\).
5/4 = 1.25.
Question 6.
\(\frac{12}{\sqrt{6}}\)
Answer:
12/36 = 0.33.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
square root of 6 = 6 x 6.
6 x 6 = 36.
\(\frac{12}{\sqrt{6}}\).
12/36 = 0.33.
Solve the proportion.
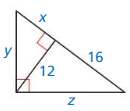
Question 7.
\(\frac{x}{12}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
x = 9.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{x}{12}=\frac{3}{4}\)
x/12 = 3/4.
4x = 12 x 3.
4x = 36.
x = 36/4.
x = 9.
Question 8.
\(\frac{x}{3}=\frac{5}{2}\)
Answer:
x = 7.5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{x}{3}=\frac{5}{2}\)
x/3 = 5/2.
2x = 5 x 3.
2x = 15.
x = 15/2.
x = 7.5.
Question 9.
\(\frac{4}{x}=\frac{7}{56}\)
Answer:
x = 32.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{4}{x}=\frac{7}{56}\)
4/x = 7/56.
7x = 56 x 4.
7x = 224.
x = 224/7.
x = 32.
Question 10.
\(\frac{10}{23}=\frac{4}{x}\)
Answer:
x = 9.2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{10}{23}=\frac{4}{x}\)
x/4 = 10/23.
10x = 23 x 4.
10x = 92.
x = 92/10.
x = 9.2.
Question 11.
\(\frac{x+1}{2}=\frac{21}{14}\)
Answer:
x = 135.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{x + 1}{2}=\frac{21}{14}\)
x+12 x 2 = 21×14.
2x + 24= 294 .
2x = 294 – 24.
2x = 270.
x = 270/2.
x = 135.
Question 12.
\(\frac{9}{3 x-15}=\frac{3}{12}\)
Answer:
x = 6.33.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{9}{3 x-15}=\frac{3}{12}\)
27x – 135 = 3×12.
27x = 36 + 135.
27x = 171.
x = 171/27.
x = 6.33.
Question 13.
ABSTRACT REASONING
The Product Property of Square Roots allows you to simplify the square root of a product. Are you able to simplify the square root of a sum? of a diffrence? Explain.
Answer:
Yes, I am able to simplify the square root of a sum.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
The product property of square roots allows you to simplify the square root of a product.
√3 + 1 = √4.
√4 = 4 x 4.
16.
√3 – 1 = √2.
√2 = 2 x 2.
4.
Right Triangles and Trigonometry Mathematical practices
Monitoring progress
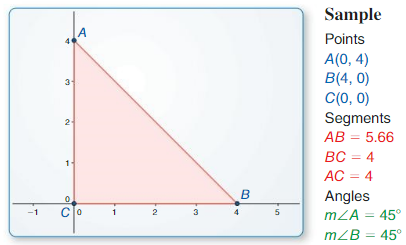
Question 1.
Use dynamic geometry software to construct a right triangle with acute angle measures of 30° and 60° in standard position. What are the exact coordinates of its vertices?
Answer:
The sum of all angles of a triangle = 180°
If one 30° and another is 90°
180° – 120° = 60°
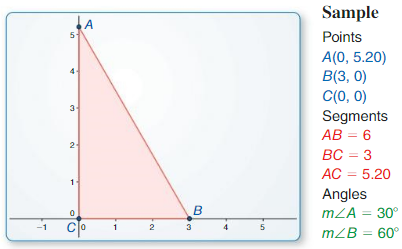
Question 2.
Use dynamic geometry software to construct a right triangle with acute angle measures of 20° and 70° in standard position. What are the approximate coordinates of its vertices?
Answer:
Given,
Use dynamic geometry software to construct a right triangle with acute angle measures of 20° and 70° in standard position.
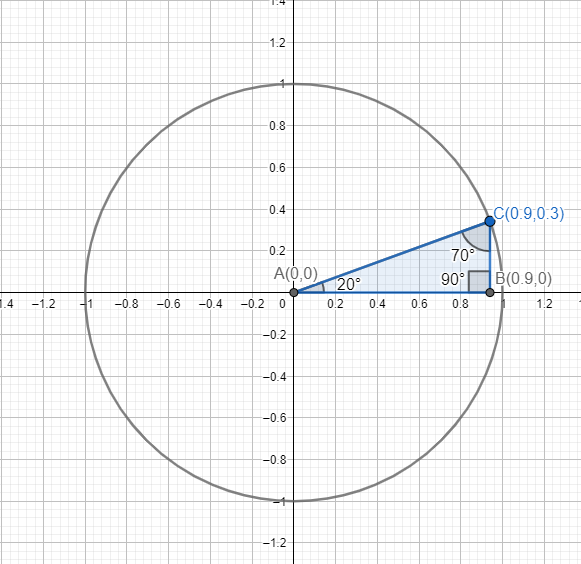
The vertices are A(0,0), B(0.9,0) and C(0.9, 0.3)
9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Exploration 1
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem without Words
Work with a partner.
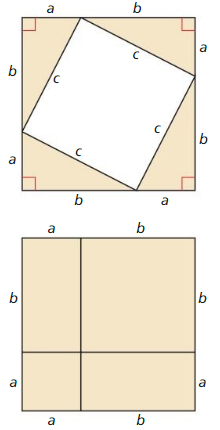
a. Draw and cut out a right triangle with legs a and b, and hypotenuse c.
Answer:
In the above-given question,
given that,
proving the Pythagorean theorem without words.
a2 + b2 = c2.
b. Make three copies of your right triangle. Arrange all tour triangles to form a large square, as shown.
Answer:
a2 + b2 = c2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
make three copies of your right triangle.
a2 + b2 = c2.
c. Find the area of the large square in terms of a, b, and c by summing the areas of the triangles and the small square.
Answer:
The area of the large square = a2 x b2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the area of the square = l x b.
where l = length, and b = breadth.
the area of the square = a x b.
area = a2 x b2.
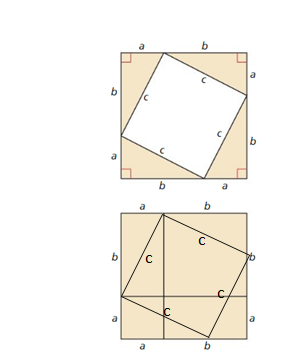
d. Copy the large square. Divide it into two smaller squares and two equally-sized rectangles, as shown.
Answer:
Divide the square into two equally-sized rectangles with dimensions a and b, a square of dimension a and another square of dimension b as follows,
The required square with two equally sized rectangles with dimensions a and b, a square of dimension a and another square of dimension b.
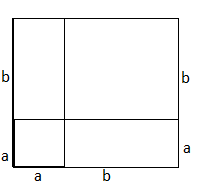
e. Find the area of the large square in terms of a and b by summing the areas of the rectangles and the smaller squares.
Answer:

The area of large square in terms of the dimensions of small squares and rectangles is a² + b² + 2ab
f. Compare your answers to parts (c) and (e). Explain how this proves the Pythagorean Theorem.
Answer:
a2 + b2 = c2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
The length of the a and b is equal to the hypotenuse.
a2 + b2 = c2.
where a = one side and b = one side.
Exploration 2
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
Work with a partner:
a. Draw a right triangle with legs a and b, and hypotenuse c, as shown. Draw the altitude from C to \(\overline{A B}\) Label the lengths, as shown.
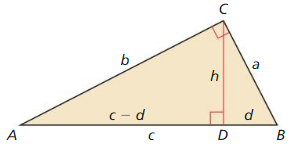
Answer:
a2 + b2 = c2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
a2 + b2 = c2.
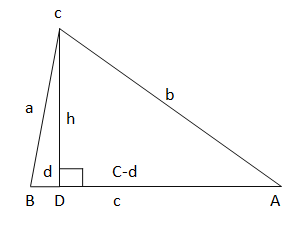
b. Explain why ∆ABC, ∆ACD, and ∆CBD are similar.
Answer:
In a right-angle triangle all the angle are equal.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
∆ABC, ∆ACD, and ∆CBD are similar.
In a right-angle triangle all the angles are equal.
REASONING ABSTRACTLY
To be proficient in math, you need to know and flexibly use different properties of operations and objects.
c. Write a two-column proof using the similar triangles in part (b) to prove that a2 + b2 = c2
Answer:
a2 + b2 = c2
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
In the pythagorean theorem.
a2 + b2 = c2
the length of the hypotenuse ie equal to the two side lengths.
a2 + b2 = c2
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you prove the Pythagorean Theorem?
Answer:
a2 + b2 = c2
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
In the pythagorean theorem,
the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the length of the other two sides.
hypotenuse = c.
length = a.
the breadth = b.
a2 + b2 = c2
Question 4.
Use the Internet or sonic other resource to find a way to prove the Pythagorean Theorem that is different from Explorations 1 and 2.
Answer:
Lesson 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Monitoring Progress
Find the value of x. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Question 1.
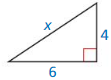
Answer:
x = √52.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 6 and 4.
a2 + b2 = c2
6 x 6 + 4 x 4 = c2
36 + 16 = c2
52 = c2.
c = √52.
Question 2.
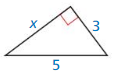
Answer:
x = 4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 3 and 5.
x2 + 3 x 3 = 5 x 5.
x2 + 9 = 25.
x2 = 25 – 9.
x2 = 16.
x = 4.
Question 3.
An anemometer is a device used to measure wind speed. The anemometer shown is attached to the top of a pole. Support wires are attached to the pole 5 feet above the ground. Each support wire is 6 feet long. How far from the base of the pole is each wire attached to the ground?
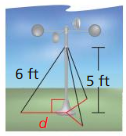
Answer:
x = √11.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
An anemometer is a device used to measure wind speed.
support wires are attached to the pole 5 feet above the ground.
Each support wire is 6 feet long.
d2 + 6 x 6 = 5 x 5.
d2 + 36 = 25.
d2 = 25 – 36.
d2 = 11.
d = √11.
Tell whether the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 4.
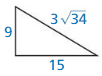
Answer:
Yes the triangle is a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the hypotenuse = 3 √34.
one side = 15.
the other side = 9.
so the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 5.
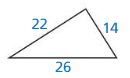
Answer:
Yes, the triangle is a actute triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the hypotenuse = 22.
one side = 26.
the other side = 14.
so the triangle is a acute triangle.
Question 6.
Verify that segments with lengths of 3, 4, and 6 form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
Answer:
Yes the lengths of the triangle form a acute triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lenths of 3, 4, and 6 form a triangle.
6 x 6 = 3 x 3 + 4 x 4.
36 = 9 + 16.
36 = 25.
so the length of the triangle forms a acute triangle.
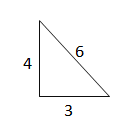
Question 7.
Verify that segments with lengths of 2.1, 2.8, and 3.5 form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
Answer:
2.1 + 2.8 > 3.5
4.9 > 3.5 > 2.8
5.6 > 2.8 > 2.1
6.3 > 2.1
Since every inequality is true, the segments with lengths 2.1, 2.8 and 3.5 form a triangle.
Exercise 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
What is a Pythagorean triple?
Answer:
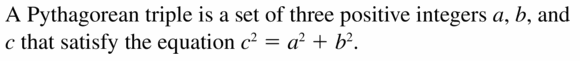
Question 2.
DIFFERENT WORDS, SAME QUESTION
Which is different? Find “both” answers.
Find the length of the longest side.
Answer:
The length of the longest side = 5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 3 and 4.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 4 x 4 + 3 x 3.
X x X = 16 + 9.
X x X = 25.
X = 5.
Find the length of the hypotenuse
Answer:
The length of the hypotenuse = 5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 3 and 4.
in the Pythagorean theorem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 4 x 4 + 3 x 3.
X x X = 16 + 9.
X x X = 25.
X = 5.
Find the length of the longest leg.
Answer:
The length of the longest leg = 5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 3 and 4.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 4 x 4 + 3 x 3.
X x X = 16 + 9.
X x X = 25.
X = 5.
Find the length of the side opposite the right angle.
Answer:
The length of the side opposite to the right angle = 5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 3 and 4.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 4 x 4 + 3 x 3.
X x X = 16 + 9.
X x X = 25.
X = 5.
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3-6, find the value of x. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
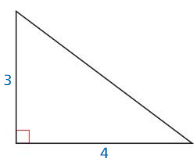
Question 3.
Answer:

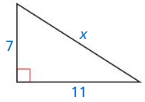
Question 4.
Answer:
The length of the x = 34.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 30 and 16.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 16 x 16 + 30 x 30.
X x X = 256 + 900.
X x X = 1156.
X = 34.
Question 5.
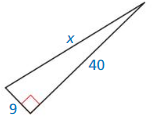
Answer:

Question 6.
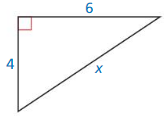
Answer:
The length of the x = 7.2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 6 and 4.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 4 x 4 + 6 x 6.
X x X = 16 + 36.
X x X = 52.
X = 7.2.
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the value of x. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Question 7.
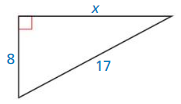
Answer:

Question 8.
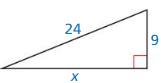
Answer:
The length of the X = 25.6.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 24 and 9.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 24 x 24 + 9 x 9.
X x X = 576 + 81.
X x X = 657.
X = 25.6.
Question 9.
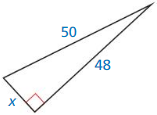
Answer:

Question 10.
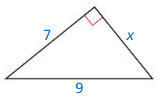
Answer:
The length of the x = 11.4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 7 and 9.
in the pythagorean threoem,
the longest side is equal to the side lengths.
X = 7 x 7 + 9 x 9.
X x X = 49 + 81.
X x X = 130.
X = 11.4.
ERROR ANALYSIS
In Exercises 11 and 12, describe and correct the error in using the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.1).
Question 11.
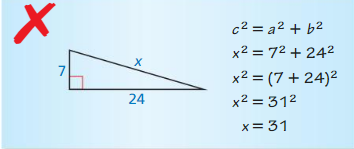
Answer:

Question 12.
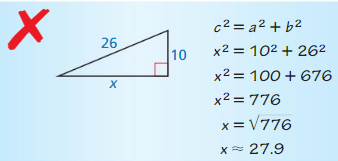
Answer:
x = 24.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 26 and 10.
26 x 26 = a x a + 10 x 10.
676 = a x a + 100.
676 – 100 = a x a.
576 = a x a.
a = 24.
x = 24.
Question 13.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The fire escape forms a right triangle, as shown. Use the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9. 1) to approximate the distance between the two platforms. (See Example 3.)
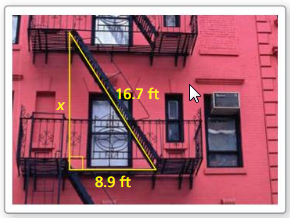
Answer:
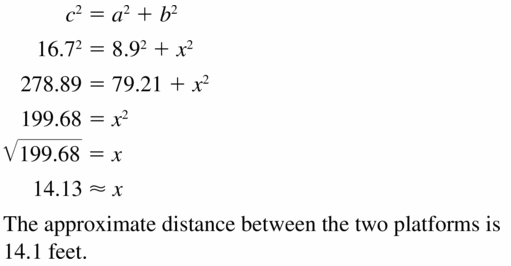
Question 14.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The backboard of the basketball hoop forms a right triangle with the supporting rods, as shown. Use the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.1) to approximate the distance between the rods where the meet the backboard.
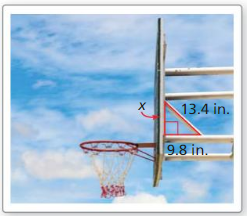
Answer:
x = 9.1.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 13.4 and 9.8.
13.4 x 13.4 = X x X + 9.8 x 9.8.
179.56 = X x X + 96.04.
179.56 – 96.04 = X x X.
83.52 = X x X.
X = 9.1.
In Exercises 15 – 20, tell whether the triangle is a right triangle.
Question 15.
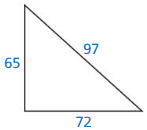
Answer:
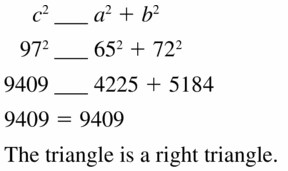
Question 16.
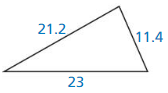
Answer:
No, the triangle is not a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 23 and 11.4.
the hypotenuse = 21.2.
21.2 x 21.2 = 23 x 23 + 11.4 x 11.4.
449.44 = 529 + 129.96.
449.44 = 658.96.
449 is not equal to 658.96.
so the triangle is not a right triangle.
Question 17.
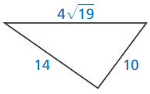
Answer:
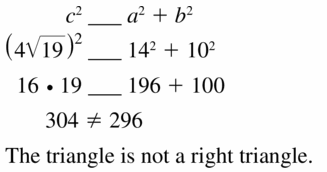
Question 18.
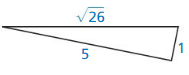
Answer:
No, the triangle is not a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 5 and 1.
the hypotenuse = √26.
26 x 26 = 5 x 5 + 1 x 1.
676 = 25 + 1.
676 = 26.
676 is not equal to 26.
so the triangle is not a right triangle.
Question 19.
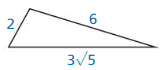
Answer:
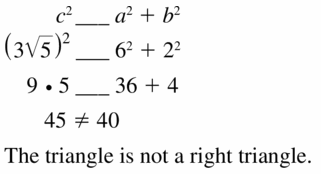
Question 20.
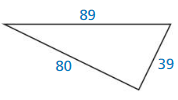
Answer:
Yes, the triangle forms a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 80 and 39.
the hypotenuse = 89.
89 x 89 = 80 x 80 + 39 x 39.
7921 = 6400 + 1521.
7921 = 7921.
7921 is equal to 7921.
so the triangle forms a right triangle.
In Exercises 21 – 28, verify that the segment lengths form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
Question 21.
10, 11, and 14
Answer:

Question 22.
6, 8, and 10
Answer:
Yes, the triangle is forming a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 8 and 6.
the hypotenuse = 10.
10 x 10 = 8 x 8 + 6 x 6.
100 = 64 + 36.
100 = 100.
100 is equal to 100.
so the triangle is forming a right triangle.
Question 23.
12, 16, and 20
Answer:

Question 24.
15, 20, and 36
Answer:
Yes, the triangle is obtuse triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 15 and 20.
the hypotenuse = 36.
36 x 36 = 20 x 20 + 15 x 15.
1296 = 400 + 225.
1296 > 625.
1296 is greater than 625.
so the triangle is not a obtuse triangle.
Question 25.
5.3, 6.7, and 7.8
Answer:

Question 26.
4.1, 8.2, and 12.2
Answer:
No, the triangle is obtuse triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 4.1 and 8.2.
the hypotenuse = 12.2.
12.2 x 12.2 = 4.1 x 4.1 + 8.2 x 8.2`.
148.84 = 16.81 + 67.24.
148.84 > 84.05.
148.84 is greater than 84.05.
so the triangle is obtuse triangle.
Question 27.
24, 30, and 6√43
Answer:
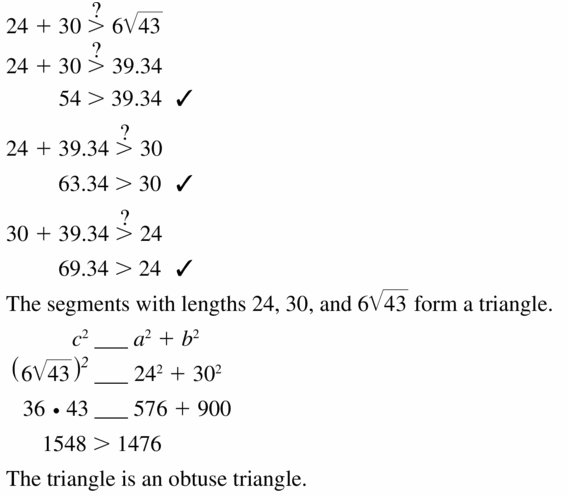
Question 28.
10, 15 and 5√13
Answer:
Yes, the triangle is an acute triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 10 and 5√13.
the hypotenuse = 15.
15 x 15 = 10 x 10 + 5√13 x 5√13.
225 = 100 + 34.81.
225 < 134.81.
225 is less than 134.81.
so the triangle is acute triangle.
Question 29.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
In baseball, the lengths of the paths between consecutive bases are 90 feet, and the paths form right angles. The player on first base tries to steal second base. How far does the ball need to travel from home plate to second base to get the player out?
Answer:

Question 30.
REASONING
You are making a canvas frame for a painting using stretcher bars. The rectangular painting will be 10 inches long and 8 inches wide. Using a ruler, how can you be certain that the corners of the frame are 90°

Answer:
x = 12.8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 10 and 8.
the hypotenuse = x.
X x X = 10 x 10 + 8 x 8.
X = 100 + 64.
X = 12.8.
In Exercises 31 – 34, find the area of the isosceles triangle.
Question 31.
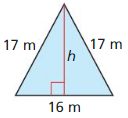
Answer:
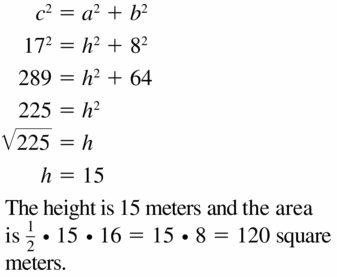
Question 32.
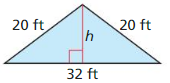
Answer:
The area of the Isosceles triangle = 12 ft.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
base = 32 ft.
hypotenuse = 20ft.
a2 + b2 = c2
h x h + 16 x 16 = 20 x 20.
h x h + 256 = 400.
h x h = 400 – 256.
h x h = 144.
h = 12 ft.
so the area of the isosceles triangle = 12 ft.
Question 33.
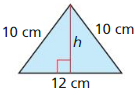
Answer:

Question 34.
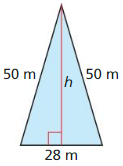
Answer:
The area of the Isosceles triangle = 48 m.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
base = 28 m.
hypotenuse = 50 m.
a2 + b2 = c2
h x h + 14 x 14 = 50 x 50.
h x h + 196 = 2500.
h x h = 2500 – 196.
h x h = 2304.
h = 48 m.
so the area of the isosceles triangle = 48 m.
Question 35.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
Justify the Distance Formula using the Pythagorean Theorem (Thin. 9. 1).
Answer:

Question 36.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
How do you know ∠C is a right angle without using the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.1) ?
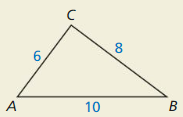
Answer:
Yes, the triangle is forming a right triangle.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
the side lengths are 8 and 6.
the hypotenuse = 10.
10 x 10 = 8 x 8 + 6 x 6.
100 = 64 + 36.
100 = 100.
100 is equal to 100.
so the triangle is forming a right triangle.
Question 37.
PROBLEM SOLVING
You are making a kite and need to figure out how much binding to buy. You need the binding for the perimeter of the kite. The binding Comes in packages of two yards. How many packages should you buy?
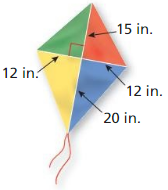
Answer:

Question 38.
PROVING A THEOREM
Use the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9. 1) to prove the Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Congruence Theorem (Theorem 5.9).
Answer:
Question 39.
PROVING A THEOREM
Prove the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.2). (Hint: Draw ∆ABC with side lengths a, b, and c, where c is the length of the longest side. Then draw a right triangle with side lengths a, b, and x, where x is the length of the hypotenuse. Compare lengths c and x.)
Answer:
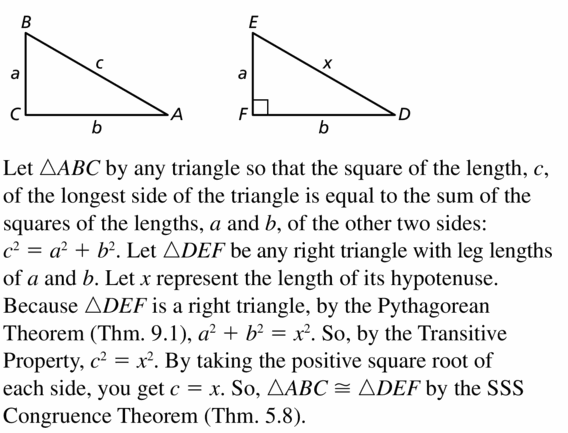
Question 40.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Consider two integers m and n. where m > n. Do the following expressions produce a Pythagorean triple? If yes, prove your answer. If no, give a counterexample.
2mn, m2 – n2, m2 + n2
Answer:
Question 41.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims 72 and 75 Cannot be part of a pythagorean triple because 722 + 752 does not equal a positive integer squared. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
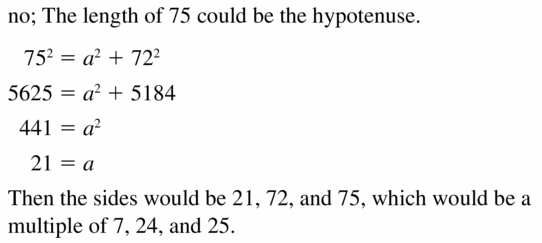
Question 42.
PROVING A THEOREM
Copy and complete the proof of the pythagorean Inequalities Theorem (Theorem 9.3) when c2 < a2 + b2.
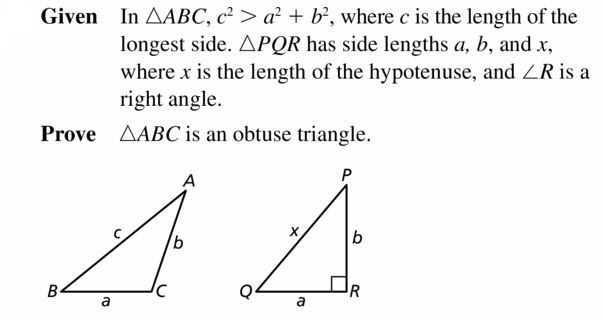
Given In ∆ABC, c2 < a2 + b2 where c is the length
of the longest side.
∆PQR has side lengths a, b, and x, where x is the length of the hypotenuse, and ∠R is a right angle.
Prove ∆ABC is an acute triangle.
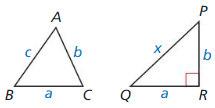
| Statements | Reasons |
| 1. In ∆ABC, C2 < (12 + h2, where c is the length of the longest side. ∆PQR has side lengths a, b, and x, where x is the length of the hypotenuse, and ∠R is a right angle. | 1. _____________________________ |
| 2. a2 + b2 = x2 | 2. _____________________________ |
| 3. c2 < r2 | 3. _____________________________ |
| 4. c < x | 4. Take the positive square root of each side. |
| 5. m ∠ R = 90° | 5. _____________________________ |
| 6. m ∠ C < m ∠ R | 6. Converse of the Hinge Theorem (Theorem 6.13) |
| 7. m ∠ C < 90° | 7. _____________________________ |
| 8. ∠C is an acute angle. | 8. _____________________________ |
| 9. ∆ABC is an acute triangle. | 9. _____________________________ |
Answer:
Question 43.
PROVING A THEOREM
Prove the Pythagorean Inequalities Theorem (Theorem 9.3) when c2 > a2 + b2. (Hint: Look back at Exercise 42.)
Answer:
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Simplify the expression by rationalizing the denominator.
Question 44.
\(\frac{7}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Answer:
7/√2 = 7√2 /2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{7}{\sqrt{2}}\) = 7/√2.
7/√2 = 7/√2 x √2 /√2 .
7 √2 /√4.
7√2 /2.
Question 45.
\(\frac{14}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Answer:
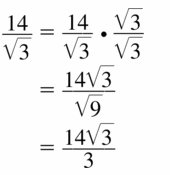
Question 46.
\(\frac{8}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Answer:
8/√2 = 8√2 /2.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
\(\frac{8}{\sqrt{2}}\) = 8/√2.
8/√2 = 8/√2 x √2 /√2 .
8 √2 /√4.
8√2 /2.
Question 47.
\(\frac{12}{\sqrt{3}}\)
Answer:
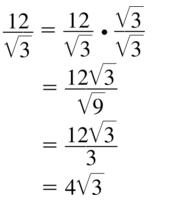
9.2 Special Right Triangles
Exploration 1
Side Ratios of an Isosceles Right Triangle
Work with a partner:
a. Use dynamic geometry software to construct an isosceles right triangle with a leg length of 4 units.
Answer:
b. Find the acute angle measures. Explain why this triangle is called a 45° – 45° – 90° triangle.
Answer:
c. Find the exact ratios of the side lenghts (using square roots).
\(\frac{A B}{A C}\) = ____________
\(\frac{A B}{B C}\) = ____________
\(\frac{A B}{B C}\) = ____________
ATTENDING TO PRECISION
To be proficient in math, you need to express numerical answers with a degree of precision appropriate for the problem context.
Answer:
d. Repeat parts (a) and (c) for several other isosceles right triangles. Use your results to write a conjecture about the ratios of the side lengths of an isosceles right triangle.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Work with a partner.
a. Use dynamic geometry software to construct a right triangle with acute angle measures of 30° and 60° (a 30° – 60° – 90° triangle), where the shorter leg length is 3 units.
b. Find the exact ratios of the side lengths (using square roots).
\(\frac{A B}{A C}\) = ____________
\(\frac{A B}{B C}\) = ____________
\(\frac{A B}{B C}\) = ____________
Answer:
C. Repeat parts (a) and (b) for several other 30° – 60° – 90° triangles. Use your results to write a conjecture about the ratios of the side lengths of a 30° – 60° – 90° triangle.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
What is the relationship among the side lengths of 45°- 45° – 90° triangles? 30° – 60° – 90° triangles?
Answer:
One of the triangles is named 45, 45, and 90 triangles. The triangle angles are 45 degrees, 45 degrees, and 90 degrees. Then it is an isosceles right triangle.
The other triangle is the 30, 60, and 90 triangles. The triangle angles are 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees.
In both triangles, the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the legs of the triangle.
Lesson 9.2 Special Right Triangles
Monitoring Progress
Find the value of the variable. Write your answer in simplest form.
Question 1.
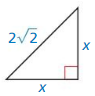
Answer:
x = 4
Explanation:
(2√2)² = x² + x²
8 = 2x²
x² = 4
x = 4
Question 2.
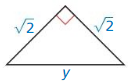
Answer:
y = 2
Explanation:
y² = 2 + 2
y² = 4
y = 2
Question 3.
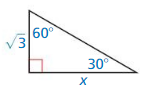
Answer:
x = 3, y = 2√3
Explanation:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
x = √3 • √3
x = 3
hypotenuse = shorter leg • 2
= √3 • 2 = 2√3
Question 4
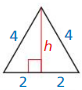
Answer:
h = 2√3
Explanation:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
h = 2√3
Question 5.
The logo on a recycling bin resembles an equilateral triangle with side lengths of 6 centimeters. Approximate the area of the logo.
Answer:
Area is \(\frac { 1 }{ 3√3 } \)
Explanation:
Area = \(\frac { √3 }{ 4 } \) a²
= \(\frac { √3 }{ 4 } \)(6)²
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3√3 } \)
Question 6.
The body of a dump truck is raised to empty a load of sand. How high is the 14-foot-long body from the frame when it is tipped upward by a 60° angle?
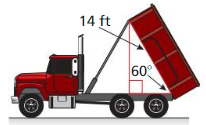
Answer:
28/3 ft high is the 14-foot-long body from the frame when it is tipped upward by a 60° angle.
Explanation:
Height of body at 90 degrees = 14 ft
Height of body at 1 degree = 14/90
Height of body at 60 degrees = 14 x 60/90
= 14 x 2/3
= 28/3 ft
Exercise 9.2 Special Right Triangles
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
Name two special right triangles by their angle measures.
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
WRITING
Explain why the acute angles in an isosceles right triangle always measure 45°.
Answer:
Because the acute angles of a right isosceles triangle must be congruent by the base angles theorem and complementary, their measures must be 90°/2 = 45°.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the value of x. Write your answer in simplest form.
Question 3.
Answer:
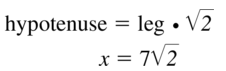
Question 4.
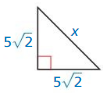
Answer:
x = 10
Explanation:
hypotenuse = leg • √2
x = 5√2 • √2
x = 10
Question 5.
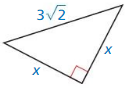
Answer:
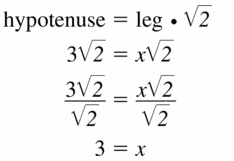
Question 6.
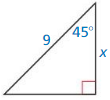
Answer:
x = \(\frac { 9 }{ √2 } \)
Explanation:
hypotenuse = leg • √2
9 = x • √2
x = \(\frac { 9 }{ √2 } \)
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the values of x and y. Write your answers in simplest form.
Question 7.
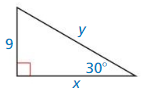
Answer:
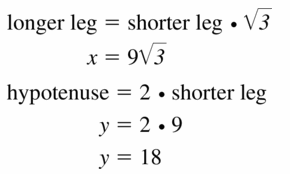
Question 8.
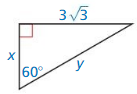
Answer:
x = 3, y = 6
Explanation:
hypotenuse = 2 • shorter leg
y = 2 • 3
y = 6
longer leg = √3 • shorter leg
3√3 = √3x
x = 3
Question 9.
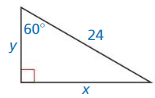
Answer:
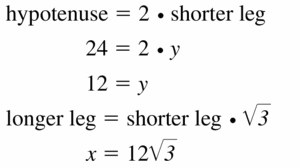
Question 10.
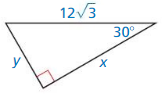
Answer:
x = 18, y = 6√3
Explanation:
hypotenuse = 2 • shorter leg
12√3 = 2y
y = 6√3
longer leg = √3 • shorter leg
x = √3 . 6√3
x = 18
ERROR ANALYSIS
In Exercises 11 and 12, describe and correct the error in finding the length of the hypotenuse.
Question 11.
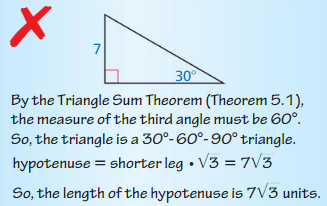
Answer:
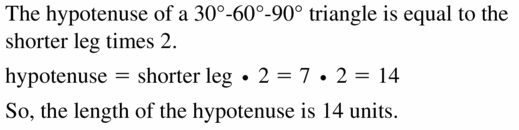
Question 12.
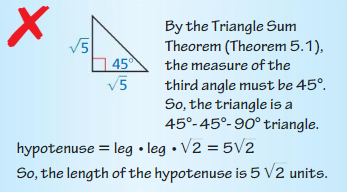
Answer:
hypotenuse = leg • √2 = √5 . √2 = √10
In Exercises 13 and 14. sketch the figure that is described. Find the indicated length. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
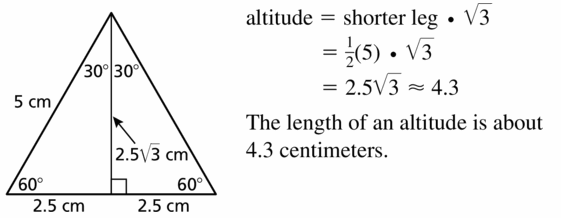
Question 13.
The side length of an equilateral triangle is 5 centimeters. Find the length of an altitude.
Answer:
Question 14.
The perimeter of a square is 36 inches. Find the length of a diagonal.
Answer:
The length of a diagonal is 9√2
Explanation:
Side of the square = 36/4 = 9
square diagonal = √2a = √2(9) = 9√2
In Exercises 15 and 16, find the area of the figure. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 15.
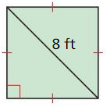
Answer:

Question 16.
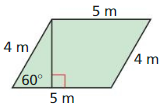
Answer:
Area is 40√(1/3) sq m
Explanation:
longer leg = √3 • shorter leg
4 = √3 • shorter leg
shorter leg = 4/√3
h² = 16/3 + 16
h² = 16(4/3)
h = 8√(1/3)
Area of the parallelogram = 5(8√(1/3)) = 40√(1/3) sq m
Question 17.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Each half of the drawbridge is about 284 feet long. How high does the drawbridge rise when x is 30°? 45°? 60°?
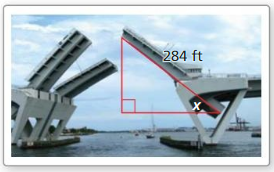
Answer:

Question 18.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A nut is shaped like a regular hexagon with side lengths of 1 centimeter. Find the value of x. (Hint: A regular hexagon can be divided into six congruent triangles.)
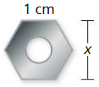
Answer:
Side length = 1cm
A regular hexagon has six equal the side length. A line drawn from the centre to any vertex will have the same length as any side.
This implies the radius is equal to the side length.
As a result, when lines are drawn from the centre to each of the vertexes, a
regular hexagon is said to be made of six equilateral triangles.
From the diagram, x = 2× apothem
Apothem is the distance from the centre of a regular polygon to the midpoint of side.
Using Pythagoras theorem, we would get the apothem
Hypotenuse² = opposite² + adjacent²
1² = apothem² + (½)²
Apothem = √(1² -(½)²)
= √(1-¼) = √¾
Apothem = ½√3
x = 2× Apothem = 2 × ½√3
x = √3
Question 19.
PROVING A THEOREM
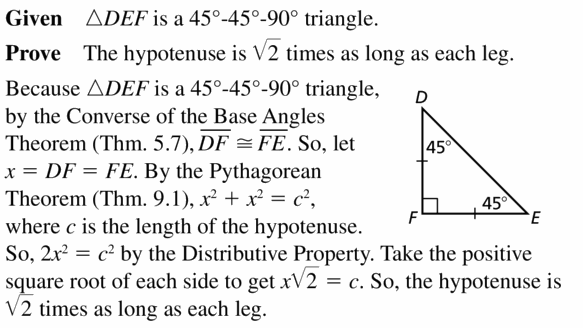
Write a paragraph proof of the 45°- 45°- 90° Triangle Theorem (Theorem 9.4).
Given ∆DEF is a 45° – 45° – 90° triangle.
Prove The hypotenuse is √2 times as long as each leg.
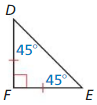
Answer:
Question 20.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
The diagram shows part of the wheel of Theodorus.
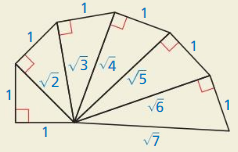
a. Which triangles, if any, are 45° – 45° – 90° triangles?
Answer:
It is required which triangles are 45° – 45° – 90° triangle.
To identify which triangles are 45° – 45° – 90° triangle.
45° – 45° – 90° triangle is an isosceles triangle with two equal sides.
The highlighted triangle is 45° – 45° – 90° triangle.
b. Which triangles, if any, are 30° – 60° – 90° triangles?
Answer:
It is required which triangles are 30° – 60° – 90° triangle.
A 30° – 60° – 90° triangle is triangle whose hypotenuse is twice as long as the shorter leg, and the longer leg is √3 times as long as the shorter leg.
In the given figure it is seen that third triangle has hypotenuse twice as long as shorter leg and longest leg √3 times the shortest leg.
The highlighted triangle is 30° – 60° – 90° triangle.
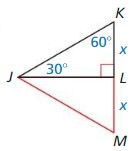
Question 21.
PROVING A THEOREM
Write a paragraph proof of the 30° – 60° – 90° Triangle Theorem (Theorem 9.5).
(Hint: Construct ∆JML congruent to ∆JKL.)
Given ∆JKL is a 30° 60° 9o° triangle.
Prove The hypotenuse is twice as long as the shorter leg, and the longer leg is √3 times as long as the shorter leg.
Answer:

Question 22.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
A special right triangle is a right triangle that has rational angle measures and each side length contains at most one square root. There are only three special right triangles. The diagram below is called the Ailles rectangle. Label the sides and angles in the diagram. Describe all three special right triangles.
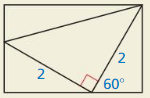
Answer:
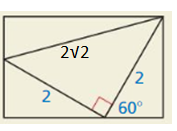
Question 23.
WRITING
Describe two ways to show that all isosceles right triangles are similar to each other.
Answer:

Question 24.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Each triangle in the diagram is a 45° – 45° – 90° triangle. At Stage 0, the legs of the triangle are each 1 unit long. Your brother claims the lengths of the legs of the triangles added are halved at each stage. So, the length of a leg of a triangle added in Stage 8 will be \(\frac{1}{256}\) unit. Is your brother correct? Explain your reasoning.
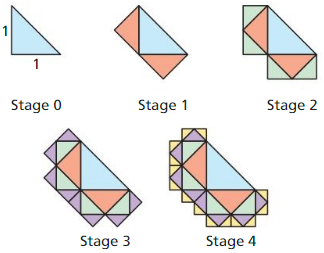
Answer:
Given,
Each triangle in the diagram is a 45° – 45° – 90° triangle. At Stage 0, the legs of the triangle are each 1 unit long. Your brother claims the lengths of the legs of the triangles added are halved at each stage. So, the length of a leg of a triangle added in Stage 8 will be \(\frac{1}{256}\) unit.
At stage 0: The side lengths of an isosceles right triangle are always the quotient of the hypotenuse of the given isosceles right triangle and the constant √2.
Stage 1: This implies that the right isosceles triangle of Stage 0 will have side lengths of 1 unit. These will be the hypotenuses of the triangles formed in stage 1 and so the side lengths of the right isosceles triangles formed in stage 1 will be
1/ √2 = √2/2 units.
Stage 2: This implies that the right isosceles triangle of Stage 1 will have side lengths of √2/2 unit. These will be the hypotenuses of the triangles formed in stage 2 and so the side lengths of the right isosceles triangles formed in stage 2 will be √2/2⋅√2 =1/2 units.
From the results of stage 1 and 2, it can be seen that the side lengths of the right isosceles triangles formed is decreasing by a factor of 1/√2 times the stage number, therefore, it can be said that this is a geometric series and so the side lengths of the right triangles formed in stage 8
is 1/(√2)^8 =1/16 units.
Therefore the brother’s claim is incorrect.
Question 25.
USING STRUCTURE
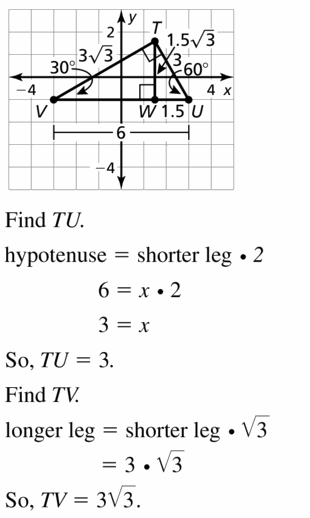
ΔTUV is a 30° – 60° – 90° triangle. where two vertices are U(3, – 1) and V( – 3, – 1), \(\overline{U V}\) is the hypotenuse. and point T is in Quadrant I. Find the coordinates of T.
Answer:

Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the Value of x.
Question 26.
ΔDEF ~ ΔLMN
Answer:
x = 18
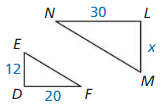
Explanation:
\(\frac { DE }{ LM } \) = \(\frac { DF }{ LN } \)
\(\frac { 12 }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 20 }{ 30 } \)
\(\frac { 12 }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)
x = 12(\(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)) = 18
Question 27.
ΔABC ~ ΔQRS
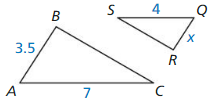
Answer:
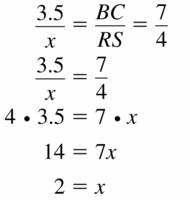
9.3 Similar Right Triangles
Exploration 1
Writing a Conjecture
a. Use dynamic geometry software to construct right ∆ABC, as shown. Draw \(\overline{C D}\) so that it is an altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse of ∆ABC.
Answer:
b. The geometric mean of two positive numbers a and b is the positive number x that satisfies
\(\frac{a}{x}=\frac{x}{b}\)
x is the geometric mean of a and b.
Write a proportion involving the side lengths of ∆CBD and ∆ACD so that CD is the geometric mean of two of the other side lengths. Use similar triangles to justify your steps.
Answer:
c. Use the proportion you wrote in part (b) to find CD.
Answer:
d. Generalize the proportion you wrote in part (b). Then write a conjecture about how the geometric mean is related to the altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS
To be proficient in math, you need to understand and use stated assumptions, definitions, and previously established results in constructing arguments.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Comparing Geometric and Arithmetic Means
Work with a partner:
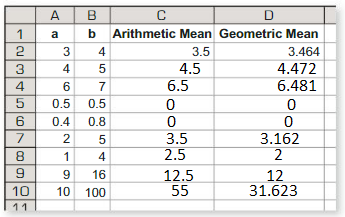
Use a spreadsheet to find the arithmetic mean and the geometric mean of several pairs of positive numbers. Compare the two means. What do you notice?
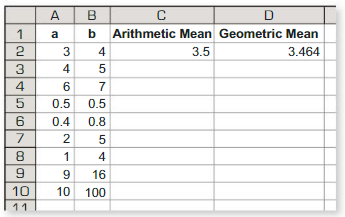
Answer:
The formula for the arithmetic means = sum of the observations/Total number of observations.
The formula for the Geometric mean = square root of (ab)
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
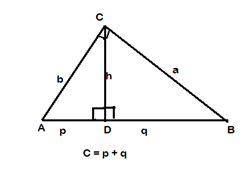
How are altitudes and geometric means of right triangles related?
Answer:
The right triangle altitude theorem or geometric mean theorem is an elementary geometry that relates the altitude on the hypotenuse in a right triangle and the two-line segments. It states that the geometric mean of the segments equals the altitude.
Lesson 9.3 Similar Right Triangles
Monitoring progress
Identify the similar triangles.
Question 1.
Answer:
△QRS ~ △ QST
Question 2.
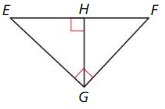
Answer:
△EFG ~ △ EHG
Question 3.
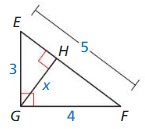
Answer:
△EGH ~ △EFG
\(\frac { EF }{ EG } \) = \(\frac { GF }{ GH } \)
\(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ x } \)
x = 2.4
Question 4.
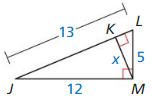
Answer:
△JLM ~ △LMK
\(\frac { JL }{ LM } \) = \(\frac { JM }{ KM } \)
\(\frac { 13 }{ 5 } \) = \(\frac { 12 }{ x } \)
x = 4.615
Find the geometric mean of the two numbers.
Question 5.
12 and 27
Answer:
x = √(12 x 27)
x = √324 = 18
Question 6.
18 and 54
Answer:
x = √(18 x 54) = √(972)
x = 31.17
Question 7.
16 and 18
Answer:
x = √(16 x 18) = √(288)
x = 16.970
Question 8.
Find the value of x in the triangle at the left.
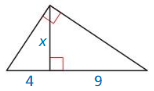
Answer:
x = √(9 x 4)
x = 6
Question 9.
WHAT IF?
In Example 5, the vertical distance from the ground to your eye is 5.5 feet and the distance from you to the gym wall is 9 feet. Approximate the height of the gym wall.
Answer:
9² = 5.5 x w
81 = 5.5 x w
w = 14.72
The height of the wall = 14.72 + 5.5 = 20.22
Exercise 9.3 Similar Right Triangles
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
If the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, then the two triangles formed are similar to the original triangle and ____________ .
Answer:

Question 2.
WRITING
In your own words, explain geometric mean.
Answer:
The geometric mean is the average value or mean that signifies the central tendency of set of numbers by finding the product of their values.
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 and 4, identify the similar triangles.
Question 3.
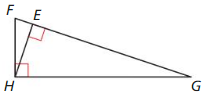
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
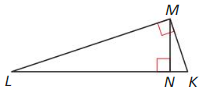
Answer:
△LKM ~ △LMN ~ △MKN
In Exercises 5 – 10, find the value of x.
Question 5.
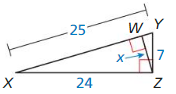
Answer:
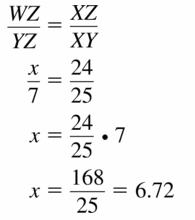
Question 6.
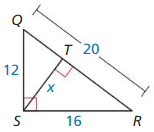
Answer:
x = 9.6
Explanation:
\(\frac { QR }{ SR } \) = \(\frac { SR }{ TS } \)
\(\frac { 20 }{ 16 } \) = \(\frac { 12 }{ x } \)
1.25 = \(\frac { 12 }{ x } \)
x = 9.6
Question 7.
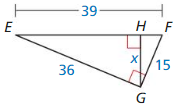
Answer:
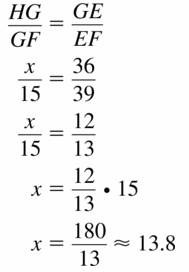
Question 8.
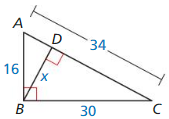
Answer:
x = 14.11
Explanation:
\(\frac { AB }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { BD }{ BC } \)
\(\frac { 16 }{ 34 } \) = \(\frac { x }{ 30 } \)
x = 14.11
Question 9.

Answer:
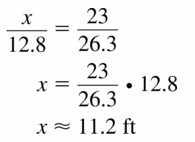
Question 10.
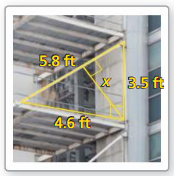
Answer:
x = 2.77
Explanation:
\(\frac { 5.8 }{ 3.5 } \) = \(\frac { 4.6 }{ x } \)
x = 2.77
In Exercises 11 – 18, find the geometric mean of the two numbers.
Question 11.
8 and 32
Answer:
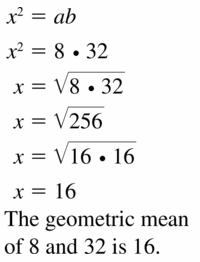
Question 12.
9 and 16
Answer:
x = √(9 x 16)
x = 12
Question 13.
14 and 20
Answer:
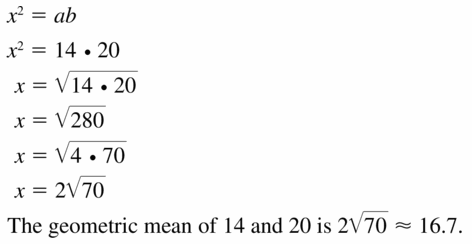
Question 14.
25 and 35
Answer:
x = √(25 x 35)
x = 29.5
Question 15.
16 and 25
Answer:
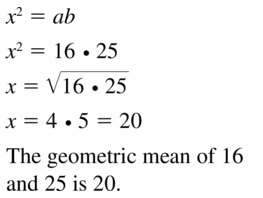
Question 16.
8 and 28
Answer:
x = √(8 x 28)
x = 14.96
Question 17.
17 and 36
Answer:
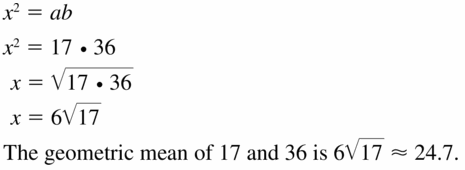
Question 18.
24 and 45
Answer:
x = √(24 x 45)
x = 32.86
In Exercises 19 – 26. find the value of the variable.
Question 19.
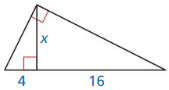
Answer:
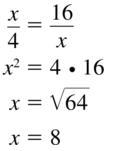
Question 20.
Answer:
y = √(5 x 8)
y = √40
y = 2√10
Question 21.
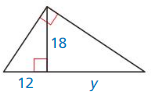
Answer:
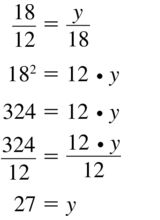
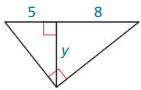
Question 22.
Answer:
10 • 10 = 25 • x
100 = 25x
x = 4
Question 23.
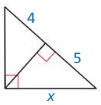
Answer:
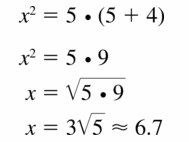
Question 24.
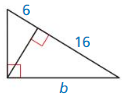
Answer:
b² = 16(16 + 6)
b² = 16(22) = 352
b = 18.76
Question 25.
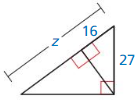
Answer:
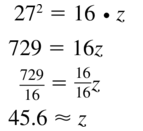
Question 26.
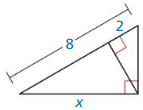
Answer:
x² = 8(8 + 2)
x² = 8(10) = 80
x = 8.9
ERROR ANALYSIS
In Exercises 27 and 28, describe and correct the error in writing an equation for the given diagram.
Question 27.
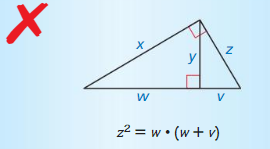
Answer:

Question 28.
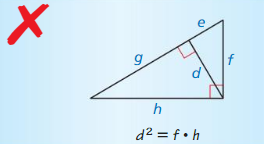
Answer:
d² = g • e
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
In Exercises 29 and 30, use the diagram.
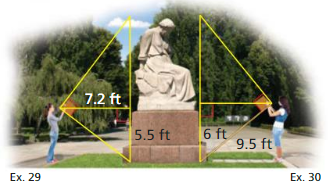
Question 29.
You want to determine the height of a monument at a local park. You use a cardboard square to line up the top and bottom of the monument, as shown at the above left. Your friend measures the vertical distance from the ground to your eye and the horizontal distance from you to the monument. Approximate the height of the monument.
Answer:

Question 30.
Your classmate is standing on the other side of the monument. She has a piece of rope staked at the base of the monument. She extends the rope to the cardboard square she is holding lined up to the top and bottom of the monument. Use the information in the diagram above to approximate the height of the monument. Do you get the same answer as in Exercise 29? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
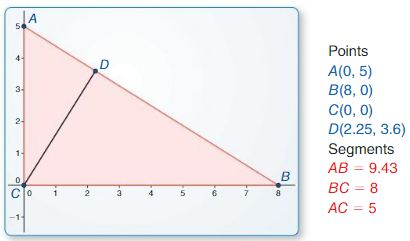
The height is the hypotenuse side of the right triangle formed by the cardboard and the ropes to the top and bottom of the monument.
The approx height of the monument is 14.63 feet.
θ1 = arctan(5.5/7.2) = 37.37
90° = θ1 + θ2
θ2 = 90 – 37.37 = 52.62
tan(θ2) = d/7.2
d = 7.2 × tan(θ2)
d = 7.2 × tan(52.62)
tan(52.624) = 72/55
d = 7.2 × 72/55 = 9.43
height of the monument, h = d + 5.2
h = 9.43 + 5.2 = 14.63 feet
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
In Exercises 31 – 34. find the value(s) of the variable(s).
Question 31.
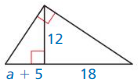
Answer:
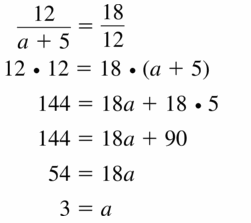
Question 32.
Answer:
\(\frac { 6 }{ b + 3 } \) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 6 } \)
36 = 8(b + 3)
36 = 8b + 24
8b = 12
b = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
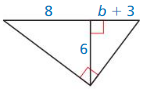
Question 33.
Answer:
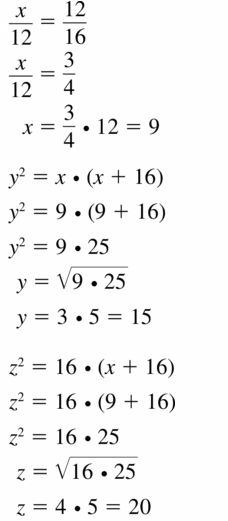
Question 34.
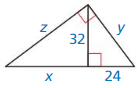
Answer:
x = 42.66, y = 40, z = 53
Explanation:
\(\frac { 24 }{ 32 } \) = \(\frac { 32 }{ x } \)
0.75 = \(\frac { 32 }{ x } \)
x = 42.66
y = √24² + 32²
y = √576 + 1024 = 40
z = √42.66² + 32² = √1819.87 + 1024 = 53
Question 35.
REASONING
Use the diagram. Decide which proportions are true. Select all that apply.
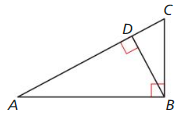
(A) \(\frac{D B}{D C}=\frac{D A}{D B}\)
(B) \(\frac{B A}{C B}=\frac{C B}{B D}\)
(C) \(\frac{C A}{B \Lambda}=\frac{B A}{C A}\)
(D) \(\frac{D B}{B C}=\frac{D A}{B A}\)
Answer:
![]()
Question 36.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
You are designing a diamond-shaped kite. You know that AD = 44.8 centimeters, DC = 72 centimeters, and AC = 84.8 centimeters. You Want to use a straight crossbar \(\overline{B D}\). About how long should it be? Explain your reasoning.
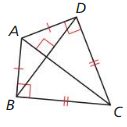
Answer:
BD = 76.12
Explanation:
AD = 44.8 cm, DC = 72 cm, and AC = 84.8 cm
Two disjoint pairs of consecutive sides are congruent.
So, AD = AB = 44.8 cm
DC = BC = 72 cm
The diagonals are perpendicular.
So, AC ⊥ BD
AC = AO + OC
AX = x + y = 84.8 — (i)
Perpendicular bisects the diagonal BD into equal parts let it be z.
BD = BO + OD
BD = z + z
Using pythagorean theorem
44.8² = x² + z² —- (ii)
72² = y² + z² —– (iii)
Subtract (ii) and (iii)
72² – 44.8² = y²+ z² – x² – z²
5184 – 2007.04 = (x + y) (x – y)
3176.96 = (84.8)(x – y)
37.464 = x – y —- (iv)
Add (i) & (iv)
x + y + x – y = 84.8 + 37.464
2x = 122.264
x = 61.132
x + y = 84.8
61.132 + y = 84.8
y = 23.668
44.8² = x² + z²
z = 38.06
BD = z + z
BD = 76.12
Question 37.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
Use the Geometric Mean Theorems (Theorems 9.7 and 9.8) to find AC and BD.
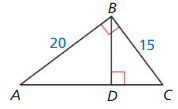
Answer:
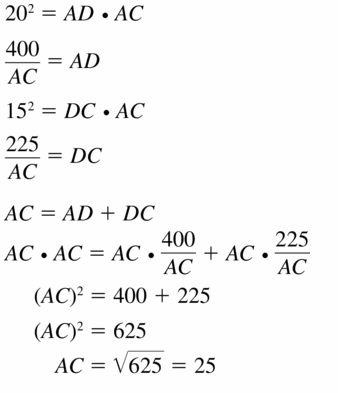
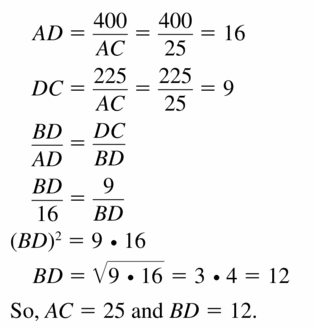
Question 38.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
In which of the following triangles does the Geometric Mean (Altitude) Theorem (Theorem 9.7) apply?
(A)
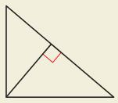
(B)
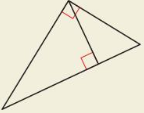
(C)
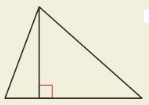
(D)
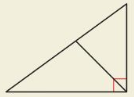
Answer:
The length of each leg of the right triangle is the geometric mean of the lengths of the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to the leg.

CD² = AD × BD
CD/AD = BD/CD
Option B is the correct answer.
Question 39.
PROVING A THEOREM
Use the diagram of ∆ABC. Copy and complete the proof of the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9. 1).
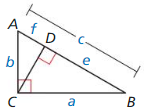
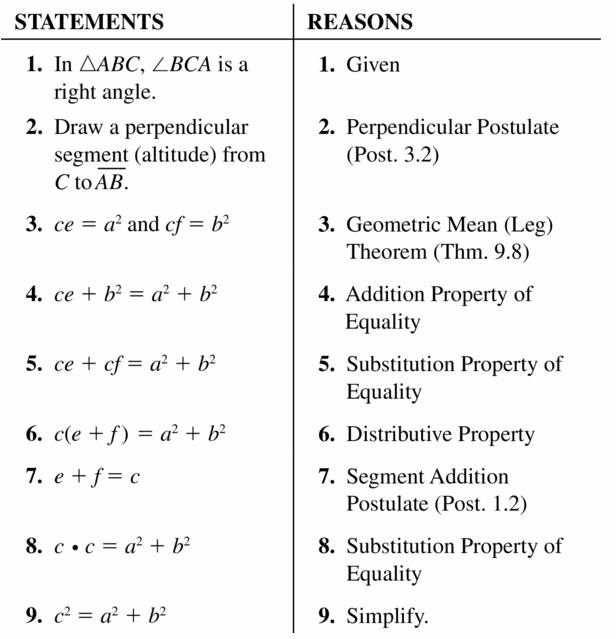
Given In ∆ABC, ∆BCA is a right angle.
Prove c2 = a2 + b2
| Statements | Reasons |
| 1. In ∆ABC, ∠BCA is a right angle. | 1. ________________________________ |
| 2. Draw a perpendicular segment (altitude) from C to \(\overline{A B}\). | 2. Perpendicular Postulate (Postulate 3.2) |
| 3. ce = a2 and cf = b2 | 3. ________________________________ |
| 4. ce + b2 = ___ + b2 | 4. Addition Property of Equality |
| 5. ce + cf = a2 + b2 | 5. ________________________________ |
| 6. c(e + f) a2 + b2 | 6. ________________________________ |
| 7. e + f = ________ | 7. Segment Addition Postulate (Postulate 1.2) |
| 8. c • c = a2 + b2 | 8. ________________________________ |
| 9. c2 = a2 + b2 | 9. Simplify. |
Answer:
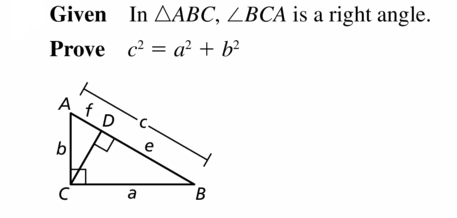
Question 40.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims the geometric mean of 4 and 9 is 6. and then labels the triangle, as shown. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
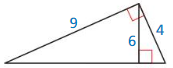
Answer:
G.M = √(4 x 9) = √36 = 6
My friend is correct.
In Exercises 41 and 42, use the given statements to prove the theorem.
Gien ∆ABC is a right triangle.
Altitude \(\overline{C D}\) is dravn to hypotenuse \(\overline{A B}\).
Question 41.
PROVING A THEOREM
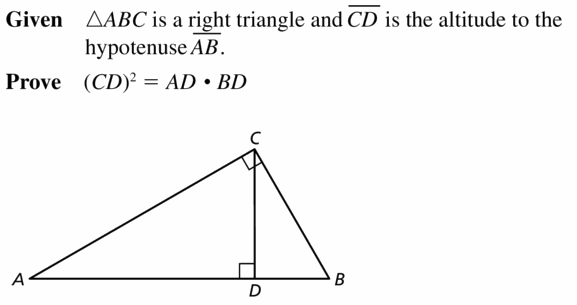
Prove the Geometric Mean (Altitude) Theorem (Theorem 9.7) b showing that CD2 = AD • BD.
Answer:
Question 42.
PROVING A THEOREM
Prove the Geometric Mean ( Leg) Theorem (Theorem 9.8) b showing that CB2 = DB • AB and AC2 = AD • AB.
Answer:
CB² = DB x AB
AC² = AD x AB
Proof:
From the given triangle
We know that,
CB/DB = AB/CD is an equation 1
And
AC/AD = AB/AC is an equation 2
From equation 1
CB² = DB x AB
From equation 2
AC² = AD x AB
Hence proved.
Question 43.
CRITICAL THINKING
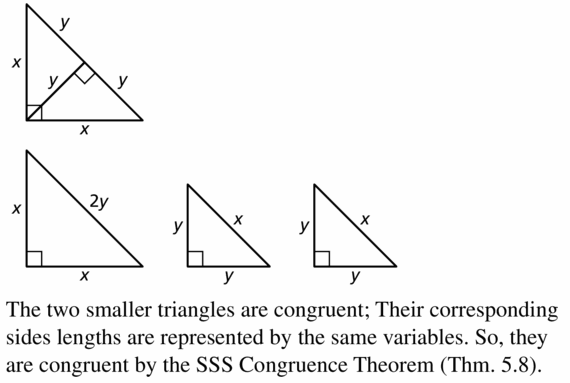
Draw a right isosceles triangle and label the two leg lengths x. Then draw the altitude to the hypotenuse and label its length y. Now, use the Right Triangle Similarity Theorem (Theorem 9.6) to draw the three similar triangles from the image and label an side length that is equal to either x or y. What can you conclude about the relationship between the two smaller triangles? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 44.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
The arithmetic mean and geometric mean of two nonnegative numbers x and y are shown.
arithmetic mean = \(\frac{x+y}{2}\)
geometric mean = \(\sqrt{x y}\)
Write an inequality that relates these two means. Justify your answer.
Answer:
The inequality of arithmetic and geometric means. the arithmetic means of non-negative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same numbers.
Here x and y are two non-negative numbers.
x + y/2 = square root of (xy) with equality
If x = y
The square of a real number is always non-negative. According to the binomial formula.
(a + or – b) ² = a² + or – 2ab + b
0 < or = (x – y) ²
= x² – 2xy + y²
= x² + 2xy + y² – 4xy
= (x + y) ² – 4xy
Hence (x + y) ² = 4xy with equality
When (x – y) ² = 0 then x = y
Therefore the AM and GM is an inequality.
Question 45.
PROVING A THEOREM
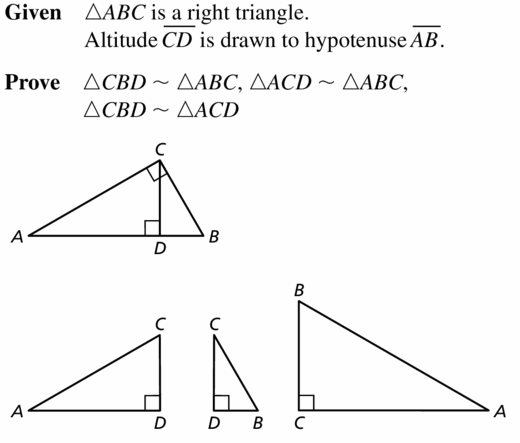
Prove the Right Triangle Similarity Theorem (Theorem 9.6) by proving three similarity statements.
Given ∆ABC is a right triangle.
Altitude \(\overline{C D}\) is drawn to hvpotenuse \(\overline{A B}\).
Prove ∆CBD ~ ∆ABC, ∆ACD ~ ∆ABC,
∆CBD ~ ∆ACD
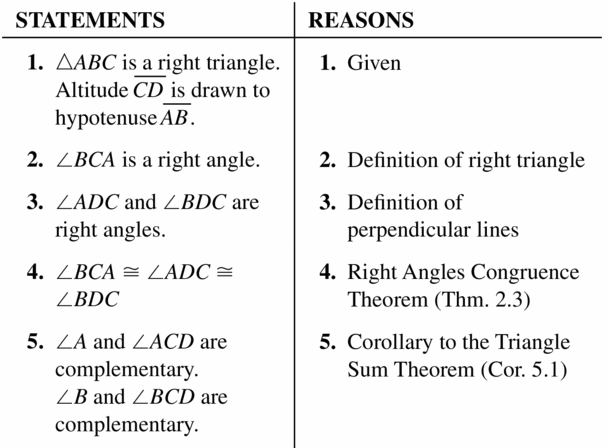
Answer:

Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
Solve the equation for x.
Question 46.
13 = \(\frac{x}{5}\)
Answer:
13 = \(\frac{x}{5}\)
x = 65
Question 47.
29 = \(\frac{x}{4}\)
Answer:
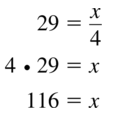
Question 48.
9 = \(\frac{78}{x}\)
Answer:
9 = \(\frac{78}{x}\)
9x = 78
x = 8.6
Question 49.
30 = \(\frac{115}{x}\)
Answer:
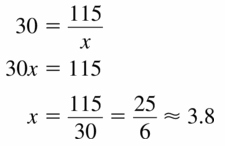
9.1 to 9.3 Quiz
Find the value of x. Tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Question 1.
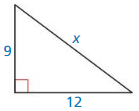
Answer:
x = 15
Explanation:
x² = 9² + 12²
x² = 81 + 144
x² = 225
x = 15
Question 2.
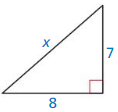
Answer:
x = 10.63
Explanation:
x² = 7² + 8² = 49 + 64
x = √113
x = 10.63
Question 3.
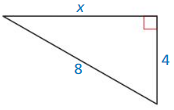
Answer:
x = 4√3
Explanation:
8² = x² + 4²
64 = x² + 16
x² = 48
x = 4√3
Verify that the segment lengths form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
(Section 9.1)
Question 4.
24, 32, and 40
Answer:
Triangle is a right angle trinagle.
Explanation:
40² = 1600
24² + 32² = 576 + 1024 = 1600
40² = 24² + 32²
So, the triangle is a right angle trinagle.
Question 5.
7, 9, and 13
Answer:
Triangle is an obtuse trinagle.
Explanation:
13² = 169
7² + 9² = 49 + 81 = 130
13² > 7² + 9²
So, the triangle is an obtuse trinagle.
Question 6.
12, 15, and 10√3
Answer:
Triangle is an acute trinagle.
Explanation:
15² = 225
12² + (10√3)² = 144 + 300 = 444
15² < 12² + (10√3)²
So, the triangle is an acute trinagle.
Find the values of x and y. Write your answers in the simplest form.
Question 7.
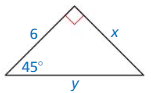
Answer:
x = 6, y = 6√2
Explanation:
x = 6
hypotenuse = leg • √2
y = 6√2
Question 8.
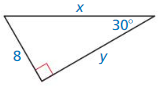
Answer:
y = 8√3, x = 16
Explanation:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
y = 8√3
x² = 8² + (8√3)² = 64 + 192
x = 16
Question 9.
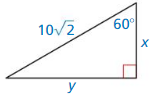
Answer:
x = 5√2, y = 5√6
Explanation:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
y = x√3
y = 5√6
hypotenuse = shorter leg • 2
10√2 = 2x
x = 5√2
Find the geometric mean of the two numbers.
Question 10.
6 and 12
Answer:
G.M = √(6 • 12) = 6√2
Question 11.
15 and 20
Answer:
G.M = √(15 • 20) = 10√3
Question 12.
18 and 26
Answer:
G.M = √(18 • 26) = 6√13
Identify the similar right triangles. Then find the value of the variable.
Question 13.
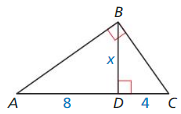
Answer:
x = √(8 • 4)
x = 4√2
Question 14.
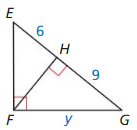
Answer:
y = √(9 • 6) = 3√6
Question 15.
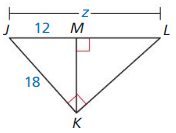
Answer:
Question 16.
Television sizes are measured by the length of their diagonal. You want to purchase a television that is at least 40 inches. Should you purchase the television shown? Explain your reasoning.

Answer:
x² = 20.25² + 36²
x² = 410.0625 + 1296 = 1706.0625
x = 41.30
Yes, i will purchase the television.
Question 17.
Each triangle shown below is a right triangle.
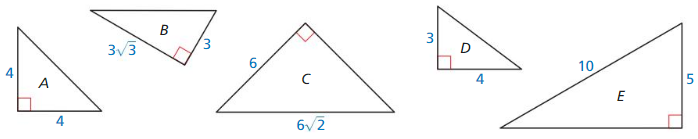
a. Are any of the triangles special right triangles? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
A is a similar triangle.
b. List all similar triangles. if any.
Answer:
B, C and D, E are similar triangles.
c. Find the lengths of the altitudes of triangles B and C.
Answer:
B altitude = √(9 + 27) = 6
C altitude = √(36 + 72) = 6√3
9.4 The Tangent Ratio
Exploration 1
Calculating a Tangent Ratio
Work with a partner
a. Construct ∆ABC, as shown. Construct segments perpendicular to \(\overline{A C}\) to form right triangles that share vertex A and arc similar to ∆ABC with vertices, as shown.
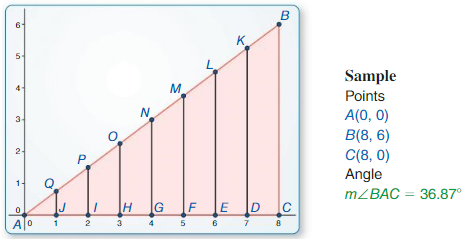
Answer:
b. Calculate each given ratio to complete the table for the decimal value of tan A for each right triangle. What can you Conclude?
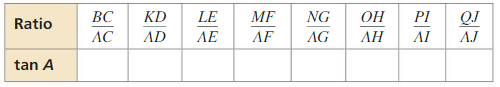
Answer:
Exploration 2
Using a calculator
Work with a partner: Use a calculator that has a tangent key to calculate the tangent of 36.87°. Do you get the same result as in Exploration 1? Explain.
ATTENDING TO PRECISION
To be proficient in math, you need to express numerical answers with a degree of precision appropriate for the problem context.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
Repeat Exploration 1 for ∆ABC with vertices A(0, 0), B(8, 5), and C(8, 0). Construct the seven perpendicular segments so that not all of them intersect \(\overline{A C}\) at integer values of x. Discuss your results.
Answer:
Question 4.
How is a right triangle used to find the tangent of an acute angle? Is there a unique right triangle that must be used?
Answer:
A right triangle can be used to determine the tangent of any acute angle by taking the ratio of the length of the side opposite to the angle with respect to the length of the side adjacent to the acute angle.
Any right triangle can be used to determine the tangent of the acute angles on it.
Lesson 9.4 The Tangent Ratio
Monitoring progress
Find tan J and tan K. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to four places.
Question 1.
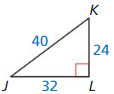
Answer:
tan K = \(\frac { opposite side }{ adjacent side } \) = \(\frac { JL }{ KL } \)
= \(\frac { 32 }{ 24 } \) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) = 1.33
tan J = \(\frac { KL }{ JL } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 32 } \) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 } \) = 0.75
Question 2.
Answer:
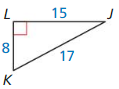
tan K = \(\frac { LJ }{ LK } \) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 8 } \)
tan J = \(\frac { LK }{ LJ } \) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 15 } \)
Find the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Question 3.
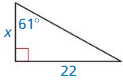
Answer:
Tan 61 = \(\frac { 22 }{ x } \)
1.804 = \(\frac { 22 }{ x } \)
x = 12.1951
Question 4.
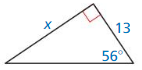
Answer:
tan 56 = \(\frac { x }{ 13 } \)
1.482 = \(\frac { x }{ 13 } \)
x = 19.266
Question 5.
WHAT IF?
In Example 3, the length of the shorter leg is 5 instead of 1. Show that the tangent of 60° is still equal to √3.
Answer:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
= 5√3
tan 60 = \(\frac { 5√3 }{ 5 } \)
= √3
Question 6.
You are measuring the height of a lamppost. You stand 40 inches from the base of the lamppost. You measure the angle ot elevation from the ground to the top of the lamppost to be 70°. Find the height h of the lamppost to the nearest inch.
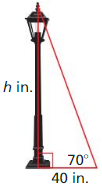
Answer:
tan 70 = \(\frac { h }{ 40 } \)
2.7474 = \(\frac { h }{ 40 } \)
h = 109.896 in
Exercise 9.4 The Tangent Ratio
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
The tangent ratio compares the length of _________ to the length of ___________ .
Answer:

Question 2.
WRITING
Explain how you know the tangent ratio is constant for a given angle measure.
Answer:
When two triangles are similar, the corresponding sides are proportional which makes the ratio constant for a given acute angle measurement.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the tangents of the acute angles in the right triangle. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to four decimal places.
Question 3.
Answer:

Question 4.
Answer:
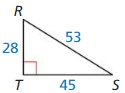
tan F = \(\frac { DE }{ EF } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 7 } \)
tan D = \(\frac { EF }{ DE } \) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 24 } \)
Question 5.
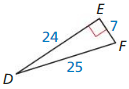
Answer:
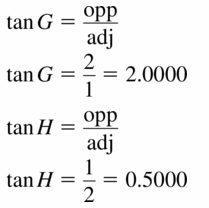
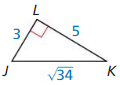
Question 6.
Answer:
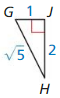
tan K = \(\frac { JL }{ LK } \) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
tan J = \(\frac { LK }{ JL } \) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \)
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
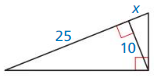
Question 7.
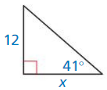
Answer:
Question 8.
Answer:
tan 27 = \(\frac { x }{ 15 } \)
0.509 = \(\frac { x }{ 15 } \)
x = 7.635
Question 9.
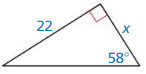
Answer:
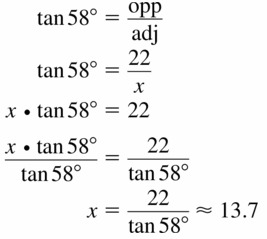
Question 10.
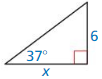
Answer:
tan 37 = \(\frac { 6 }{ x } \)
0.753 = \(\frac { 6 }{ x } \)
x = 7.968
ERROR ANALYSIS
In Exercises 11 and 12, describe the error in the statement of the tangent ratio. Correct the error if possible. Otherwise, write not possible.
Question 11.
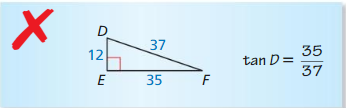
Answer:
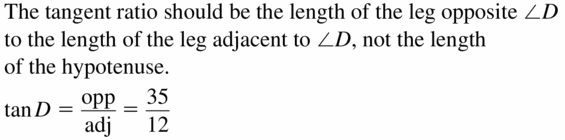
Question 12.
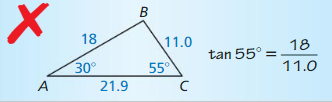
Answer:
Given,
∠A = 30
∠c = 55
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
30 + ∠B + 55 = 180
∠B = 180 – 85 = 95°
Substituting the values in the below equation
∠B ≠ 90° it is not right-angled triangle.
tan55 = 18/11.0 is not possible.
Hence ΔABC is not right angled triangle.
In Exercises 13 and 14, use a special right triangle to find the tangent of the given angle measure.
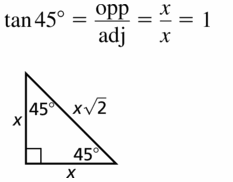
Question 13.
45°
Answer:
Question 14.
30°
Answer:
tan 30° = \(\frac { 1 }{ √3 } \)
Question 15.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A surveyor is standing 118 Feet from the base of the Washington Monument. The surveyor measures the angle of elevation from the ground to the top of the monument to be 78°. Find the height h of the Washington Monument to the nearest foot.

Answer:

Question 16.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Scientists can measure the depths of craters on the moon h looking at photos of shadows. The length of the shadow cast by the edge of a crater is 500 meters. The angle of elevation of the rays of the Sun is 55°. Estimate the depth d of the crater.
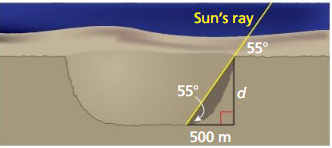
Answer:
tan 55 = \(\frac { d }{ 500 } \)
1.428 = \(\frac { d }{ 500 } \)
d = 714 m
The depth of the crater is 714 m
Question 17.
USING STRUCTURE
Find the tangent of the smaller acute angle in a right triangle with side lengths 5, 12, and 13.
Answer:
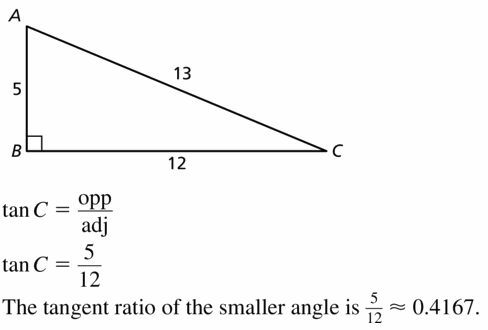
Question 18.
USING STRUCTURE
Find the tangent 0f the larger acute angle in a right triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5.
Answer:
tan x = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)
Question 19.
REASONING
How does the tangent of an acute angle in a right triangle change as the angle measure increases? Justify your answer.
Answer:

Question 20.
CRITICAL THINKING
For what angle measure(s) is the tangent of an acute angle in a right triangle equal to 1? greater than 1? less than 1? Justify your answer.
Answer:
In order for the tangent of an angle to equal 1, the opposite and adjacent sides of a right triangle must be the same. This means the right triangle is an isosceles right triangle so the angles are 45 – 45 – 90. The acute angle must be 1. In order for the tangent to be greater than 1, the opposite side must be greater than the adjacent side. This means the angle must be between 45 and 90 degrees. If the tangent is less than 1, this means the opposite side must be smaller than the adjacent side. The acute angle must be between 0 and 45.
Question 21.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
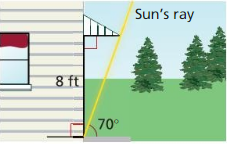
Your family room has a sliding-glass door. You want to buy an awning for the door that will be just long enough to keep the Sun out when it is at its highest point in the sky. The angle of elevation of the rays of the Sun at this points is 70°, and the height of the door is 8 feet. Your sister claims you can determine how far the overhang should extend by multiplying 8 by tan 70°. Is your sister correct? Explain.
Answer:

Question 22.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
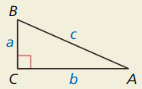
Write expressions for the tangent of each acute angle in the right triangle. Explain how the tangent of one acute angle is related to the tangent of the other acute angle. What kind of angle pair is ∠A and ∠B?
Answer:
tan A = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { a }{ b } \)
tan B = \(\frac { AC }{ BC } \) = \(\frac { b }{ a } \)
Question 23.
REASONING
Explain why it is not possible to find the tangent of a right angle or an obtuse angle.
Answer:

Question 24.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
To create the diagram below. you begin with an isosceles right triangle with legs 1 unit long. Then the hypotenuse of the first triangle becomes the leg of a second triangle, whose remaining leg is 1 unit long. Continue the diagram Until you have constructed an angle whose tangent is \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}}\). Approximate the measure of this angle.
Answer:
Question 25.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Your class is having a class picture taken on the lawn. The photographer is positioned 14 feet away from the center of the class. The photographer turns 50° to look at either end of the class.
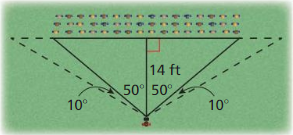
a. What is the distance between the ends of the class?
b. The photographer turns another 10° either way to see the end of the camera range. If each student needs 2 feet of space. about how many more students can fit at the end of each row? Explain.
Answer:

Question 26.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Find the perimeter of the figure. where AC = 26, AD = BF, and D is the midpoint of \(\overline{A C}\).
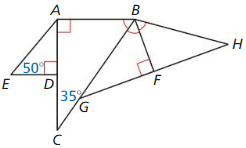
Answer:
AC = 26
AD = BF
D = The midpoint of AC
AD = CD = 26/2 = 13
AE = AD/sin(50) = 13/sin(50) = 17
ED = AD/tan50 = 13/tan50 = 10.9
AB = AC × tan35 = 26 × tan(35) = 18.2
18.2/26 = 13/GF . GF = 13 × 26/18.2 = 18.6
GF = HF = 18.6 by similar triangles
BG = BH = 22.7
BC = √(26² + 18.2²) = 31.7
GC = BC – BG
GC = 31.7 – 22.7 = 9
Perimeter = AE + AB + BH + HF + GF + GC + CD
P = 17 + 18.2 + 22.7 + 18.6 + 18.6 + 9 + 13 = 117.1
So, the perimeter of the figure is117.1
Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
Find the value of x.
Question 27.
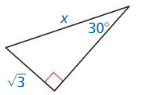
Answer:
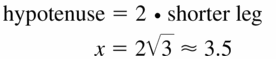
Question 28.
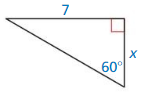
Answer:
longer side = shorter side • √3
7 = x√3
x = \(\frac { 7 }{ √3 } \)
x = 4.04
Question 29.
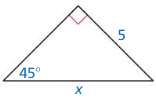
Answer:
9.5 The Sine and Cosine Ratios
Exploration 1
Work with a partner: Use dynamic geometry software.
a. Construct ∆ABC, as shown. Construct segments perpendicular to \(\overline{A C}\) to form right triangles that share vertex A arid are similar to ∆ABC with vertices, as shown.
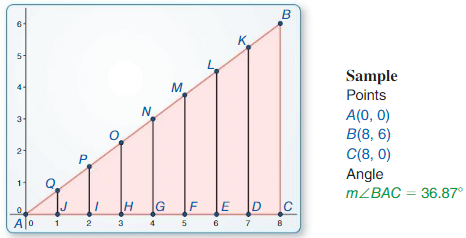
Answer:
b. Calculate each given ratio to complete the table for the decimal values of sin A and cos A for each right triangle. What can you conclude?
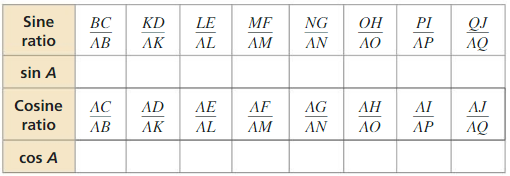
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 2.
How is a right triangle used to find the sine and cosine of an acute angle? Is there a unique right triangle that must be used?
Answer:
Let us consider the acute angles of a right triangle are added to 90 degrees
We know that acute angles are complementary
Angle A is the complement of angle B and angle B is the complement of angle A.
The sine of any acute angle is equal to the cosine of its complement.
The cosine of any acute angle is equal to the sine of its complement.
Question 3.
In Exploration 1, what is the relationship between ∠A and ∠B in terms of their measures’? Find sin B and cos B. How are these two values related to sin A and cos A? Explain why these relationships exist.
LOOKING FOR STRUCTURE
To be proficient in math, you need to look closely to discern a pattern or structure.
Answer:
Lesson 9.5 The Sine and Cosine Ratios
Monitoring Progress
Question 1.
Find sin D, sin F, cos D, and cos F. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to four places.
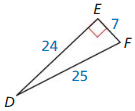
Answer:
sin D = \(\frac { 7 }{ 25 } \)
sin F = \(\frac { 24 }{ 25 } \)
cos D = \(\frac { 24 }{ 25 } \)
cos F = \(\frac { 7 }{ 25 } \)
Explanation:
sin D = \(\frac { EF }{ DF } \) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 25 } \)
sin F = \(\frac { DE }{ DF } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 25 } \)
cos D = \(\frac { DE }{ DF } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 25 } \)
cos F = \(\frac { EF }{ DF } \) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 25 } \)
Question 2.
Write cos 23° in terms of sine.
Answer:
cos X = sin(90 – X)
cos 23° = sin (90 – 23)
= sin(67)
So, cos 23° = sin 67°
Question 3.
Find the values of u and t using sine and cosine. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
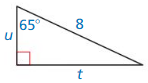
Answer:
t = 7.2, u = 3.3
Explanation:
sin 65 = \(\frac { t }{ 8 } \)
0.906 = \(\frac { t }{ 8 } \)
t = 7.2
cos 65 = \(\frac { u }{ 8 } \)
0.422 x 8 = u
u = 3.3
Question 4.
Find the sine and cosine of a 60° angle.
Answer:
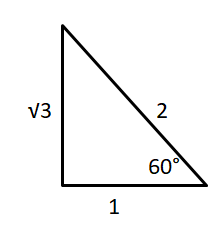
sin 60° = \(\frac { √3 }{ 2 } \)
cos 60° = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Question 5.
WHAT IF?
In Example 6, the angle of depression is 28°. Find the distance x you ski down the mountain to the nearest foot.
Answer:
sin 28° = \(\frac { 1200 }{ x } \)
x = \(\frac { 1200 }{ 0.469 } \)
x = 2558.6
Exercise 9.5 The Sine and Cosine Ratios
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
The sine raio compares the length of ______________ to the length of _____________
Answer:
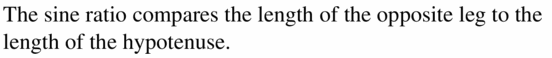
Question 2.
WHICH ONE DOESN’T BELONG?
Which ratio does not belong with the other three? Explain your reasoning.
sin B
Answer:
sin B = \(\frac { AC }{ BC } \)
cos C
Answer:
cos C = \(\frac { AC }{ BC } \)
tan B
Answer:
tan B = \(\frac { AC }{ AB } \)
Answer:
\(\frac{A C}{B C}\) = sin B
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 8, find sin D, sin E, cos D, and cos E. Write each answer as a Fraction and as a decimal rounded to four places.
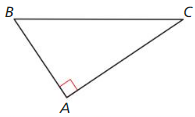
Question 3.
Answer:

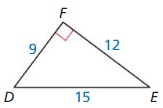
Question 4.
Answer:
sin D = \(\frac { 35 }{ 37 } \)
sin E = \(\frac { 12 }{ 37 } \)
cos D = \(\frac { 12 }{ 37 } \)
cos E = \(\frac { 35 }{ 37 } \)
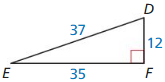
Question 5.
Answer:
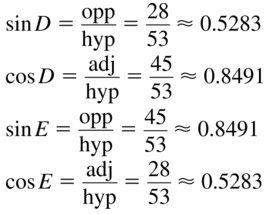
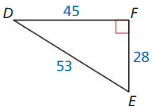
Question 6.
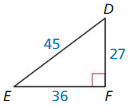
Answer:
sin D = \(\frac { 36 }{ 45 } \)
sin E = \(\frac { 27 }{ 45 } \)
cos D = \(\frac { 27 }{ 45 } \)
cos E = \(\frac { 36 }{ 45 } \)
Question 7.
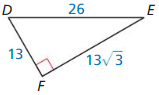
Answer:

Question 8.
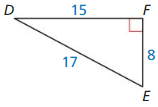
Answer:
sin D = \(\frac { 8 }{ 17 } \)
sin E = \(\frac { 15 }{ 17 } \)
cos D = \(\frac { 15 }{ 17 } \)
cos E = \(\frac { 8 }{ 17 } \)
In Exercises 9 – 12. write the expression in terms of cosine.
Question 9.
sin 37°
Answer:
![]()
Question 10.
sin 81°
Answer:
sin 81° = cos(90° – 81°) = cos9°
Question 11.
sin 29°
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
sin 64°
Answer:
sin 64° = cos(90° – 64°) = cos 26°
In Exercise 13 – 16, write the expression in terms of sine.
Question 13.
cos 59°
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
cos 42°
Answer:
cos 42° = sin(90° – 42°) = sin 48°
Question 15.
cos 73°
Answer:
![]()
Question 16.
cos 18°
Answer:
cos 18° = sin(90° – 18°) = sin 72°
In Exercises 17 – 22, find the value of each variable using sine and cosine. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 17.
Answer:

Question 18.
Answer:
p = 30.5, q = 14.8
Explanation:
sin 64° = \(\frac { p }{34 } \)
p = 0.898 x 34
p = 30.5
cos 64° = \(\frac { q }{ 34 } \)
q = 0.4383 x 34
q = 14.8
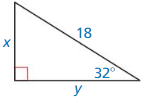
Question 19.
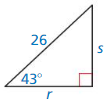
Answer:
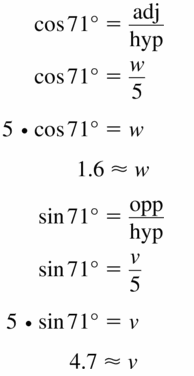
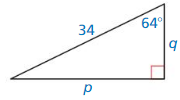
Question 20.
Answer:
s = 17.7, r = 19
Explanation:
sin 43° = \(\frac { s }{26 } \)
s = 0.681 x 26
s = 17.7
cos 43° = \(\frac { r }{ 26 } \)
r = 0.731 x 26
r = 19
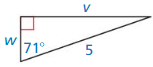
Question 21.
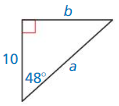
Answer:
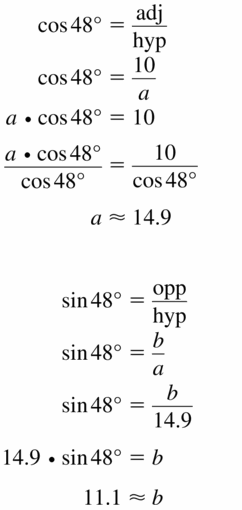
Question 22.
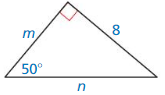
Answer:
m = 6.7, n = 10.44
Explanation:
sin 50° = \(\frac { 8 }{n } \)
0.766 = \(\frac { 8 }{n } \)
n = 10.44
cos 50° = \(\frac { m }{ n } \)
0.642 = \(\frac { m }{ 10.44 } \)
m = 6.7
Question 23.
REASONING
Which ratios are equal? Select all that apply.
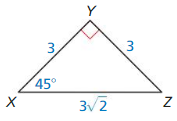
sin X
cos X
sin Z
cos Z
Answer:
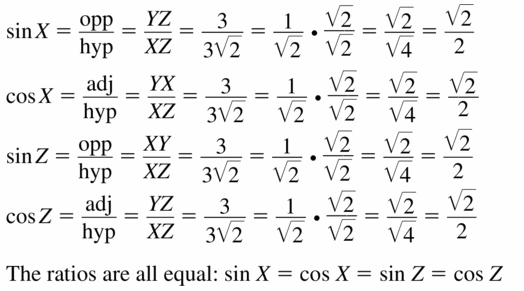
Question 24.
REASONING
Which ratios arc equal to \(\frac{1}{2}\) Select all
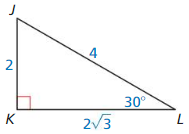
sin L
Answer:
sin L = \(\frac { 2 }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
cos L
Answer:
cos L = \(\frac { 2√3 }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { √3 }{ 2 } \)
sin J
Answer:
sin J = \(\frac { 2√3 }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { √3 }{ 2 } \)
cos J
Answer:
cos J = \(\frac { 2 }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Question 25.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding sin A.
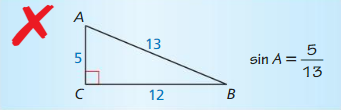
Answer:
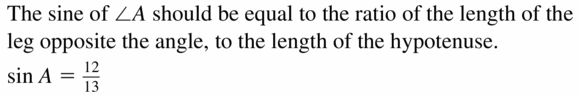
Question 26.
WRITING
Explain how to tell which side of a right triangle is adjacent to an angle and which side is the hypotenuse.
Answer:
AB is adjacent to ∠A, because if we don’t consider hypotenuse, it is the only associated segment to the angle.
The segment opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
The last one, AC segment is called opposite because it is the opposite to angle a.
Question 27.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The top of the slide is 12 feet from the ground and has an angle of depression of 53°. What is the length of the slide?
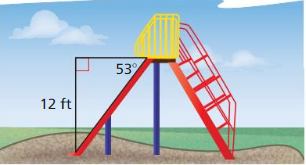
Answer:
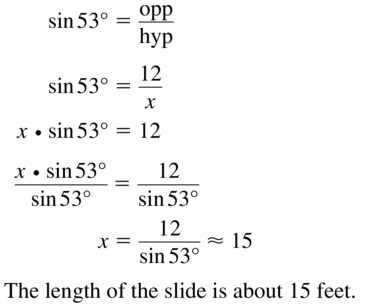
Question 28.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Find the horizontal distance x the escalator covers.
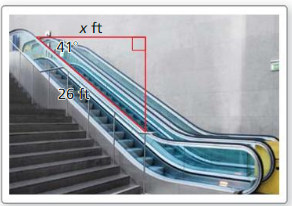
Answer:
cos 41 = \(\frac { x }{ 26 } \)
0.754 = \(\frac { x }{ 26 } \)
x = 19.6 ft
Question 29.
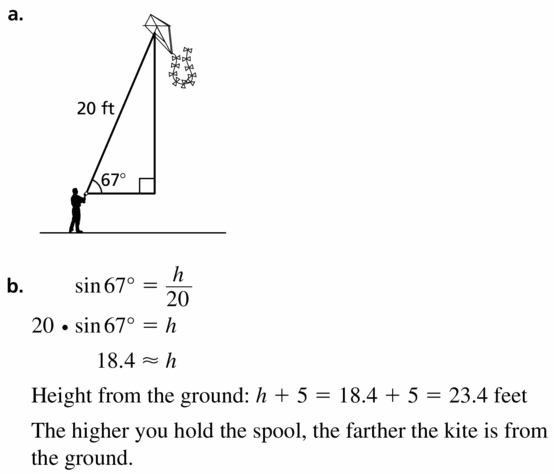
PROBLEM SOLVING
You are flying a kite with 20 feet of string extended. The angle of elevation from the spool of string to the kite is 67°.
a. Draw and label a diagram that represents the situation.
b. How far off the ground is the kite if you hold the spool 5 feet off the ground? Describe how the height where you hold the spool affects the height of the kite.
Answer:
Question 30.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Planes that fly at high speeds and low elevations have radar s sterns that can determine the range of an obstacle and the angle of elevation to the top of the obstacle. The radar of a plane flying at an altitude of 20,000 feet detects a tower that is 25,000 feet away. with an angle of elevation of 1°
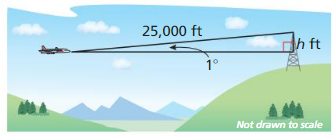
a. How many feet must the plane rise to pass over the tower?
Answer:
sin 1 = \(\frac { h }{ 25000 } \)
0.017 = \(\frac { h }{ 25000 } \)
h = 425 ft
425 ft the plane rise to pass over the tower
b. PIanes Caillot come closer than 1000 feet vertically to any object. At what altitude must the plane fly in order to pass over the tower?
Answer:
If the plane is currently flying at 20,000 feet, it needs to rise about 436 feet clear the top of the tower, and another 1000 feet to follow safety protocol, making its required 20,000 + 1000 + 436 = 21,436 feet.
Question 31.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend uses che equation sin 49° = \(\frac{x}{16}\) to find BC. Your cousin uses the equation cos 41° = \(\frac{x}{16}\) to find BC. Who is correct? Explain your reasoning.
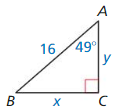
Answer:
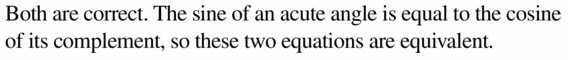
Question 32.
WRITING
Describe what you must know about a triangle in order to use the sine ratio and what you must know about a triangle in order to use the cosine ratio
Answer:
sin = \(\frac { opposite side }{ hypotenuse } \)
cos = \(\frac { adjacent side }{ hypotenuse } \)
Question 33.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
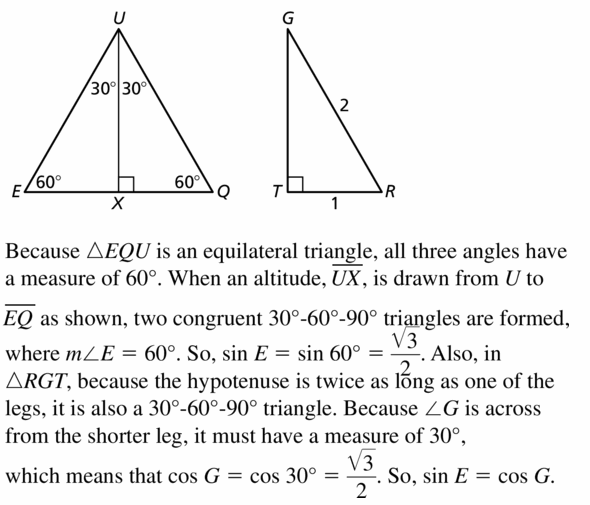
If ∆EQU is equilateral and ∆RGT is a right triangle with RG = 2, RT = 1. and m ∠ T = 90°, show that sin E = cos G.
Answer:
Question 34.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Submarines use sonar systems, which are similar to radar systems, to detect obstacles, Sonar systems use sound to detect objects under water.
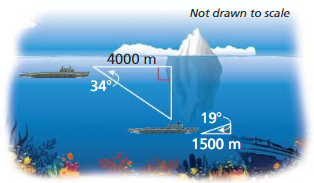
a. You are traveling underwater in a submarine. The sonar system detects an iceberg 4000 meters a head, with an angle of depression of 34° to the bottom of the iceberg. How many meters must the submarine lower to pass under the iceberg?
Answer:
tan 34 = \(\frac { x }{ 4000 } \)
.674 = \(\frac { x }{ 4000 } \)
x = 2696
b. The sonar system then detects a sunken ship 1500 meters ahead. with an angle of elevation of 19° to the highest part of the sunken ship. How many meters must the submarine rise to pass over the sunken ship?
Answer:
tan 19 = \(\frac { x }{ 1500 } \)
0.344 = \(\frac { x }{ 1500 } \)
x = 516 m
Question 35.
ABSTRACT REASONING
Make a conjecture about how you could use trigonometric ratios to find angle measures in a triangle.
Answer:

Question 36.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Using only the given information, would you use a sine ratio or a cosine ratio to find the length of the hypotenuse? Explain your reasoning.
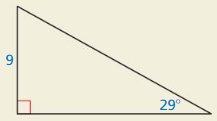
Answer:
sin 29 = \(\frac { 9 }{ x } \)
0.48 = \(\frac { 9 }{ x } \)
x = 18.75
The length of hypotenuse is 18.75
Question 37.
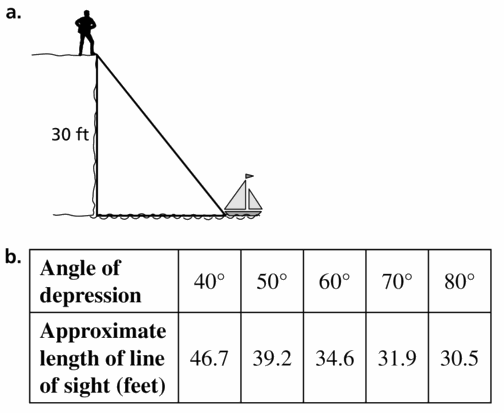
MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS
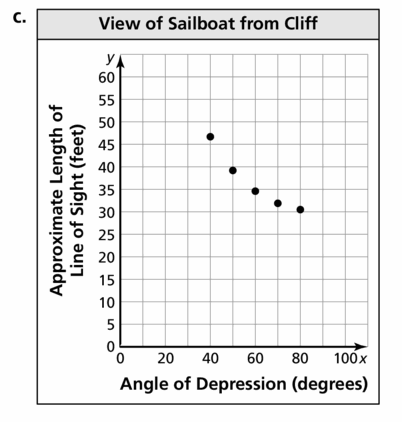
You are standing on a cliff above an ocean. You see a sailboat from your vantage point 30 feet above the ocean.
a. Draw and label a diagram of the situation.
b. Make a table showing the angle of depression and the length of your line of sight. Use the angles 40°, 50°, 60°, 70°, and 80°.
c. Graph the values you found in part (b), with the angle measures on the x-axis.
d. Predict the length of the line of sight when the angle of depression is 30°.
Answer:

Question 38.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
One of the following infinite series represents sin x and the other one represents cos x (where x is measured in radians). Which is which? Justify your answer. Then use each series to approximate the sine and cosine of \(\frac{\pi}{6}\).
(Hints: π = 180°; 5! = 5 • 4 • 3 • 2 • 1; Find the values that the sine and cosine ratios approach as the angle measure approaches zero).
a.
![]()
Answer:
For x = 0
0 – \(\frac { 0³ }{ 3! } \) + \(\frac { 0⁵ }{ 5! } \) – \(\frac { 0⁷ }{ 7! } \) + . . . = 0
sin x = x – \(\frac { x³ }{ 3! } \) + \(\frac { x⁵ }{ 5! } \) – \(\frac { x⁷ }{ 7! } \) + . . .
sin \(\frac { π }{ 6 } \) = 0.5
b.
![]()
Answer:
1 – \(\frac { 1² }{ 2! } \) + \(\frac { 1⁴ }{ 4! } \) – \(\frac { 1⁶ }{ 6! } \) + . . = 1
cos x =x1 – \(\frac { x² }{ 2! } \) + \(\frac { x⁴ }{ 4! } \) – \(\frac { x⁶ }{ 6! } \) + . .
cos \(\frac { π }{ 6 } \) = 0.86
Question 39.
CRITICAL THINKING
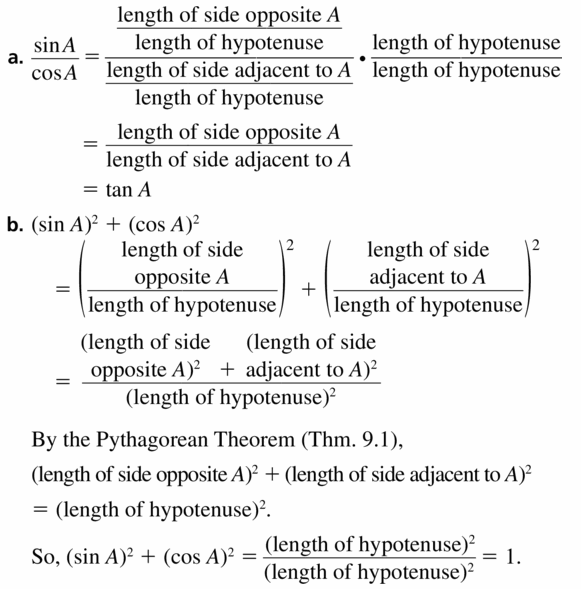
Let A be any acute angle of a right triangle. Show that
(a) tan A = \(\frac{\sin A}{\cos A}\) and
(b) (sin A)2 + (cos A)2 = 1.
Answer:
Question 40.
CRITICAL THINKING
Explain why the area ∆ ABC in the diagram can be found using the formula Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ab sin C. Then calculate the area when a = 4, b = 7, and m∠C = 40°:
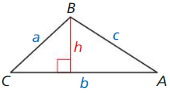
Answer:
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ab sin C
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (4 x 7) sin 40°
= 14 x 0.642
= 8.988
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the value of x. Tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Question 41.
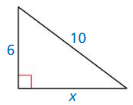
Answer:
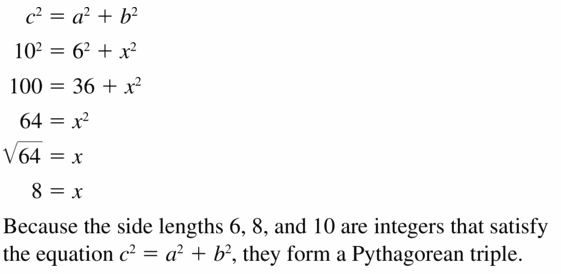
Question 42.
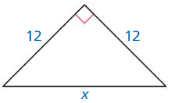
Answer:
x = 12√2
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
x² = 12² + 12²
x² = 144 + 144
x² = 288
x = 12√2
Question 43.
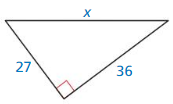
Answer:
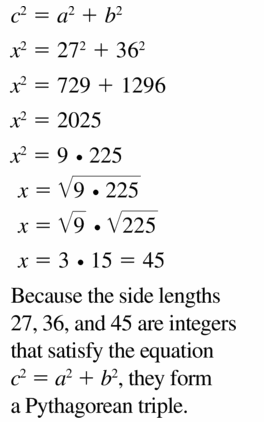
Question 44.
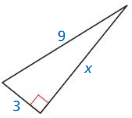
Answer:
x = 6√2
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
9² = x² + 3²
81 = x² + 9
x² = 81 – 9
x = 6√2
9.6 Solving Right Triangles
Exploration 1
Solving Special Right Triangles
Work with a partner. Use the figures to find the values of the sine and cosine of ∠A and ∠B. Use these values to find the measures of ∠A and ∠B. Use dynamic geometry software to verify your answers.
a.
Answer:
b.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Solving Right Triangles
Work with a partner: You can use a calculator to find the measure of an angle when you know the value of the sine, cosine, or tangent of the rule. Use the inverse sine, inverse cosine, 0r inverse tangent feature of your calculator to approximate the measures of ∠A and ∠B to the nearest tenth of a degree. Then use dynamic geometry software to verify your answers.
ATTENDING TO PRECISION
To be proficient in math, you need to calculate accurately and efficiently, expressing numerical answers with a degree of precision appropriate for the problem context.
a.
Answer:
b.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
When you know the lengths of the sides of a right triangle, how can you find the measures of the two acute angles?
Answer:
Sin of any angle can be calculated by the ratio of the perpendicular side in the triangle to the hypotenuse.
Cos of any angle can be calculated by the ratio of the base side in the triangle to the hypotenuse.
Tan of any angle can be calculated by the ratio of the perpendicular side in the triangle to the base side.
If sin, cos and tan of any angles are given then angles can be found easily by applying inverse function.
Question 4.
A ladder leaning against a building forms a right triangle with the building and the ground. The legs of the right triangle (in meters) form a 5-12-13 Pythagorean triple. Find the measures of the two acute angles to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Answer:
Lesson 9.6 Solving Right Triangles
Determine which of the two acute angles has the given trigonometric ratio.
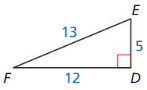
Question 1.
The sine of the angle is \(\frac{12}{13}\).
Answer:
Sin E = \(\frac{12}{13}\)
m∠E = sin-1(\(\frac{12}{13}\)) = 67.3°
Question 2.
The tangent of the angle is \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Answer:
tan F = \(\frac{5}{12}\)
m∠F = tan-1(\(\frac{5}{12}\)) = 22.6°
Let ∠G, ∠H, and ∠K be acute angles. Use a calculator to approximate the measures of ∠G, ∠H, and ∠K to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Question 3.
tan G = 0.43
Answer:
∠G = inverse tan of 0.43 = 23.3°
Question 4.
sin H = 0.68
Answer:
∠H = inverse sin of 0.68 = 42.8°
Question 5.
cos K = 0.94
Answer:
∠K = inverse cos of 0.94 = 19.9°
Solve the right triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 6.
Answer:
DE = 29, ∠D = 46.05°, ∠E = 42.84°
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
x² = 20² + 21²
x² = 400 + 441
x² = 841
x = 29
sin D = \(\frac { 21 }{ 29 } \)
∠D = 46.05
sin E = \(\frac { 20 }{ 29 } \)
∠E = 42.84
Question 7.
Answer:
GJ = 60, ∠G = 56.09°, ∠H = 33.3°
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
109² = 91² + x²
x² = 11881 – 8281
x² = 3600
x = 60
sin G = \(\frac { 91 }{ 109 } \)
∠G = 56.09
sin H = \(\frac { 60 }{ 109 } \)
∠H = 33.3
Question 8.
Solve the right triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
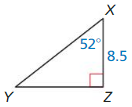
Answer:
XY = 13.82, YZ = 6.69, ∠Y = 37.5
Explanation:
cos 52 = \(\frac { 8.5 }{ XY } \)
0.615 = \(\frac { 8.5 }{ XY } \)
XY = 13.82
sin 52 = \(\frac { YZ }{ XY } \)
0.788 = \(\frac { YZ }{ 8.5 } \)
YZ = 6.69
sin Y = \(\frac { 8.5 }{ 13.82 } \)
∠Y = 37.5
Question 9.
WHAT IF?
In Example 5, suppose another raked stage is 20 feet long from front to back with a total rise of 2 feet. Is the raked stage within your desired range?
Answer:
x = inverse sine of \(\frac { 2 }{ 20 } \)
x = 5.7°
Exercise 9.6 Solving Right Triangles
Question 1.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
To solve a right triangle means to find the measures of all its ________ and _______ .
Answer:

Question 2.
WRITING
Explain when you can use a trigonometric ratio to find a side length of a right triangle and when you can use the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.1 ).
Answer:
The trigonometric ratio can be used to find a side length of a triangle when the measure of one of the two acute angles is given and the Pythagoras theorem can be used to find a side length of a triangle when the measure of one of the two side lengths is given.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6. determine which of the two acute angles has the given trigonometric ratio.
Question 3.
The cosine of the angle is \(\frac{4}{5}\)
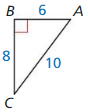
Answer:

Question 4.
The sine of the angle is \(\frac{5}{11}\)
Answer:
Sin(angle) = \(\frac { opposite }{ hypo } \)
sin A = \(\frac{5}{11}\)
The acute angle that has a sine of the angle is \(\frac{5}{11}\) is ∠A.
Question 5.
The sine of the angle is 0.95.
Answer:

Question 6.
The tangent of the angle is 1.5.
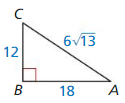
Answer:
tan(angle) = \(\frac { opposite }{ adjacent } \)
1.5 = \(\frac { 18 }{ 12 } \)
tan C = 1.5
The acute angle that has a tangent of the angle is 1.5 ∠C.
In Exercises 7 – 12, let ∠D be an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of ∠D to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Question 7.
sin D = 0.75
Answer:
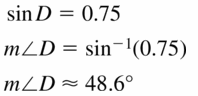
Question 8.
sin D = 0.19
Answer:
sin D = 0.19
∠D = inverse sine of 0.19
∠D = 10.9°
Question 9.
cos D = 0.33
Answer:
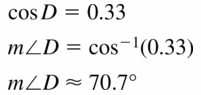
Question 10.
cos D = 0.64
Answer:
cos D = 0.64
∠D = inverse cos of 0.64
∠D = 50.2°
Question 11.
tan D = 0.28
Answer:
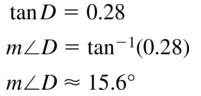
Question 12.
tan D = 0.72
Answer:
tan D = 0.72
∠D = inverse tan of 0.72
∠D = 35.8°
In Exercises 13 – 18. solve the right triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 13.
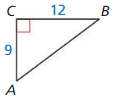
Answer:
Question 14.
Answer:
ED = 2√65, ∠E = 59.3, ∠D = 29.7
Explanation:
c² = 8² + 14²
x² = 64 + 196
x² = 260
x = 2√65
sin E = \(\frac { 14 }{ 2√65 } \)
∠E = 59.3
sin D = \(\frac { 8 }{ 2√65 } \)
∠D = 29.7
Question 15.
Answer:
Question 16.
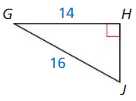
Answer:
HJ = 2√15, ∠G = 28.9, ∠J = 61
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
16² = 14² + x²
x² = 256 – 196
x² = 60
x = 2√15
sin G = \(\frac { 2√15 }{ 16 } \)
∠G = 28.9
sin J = \(\frac { 14 }{ 16 } \)
∠J = 61
Question 17.
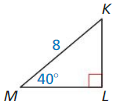
Answer:
Question 18.
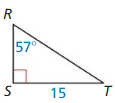
Answer:
RT = 17.8, RS = 9.68, ∠T = 32.8
Explanation:
sin 57 = \(\frac { 15 }{ x } \)
0.838 = \(\frac { 15 }{ x } \)
x = 17.899
RT = 17.8
cos 57 = \(\frac { x }{ 17.8 } \)
0.544 = \(\frac { x }{ 17.8 } \)
x = 9.68
RS = 9.68
sin T = \(\frac { 9.68 }{ 17.8 } \)
∠T = 32.8
Question 19.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in using an inverse trigonometric ratio.
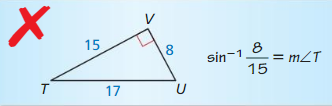
Answer:

Question 20.
PROBLEM SOLVING
In order to unload clay easily. the body of a dump truck must be elevated to at least 45° The body of a dump truck that is 14 feet long has been raised 8 feet. Will the clay pour out easily? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Angle of elevation: sin x = \(\frac { 8 }{ 14 } \)
x = inverse sine of \(\frac { 8 }{ 14 } \) = 34.9
The clay will not pour out easily.
Question 21.
PROBLEM SOLVING
You are standing on a footbridge that is 12 feet above a lake. You look down and see a duck in the water. The duck is 7 feet away from the footbridge. What is the angle of elevation from the duck to you
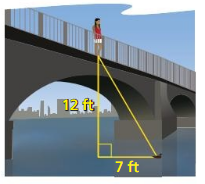
Answer:
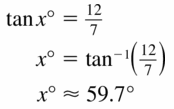
Question 22.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Write three expressions that can be used to approximate the measure of ∠A. Which expression would you choose? Explain your choice.
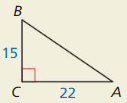
Answer:
Three expressions are ∠A = inverse tan of (\(\frac { 15 }{ 22 } \)) = 34.2°
∠A = inverse sine of (\(\frac { 15 }{ BA } \))
∠A = inverse cos of (\(\frac { 22 }{ BA } \))
Question 23.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The Uniform Federal Accessibility Standards specify that awheel chair ramp may not have an incline greater than 4.76. You want to build a ramp with a vertical rise of 8 inches. you want to minimize the horizontal distance taken up by the ramp. Draw a diagram showing the approximate dimensions of your ramp.
Answer:

Question 24.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The horizontal part of a step is called the tread. The vertical part is called the riser. The recommended riser – to – tread ratio is 7 inches : 11 inches.
a. Find the value of x for stairs built using the recommended riser-to-tread ratio.
b. you want to build stairs that are less steep than the stairs in part (a). Give an example of a riser – to – tread ratio that you could use. Find the value of x for your stairs.
Answer:
Given that,
Length of riser = 7 in
Length of thread = 11 in
Ration = 7: 11
Let us consider angles of inclination be x.
In geometry, the lines that are parallel and have the same alternate interior angles. Thus, the angles of inclination between the riser and thread is given by
Tan x = rise/Thread
Tan x = 7/11
Tan x = 0.6364
x = tan -1(0.6364)
x = 32.5 degrees.
Therefore, the value of x for these stairs built by using the recommended riser to tread ratio is 32.5 degrees.
Question 25.
USING TOOLS
Find the measure of ∠R without using a protractor. Justify your technique.
Answer:

Question 26.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims that tan-1x = \(\frac{1}{\tan x}\). Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
No
For example
tan-1(√3) = 60
\(\frac{1}{\tan √3}\) = 33.1
USING STRUCTURE
In Exercises 27 and 28, solve each triangle.
Question 27.
∆JKM and ∆LKM
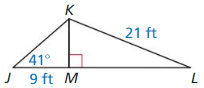
Answer:
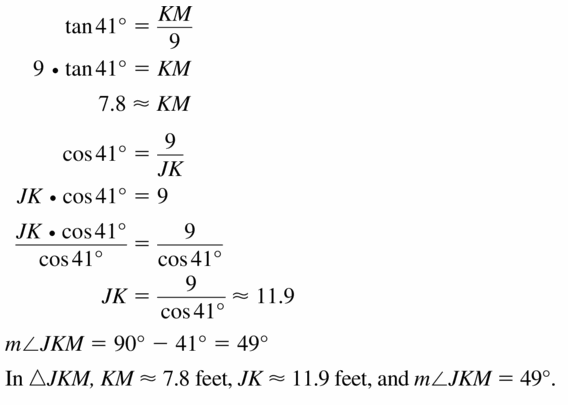
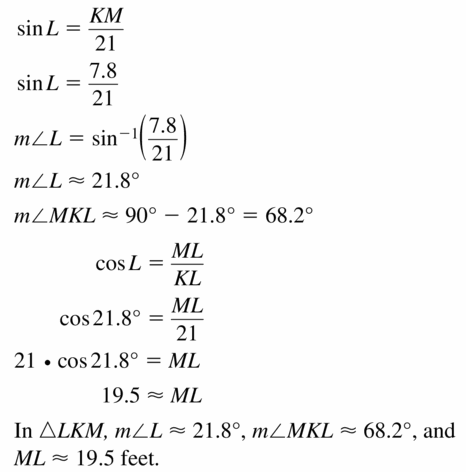
Question 28.
∆TUS and ∆VTW
Answer:
TS = 8.2, UT = 7.3, ∠T = 28.6
TV = 13.2, TW = 9.6, ∠V = 46, ∠T = 42.84
Explanation:
tan 64 = \(\frac { TS }{ 4 } \)
TS = 2.05 x 4
TS = 8.2
sin 64 = \(\frac { UT }{ 8.2 } \)
0.898= \(\frac { UT }{ 8.2 } \)
UT = 7.3
sin T = \(\frac { 4 }{ 8.2 } \)
∠T = 28.6
TV = TS + SV
TV = 8.2 + 5 = 13.2
13.2² = TW² + 9²
TW² = 174.24 – 81
TW = 9.6
sin V = \(\frac { 9.6 }{ 13.2 } \)
∠V = 46
sin T = \(\frac { 9 }{ 13.2 } \)
∠T = 42.84
Question 29.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
Write an expression that can be used to find the measure of the acute angle formed by each line and the x-axis. Then approximate the angle measure to the nearest tenth of a degree.
a. y = 3x
b. y = \(\frac{4}{3}\)x + 4
Answer:

Question 30.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Simplify each expression. Justify your answer.
a. sin-1 (sin x)
Answer:
sin-1 (sin x) = x
b. tan(tan-1 y)
Answer:
tan(tan-1 y) = y
C. cos(cos-1 z)
Answer:
cos(cos-1 z) = z
Question 31.
REASONING
Explain why the expression sin-1 (1.2) does not make sense.
Answer:

Question 32.
USING STRUCTURE
The perimeter of the rectangle ABCD is 16 centimeters. and the ratio of its width to its length is 1 : 3. Segment BD divides the rectangle into two congruent triangles. Find the side lengths and angle measures of these two triangles.
Answer:
The perimeter of the rectangle ABCD is 16 centimeters
2(l + b) = 16
l + b = 8
b : l = 1 : 3
4x = 8
x = 2
l = 6, b = 2
BD = √(6² + 2²) = √40 = 2√10
sin B = \(\frac { AD }{ BD } \) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 2√10 } \)
∠ABD = 18.4
∠CBD = 71.6
sin D = \(\frac { AB }{ BD } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2√10 } \)
∠ADB = 71
∠CDB = 19
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Solve the equation
Question 33.
\(\frac{12}{x}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer:
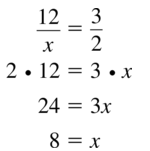
Question 34.
\(\frac{13}{9}=\frac{x}{18}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{13}{9}=\frac{x}{18}\)
x = 1.44 x 18
x = 26
Question 35.
\(\frac{x}{2.1}=\frac{4.1}{3.5}\)
Answer:
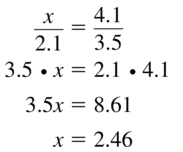
Question 36.
\(\frac{5.6}{12.7}=\frac{4.9}{x}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5.6}{12.7}=\frac{4.9}{x}\)
0.44 = 4.9/x
x = 11.13
9.7 Law of Sines and Law of Cosines
Exploration 1
Discovering the Law of Sines
Work with a partner.
a. Copy and complete the table for the triangle shown. What can you conclude?
Answer:
b. Use dynamic geometry software to draw two other triangles. Copy and complete the table in part (a) for each triangle. Use your results to write a conjecture about the relationship between the sines of the angles and the lengths of the sides of a triangle.
USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY
To be proficient in math, you need to use technology to compare predictions with data.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Discovering the Law of Cosines
Work with a partner:
a. Copy and complete the table for the triangle in Exploration 1 (a). What can you conclude?
Answer:
b. Use dynamic geometry software to draw two other triangles. Copy and complete the table in part (a) for each triangle. Use your results to write a conjecture about what you observe in the completed tables.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
What are the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines?
Answer:
Law of Sines is
sin A/a = SinB/b = sinC/c
And
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
Law of Cosines are
a² = b² + c² -2bcCosA
x² = a² + c² – 2acCosB
x² = a² + b² – 2abCosC
Question 4.
When would you use the Law of Sines to solve a triangle? When would you use the Law of Cosines to solve a triangle?
Answer:
Given in any triangle the sine law can be used if you know the two sides and one angle opposite a given side (SSA) or two angles and any side (AAS or ASA).
In any triangle, the cosine laws can be used if two sides are included with one angle of sides.
Lesson 9.7 Law of Sines and Law of Cosines
Monitoring Progress
Use a calculator to find the trigonometric ratio. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Question 1.
tan 110°
Answer:
tan 110° = -2.7474
Question 2.
sin 97°
Answer:
sin 97° = 0.9925
Question 3.
cos 165°
Answer:
cos 165° = -0.9659
Find the area of ∆ABC with the given side lengths and included angle. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Question 4.
m ∠ B = 60°, a = 19, c = 14
Answer:
Area = 155.18
Explanation:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ac sin B
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (19 x 14) sin 60°
= 133 x 0.866
= 155.18
Question 5.
m ∠ C = 29°, a = 38, b = 31
Answer:
Area = 282.72
Explanation:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ab sin C
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (38 x 31) sin 29
= 598 x 0.48
= 282.72
Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 6.
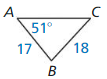
Answer:
∠C = 46.6, ∠B = 82.4, AC = 23.57
Explanation:
Using law of sines
\(\frac { c }{ sin C } \) = \(\frac { a }{ sin A } \)
\(\frac { 17 }{ sin C } \) = \(\frac { 18 }{ sin 51 } \)
\(\frac { 17 }{ sin C } \) = \(\frac { 18 }{ 0.77 } \)
sin C = 0.7274
∠C = 46.6
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
51 + 46.6 + ∠B = 180
∠B = 82.4
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { 0.99 }{ b } \) = \(\frac { 0.77 }{ 18 } \)
b = 23.57
Question 7.
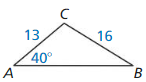
Answer:
∠B = 31.3, ∠C = 108.7, c = 23.6
Explanation:
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { sin B }{ 13 } \) = \(\frac { sin 40 }{ 16 } \)
sin B = \(\frac { .64 }{ 16 } \) x 13
sin B = 0.52
∠B = 31.3
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
40 + 31.3 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 108.7
\(\frac { c }{ sin C } \) = \(\frac { a }{ sin A } \)
\(\frac { c }{ sin 108.7 } \) = \(\frac {16 }{ sin 40 } \)
c = \(\frac {16 }{ .64 } \) x 0.947
c = 23.6
Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 8.
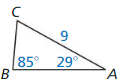
Answer:
∠C = 66, a = 4.36, c = 8.27
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
29 + 85 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 66
\(\frac { a }{ sin A } \) = \(\frac { b }{ sin B } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin C } \)
\(\frac { a }{ sin 29 } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ sin 85 } \)
\(\frac { a }{ 0.48 } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 0.99 } \)
a = 4.36
\(\frac { b }{ sin B } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin C } \)
\(\frac { 9 }{ sin 85 } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin 66 } \)
\(\frac { 9 }{ 0.99 } \) = \(\frac { c }{ 0.91 } \)
c = 8.27
Question 9.
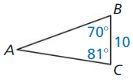
Answer:
∠A = 29, b = 19.37, c = 20.41
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
∠A + 70 + 81 = 180
∠A = 29
\(\frac { a }{ sin A } \) = \(\frac { b }{ sin B } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin C } \)
\(\frac { 10 }{ sin 29 } \) = \(\frac { b }{ sin 70 } \)
\(\frac { 10 }{ 0.48 } \) = \(\frac { b }{ 0.93 } \)
b = 19.37
\(\frac { a }{ sin A } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin C } \)
\(\frac { 10 }{ sin 29 } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin 81 } \)
\(\frac { 10 }{ 0.48 } \) = \(\frac { c }{ 0.98 } \)
c = 20.41
Question 10.
WHAT IF?
In Example 5, what would be the length of a bridge from the South Picnic Area to the East Picnic Area?
Answer:
The length of a bridge from the South Picnic Area to the East Picnic Area is 188 m.
Explanation:
\(\frac { a }{ sin A } \) = \(\frac { b }{ sin B } \) = \(\frac { c }{ sin C } \)
\(\frac { a }{ sin 71 } \) = \(\frac { 150 }{ sin 49 } \)
a = 188
Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 11.
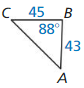
Answer:
b = 61.3, ∠A = 46, ∠C = 46
Explanation:
b² = a² + c² − 2ac cos B
b² = 45² + 43² – 2(45)(43) cos 88
b² = 2025 + 1849 – 3870 x 0.03 = 3757.9
b = 61.3
\(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \)
\(\frac { sin A }{ 45 } \) = \(\frac { sin 88 }{ 61.3 } \)
sin A = 0.72
∠A = 46
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
46 + 88 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 46
Question 12.
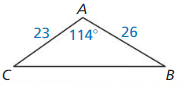
Answer:
a = 41.1, ∠C = 35.6, ∠B = 30.4
Explanation:
a² = b² + c² − 2bc cos A
a² = 23² + 26² – 2(23)(26) cos 114
a² = 529 + 676 – 1196 x -0.406
a² = 1690.5
a = 41.1
\(\frac { sin 114 }{ 41.1 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 23 } \)
0.02 = \(\frac { sin B }{ 23 } \)
sin B = 0.507
∠B = 30.4
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
114 + 30.4 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 35.6
Question 13.
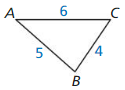
Answer:
∠A = 41.4, ∠B = 81.8, ∠C = 56.8
Explanation:
a² = b² + c² − 2bc cos A
4² = 6² + 5² – 2(6)(5) cos A
16 = 36 + 25 – 60 cos A
-45 = – 60 cos A
cos A = 0.75
∠A = 41.4
\(\frac { sin 41.4 }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 6 } \)
0.165 = \(\frac { sin B }{ 6 } \)
sin B = 0.99
∠B = 81.8
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
41.4 + 81.8 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 56.8
Question 14.
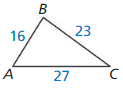
Answer:
∠B = 81.8, ∠A = 58.6, ∠C = 39.6
Explanation:
a² = b² + c² − 2bc cos A
23² = 27² + 16² – 2(27)(16) cos A
529 = 729 + 256 – 864 cos A
456 = 864 cos A
cos A = 0.52
∠A = 58.6
\(\frac { sin 58.6 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 27 } \)
0.03 = \(\frac { sin B }{ 27 } \)
sin B = 0.99
∠B = 81.8
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
58.6 + 81.8 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 39.6
Exercise 9.7 Law of Sines and Law of Cosines
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
WRITING
What type of triangle would you use the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines to solve?
Answer:

Question 2.
VOCABULARY
What information do you need to use the Law of Sines?
Answer:
The sine rule is used when the two angles and one side have given or two sides and a non-included angle are given.
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 8, use a calculator to find the trigonometric ratio, Round your answer to four decimal places.
Question 3.
sin 127°
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
sin 98°
Answer:
sin 98° = 0.9902
Question 5.
cos 139°
Answer:
![]()
Question 6.
cos 108°
Answer:
cos 108° = -0.309
Question 7.
tan 165°
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
tan 116°
Answer:
tan 116° = -2.0503
In Exercises 9 – 12, find the area of the triangle. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Question 9.
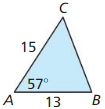
Answer:
Question 10.
Answer:
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)bc sin A
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(28)(24) sin83
Area = 332.64
Question 11.
Answer:
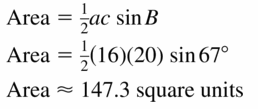
Question 12.
Answer:
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ab sin C
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(15)(7) sin 96
Area = 51.9
In Exercises 13 – 18. solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 13.
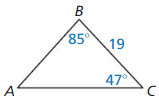
Answer:
Question 14.
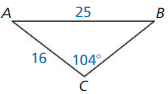
Answer:
∠B = 38.3, ∠A = 37.7, a = 15.7
Explanation:
\(\frac { sin B }{16 } \) = \(\frac { sin 104 }{ 25 } \)
sin B = 0.62
∠B = 38.3
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
∠A + 38.3 + 104 = 180
∠A = 37.7
\(\frac { sin 37.7 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 104 }{ 25 } \)
\(\frac { 0.61 }{ a } \) = 0.0388
a = 15.7
Question 15.
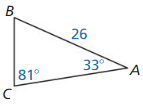
Answer:
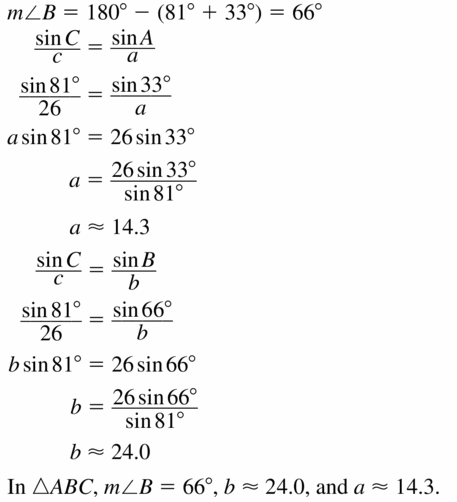
Question 16.
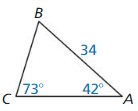
Answer:
∠B = 65, b = 33.55, a = 24.4
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
42 + 73 + ∠B = 180
∠B = 65
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 65 }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin 73 }{ 34 } \)
b = 33.55
\(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 42 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 73 }{ 34 } \)
a = 24.4
Question 17.
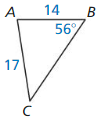
Answer:
Question 18.
Answer:
∠C = 90, b = 39.56, a = 17.6
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
24 + 66 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 90
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 66 }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin 90 }{ 43 } \)
\(\frac { .91 }{ b } \) = 0.023
b = 39.56
\(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 24 }{a } \) = \(\frac { sin 90 }{ 43 } \)
\(\frac { 0.406 }{a } \) = 0.023
a = 17.6
In Exercises 19 – 24, solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 19.
Answer:
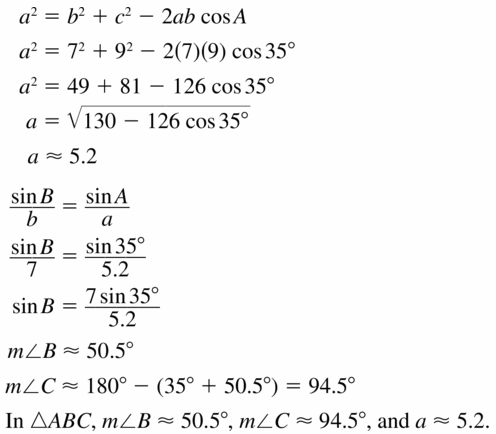
Question 20.
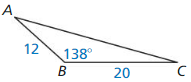
Answer:
b = 29.9, ∠A = 26.1, ∠C = 15.07
Explanation:
b² = a² + c² – 2ac cos B
b² = 20² + 12² – 2(12)(20) cos 138
b² = 400 + 144 – 480 (-0.74)
b² = 899.2
b = 29.9
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { sin 138 }{ 29.9 } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ 20 } \)
\(\frac { 0.66 }{ 29.9 } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ 20 } \)
sin A = 0.44
∠A = 26.1
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 138 }{ 29.9 } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ 12 } \)
sin C = 0.26
∠C = 15.07
Question 21.
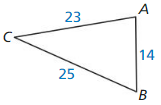
Answer:

Question 22.
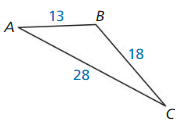
Answer:
∠A = 107.3, ∠B = 51.6, ∠C = 21.1
Explanation:
b² = a² + c² – 2ac cos B
28² = 18² + 13² – 2(18)(13) cos B
784 = 324 + 169 – 468 cos B
291 = 468 cos B
cos B = 0.62
∠B = 51.6
\(\frac { sin C }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \)
\(\frac { sin C }{ 13 } \) = \(\frac { sin 51.6 }{ 28 } \)
sin C = 0.36
∠C = 21.1
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
51.6 + 21.1 + ∠A = 180
∠A = 107.3
Question 23.
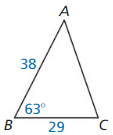
Answer:
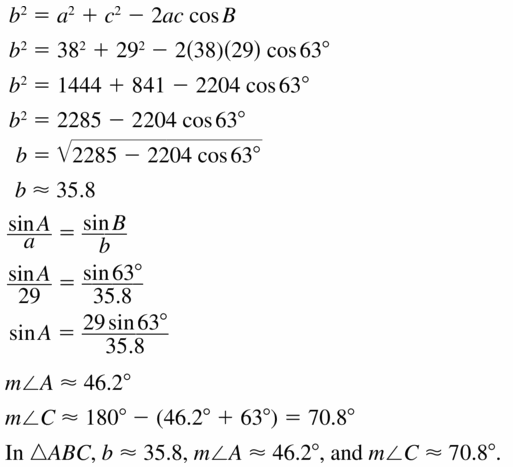
Question 24.
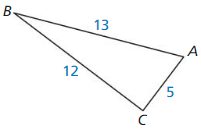
Answer:
∠A = 23, ∠B = 132.1, ∠C = 24.9
Explanation:
b² = a² + c² – 2ac cos B
5² = 12² + 13² – 2(12)(13) cos B
25 = 144 + 169 – 312 cos B
288 = 312 cos B
cos B = 0.92
∠B = 23
\(\frac { sin C }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \)
\(\frac { sin C }{ 13 } \) = \(\frac { sin 23 }{ 5 } \)
sin C = 1.014
∠C = 24.9
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
23 + 24.9 + ∠B = 180
∠B = 132.1
Question 25.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding m ∠ C.
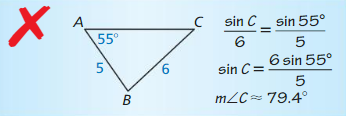
Answer:

Question 26.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding m ∠ A in ∆ABC when a = 19, b = 21, and c = 11.
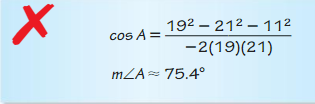
Answer:
a² = b² + c² – 2bc cos A
19² = 21² + 11² – 2(21)(11) cos A
361 = 441 + 121 – 462 cosA
201 = 462 cosA
cos A = 0.43
∠A = 64.5
COMPARING METHODS
In Exercise 27 – 32. tell whether you would use the Law of Sines, the Law of Cosines. or the Pythagorean Theorem (Theorem 9.1) and trigonometric ratios to solve the triangle with the given information. Explain your reasoning. Then solve the triangle.
Question 27.
m ∠ A = 72°, m ∠ B = 44°, b = 14
Answer:
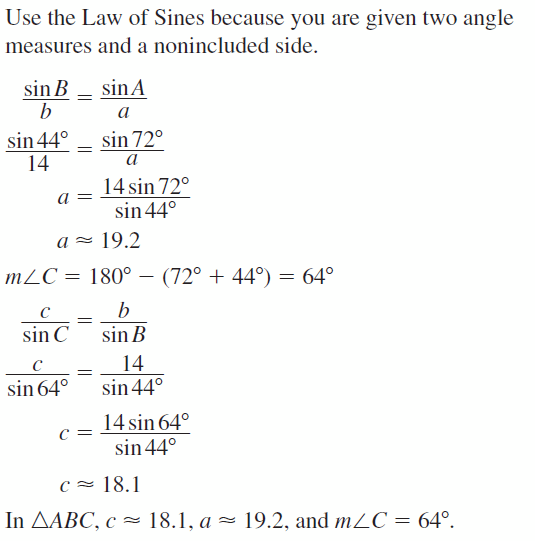
Question 28.
m ∠ B = 98°, m ∠ C = 37°, a = 18
Answer:
∠A = 45, b = 25.38, c = 15.38
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
∠A + 98 + 37 = 180
∠A = 45
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { sin 98 }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin 45 }{ 18 } \)
\(\frac { 0.99 }{ b } \) = 0.039
b = 25.38
\(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 45 }{ 18 } \) = \(\frac { sin 37 }{ c } \)
0.039 = \(\frac { sin 37 }{ c } \)
c = 15.38
Question 29.
m ∠ C = 65°, a = 12, b = 21
Answer:
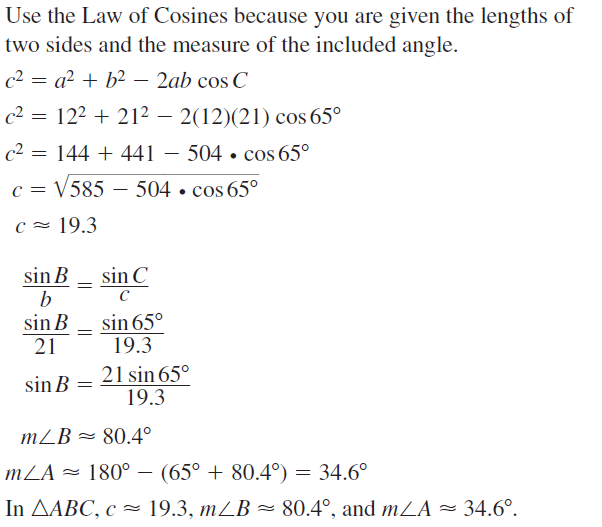
Question 30.
m ∠ B = 90°, a = 15, c = 6
Answer:
b = 3√29, ∠A = 66.9, ∠C = 23.1
Explanation:
b² = a² + c²- 2ac cos B
b² = 15² + 6² – 2(15)(6) cos 90
= 225 + 36 – 180(0)
b² = 261
b = 3√29
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { sin 90 }{ 3√29 } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ 15 } \)
sin A = 0.92
∠A = 66.9
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
66.9 + 90 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 23.1
Question 31.
m ∠ C = 40°, b = 27, c = 36
Answer:
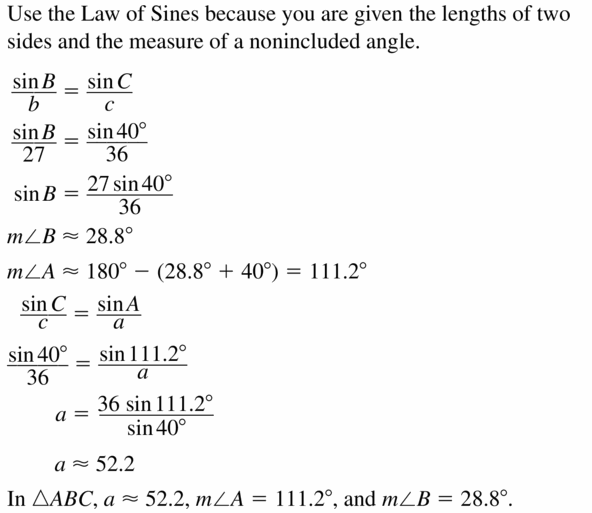
Question 32.
a = 34, b = 19, c = 27
Answer:
∠B = 33.9, ∠A = 78.5, ∠C = 67.6
Explanation:
b² = a² + c²- 2ac cos B
19² = 34² + 27²- 2(34)(27) cos B
361 = 1156 + 729 – 1836 cos B
cos B = 0.83
∠B = 33.9
\(\frac { sin 33.9 }{ 19 } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ 34 } \)
sin A = 0.98
∠A = 78.5
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
78.5 + 33.9 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 67.6
Question 33.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
You and your friend are standing on the baseline of a basketball court. You bounce a basketball to your friend, as shown in the diagram. What is the distance between you and your friend?
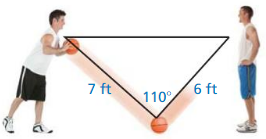
Answer:
Question 34.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A zip line is constructed across a valley, as shown in the diagram. What is the width w of the valley?
Answer:
w = 92.5 ft
Explanation:
w² = 25² + 84² – 2(25)(84) cos 102
w² = 7681 – 4200 cos 102
w = 92.5 ft
Question 35.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
You are on the observation deck of the Empire State Building looking at the Chrysler Building. When you turn 145° clockwise, you see the Statue of Liberty. You know that the Chrysler Building and the Empire Slate Building arc about 0.6 mile apart and that the Chrysler Building and the Statue of Liberty are about 5.6 miles apart. Estimate the distance between the Empire State Building and the Statue of Liberty.
Answer:

Question 36.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The Leaning Tower of Pisa in Italy has a height of 183 feet and is 4° off vertical. Find the horizontal distance d that the top of the tower is off vertical.

Answer:
The horizontal distance will be given by the trigonometry formula.
Tan theta = opposite/adjacent
Theta = 4
Opposite = height = 183 ft
Horizontal = adjacent = a
Thus
Tan 4 = 183/a
Hence a = 183/tan 4
A = 2617.82 ft.
Question 37.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend says that the Law of Sines can be used to find JK. Your cousin says that the Law of Cosines can be used to find JK. Who is correct’? Explain your reasoning.
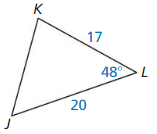
Answer:

Question 38.
REASONING
Use ∆XYZ
a. Can you use the Law of Sines to solve ∆XYZ ? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Given
y = 17, X = 64° and Y = 90°
Law of Sines can be used to solve triangles when two angles and the length of any side are known.
In triangle XYZ, two angles and the length of one side are given.
Therefore we can use Law of Sines to solve ∆XYZ.
b. Can you use another method to solve ∆XYZ ? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
The two angles of the triangle and one side opposite to the right side angle is given.
sin X/YZ = sinY/XZ = sin Z/XY
m∠X = 64, m∠Y = 90, XY = 17
sin X/YZ = sinY/XZ
sin 64/YZ = sin 90/XZ
The length of the leg YZ = 15.3
m∠X + m∠Y + m∠Z = 180
m∠Z = 26
The value of XY can be found using the right hand side of equation in law of sine and subs m∠Y = 90, m∠Z = 26 and XY = 17
sin 90/17 = sin 26/XZ
XY = 7.5
Question 39.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend calculates the area of the triangle using the formula A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)qr sin S and says that the area is approximately 208.6 square units. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
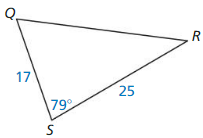
Answer:
Question 40.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
You are fertilizing a triangular garden. One side of the garden is 62 feet long, and another side is 54 feet long. The angle opposite the 62-foot side is 58°.
a. Draw a diagram to represent this situation.
b. Use the Law of Sines to solve the triangle from part (a).
c. One bag of fertilizer covers an area of 200 square feet. How many bags of fertilizer will you need to cover the entire garden?
Answer:
C = 47.6, A = 74.4, a = 70.4
9 bags of fertilizer.
Question 41.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A golfer hits a drive 260 yards on a hole that is 400 yards long. The shot is 15° off target.

a. What is the distance x from the golfer’s ball to the hole?
b. Assume the golfer is able to hit the ball precisely the distance found in part (a). What is the maximum angle θ (theta) by which the ball can be off target in order to land no more than 10 yards fr0m the hole?
Answer:

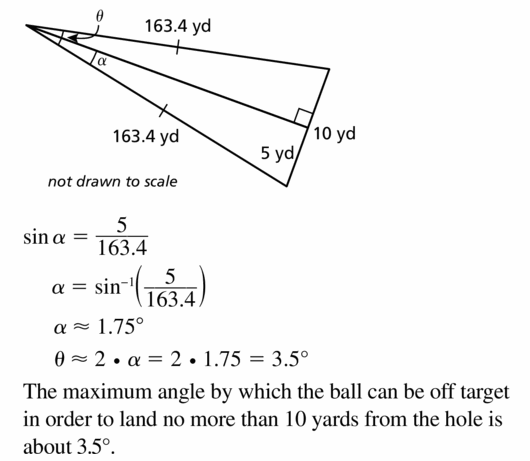
Question 42.
COMPARING METHODS
A building is constructed on top of a cliff that is 300 meters high. A person standing on level ground below the cliff observes that the angle of elevation to the top of the building is 72° and the angle of elevation to the top of the cliff is 63°.
a. How far away is the person from the base of the cliff?
Answer:
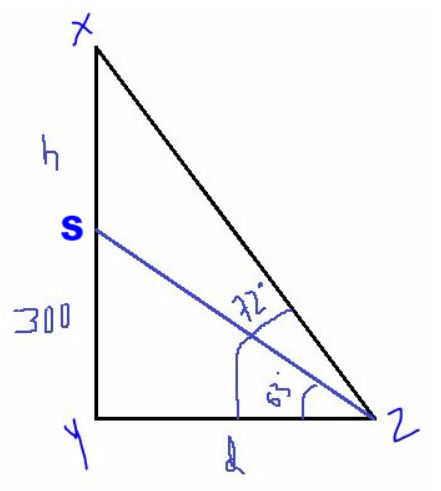
b. Describe two different methods you can use to find the height of the building. Use one of these methods to find the building’s height.
Answer:
Consider △SYZ and evaluate d using tangent function
tan SYZ = \(\frac { 300 }{ d } \)
d = \(\frac { 300 }{ tan 63 } \)
d = 152.86
The person is standing 152.86 m away from the base of the cliff.
Consider △XYS and evaluate h + 300
tan XYZ = \(\frac { h + 300 }{ d } \)
h = 152.86 x tan 72 – 300
h = 170.45
The building is 170.45 m high.
Question 43.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
Find the values of x and y.
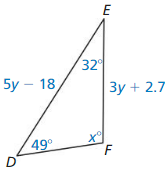
Answer:
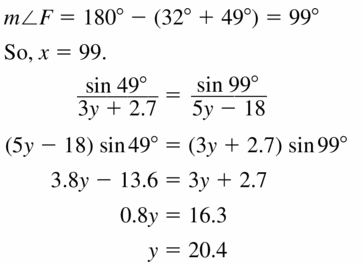
Question 44.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Would you use the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines to solve the triangle?
Answer:
Given in any triangle the sine law can be used if you know the two sides and one angle opposite a given side (SSA) or two angles and any side (AAS or ASA).
In any triangle, the cosine laws can be used if two sides are included with one angle of sides.
Question 45.
REWRITING A FORMULA
A Simplify the Law of Cosines for when the given angle is a right angle.
Answer:

Question 46.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Consider any triangle with side lengths of a, b, and c. Calculate the value of s, which is half the perimeter of the triangle. What measurement of the triangle is represented by \(\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)} ?\)
Answer:
Question 47.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
The ambiguous case of the Law of Sines occurs when you are given the measure of one acute angle. the length of one adjacent side, and the length of the side opposite that angle, which is less than the length of the adjacent side. This results in two possible triangles. Using the given information, find two possible solutions for ∆ABC
Draw a diagram for each triangle.
(Hint: The inverse sine function gives only acute angle measures. so consider the acute angle and its supplement for ∠B.)
a. m ∠ A = 40°, a = 13, b = 16
b. m ∠ A = 21°, a = 17, b = 32
Answer:
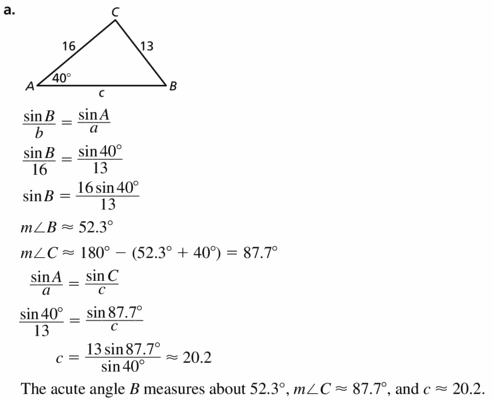
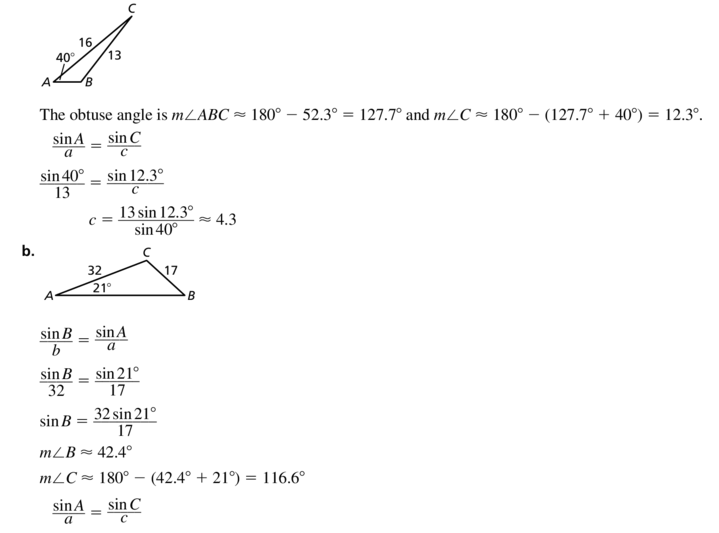

Question 48.
ABSTRACT REASONING
Use the Law of Cosines to show that the measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°. Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
a² = b² + c²- 2bc cos A
a² = a² + a² – 2 aa cos A
a² = 2a² coas A
cos A = 1/2
∠A = 60
Question 49.
CRITICAL THINKING
An airplane flies 55° east of north from City A to City B. a distance of 470 miles. Another airplane flies 7° north of east from City A to City C. a distance of 890 miles. What is the distance between Cities B and C?
Answer:
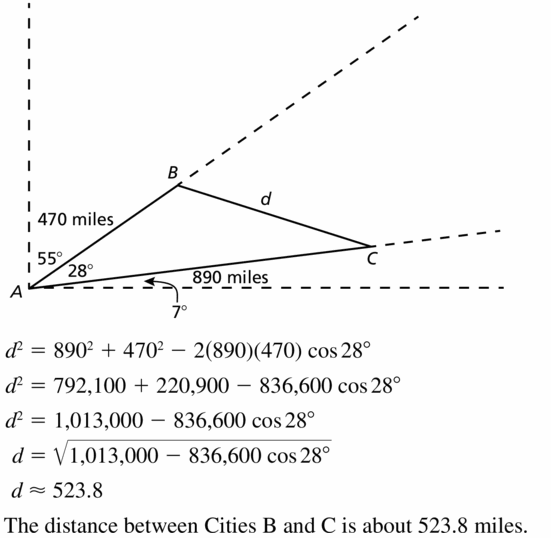
Question 50.
REWRITING A FORMULA
Follow the steps to derive the formula for the area of a triangle.
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ab sin C.
a. Draw the altitude from vertex B to \(\overline{A C}\). Label the altitude as h. Write a formula for the area of the triangle using h.
Answer:
Base of the triangle as b.
Writing area of the triangle in the form of h using area of the triangle.
Area of the triangle = 1/2 × base × height
ΔABC = 1/2 × b × h
b. Write an equation for sin C
Answer: We have to find an equation for sin C when ΔABC is given with sides a, b, c.
c. Use the results of parts (a) and (b) to write a formula for the area of a triangle that does not include h.
Answer:
ΔABC = 1/2 × b × h
sin C = h/a
solving for h,
h = a sin C
= 1/2 ab sinC
Hence proved.
Question 51.
PROVING A THEOREM
Follow the steps to use the formula for the area of a triangle to prove the Law of Sines (Theorem 9.9).
a. Use the derivation in Exercise 50 to explain how to derive the three related formulas for the area of a triangle.
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)bc sin A,
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ac sin B,
Area = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ab sin C
b. why can you use the formulas in part (a) to write the following statement?
\(\frac{1}{2}\)bc sin A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ac sin B = \(\frac{1}{2}\)ab sin C
c. Show how to rewrite the statement in part (b) to prove the Law of Sines. Justify each step.
Answer:
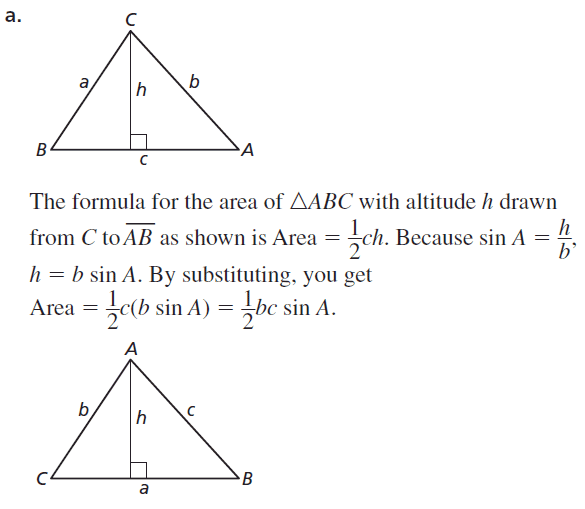

Question 52.
PROVING A THEOREM
Use the given information to complete the two – column proof of the Law of Cosines (Theorem 9.10).
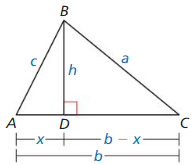
Given \(\overline{B D}\) is an altitude of ∆ABC.
Prove a2 = b2 + c2 – 2bc cos A
| Statements | Reasons |
| 1. \(\overline{B D}\) is an altitude of ∆ABC. | 1. Given |
| 2. ∆ADB and ∆CDB are right triangles. | 2. _______________________ |
| 3. a2 = (b – x)2 + h2 | 3. _______________________ |
| 4. _______________________ | 4. Expand binomial. |
| 5. x2 + h2 = c2 | 5. _______________________ |
| 6. _______________________ | 6. Substitution Property of Equality |
| 7. cos A = \(\frac{x}{c}\) | 7. _______________________ |
| 8. x = c cos A | 8. _______________________ |
| 9. a2 = b2 + c2 – 2bc Cos A | 9. _______________________ |
Answer:
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the radius and diameter of the circle.
Question 53.
Answer:
![]()
Question 54.
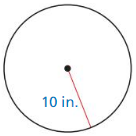
Answer:
The radius is 10 in and the diameter is 20 in.
Question 55.
Answer:
![]()
Question 56.
Answer:
The radius is 50 in and the diameter is 100 in.
Right Triangles and Trigonometry Review
9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
Find the value of x. Then tell whether the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple.
Question 1.
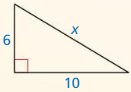
Answer:
x = 2√34
The sides will not form a Pythagorean triple.
Explanation:
x² = 6² + 10²
x²= 36 + 100
x = 2√34
Question 2.
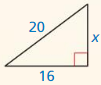
Answer:
x = 12
The sides form a Pythagorean triple.
Explanation:
20² = 16²+ x²
400 = 256 + x²
x² = 144
x = 12
Question 3.
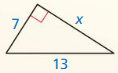
Answer:
x = 2√30
The sides will not form a Pythagorean triple.
Explanation:
13² = 7² + x²
169 = 49 + x²
x = 2√30
Verify that the segments lengths form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
Question 4.
6, 8, and 9
Answer:
9² = 81
6² + 8² = 36 + 64 = 100
9² < 6² + 8²
So, the triangle is acute
Question 5.
10, 2√2, and 6√3
Answer:
10² = 100
(2√2)² + (6√3)² = 8 + 108 = 116
So, the triangle is acute.
Question 6.
13, 18 and 3√55
Answer:
18² = 324
13² + (3√55)² = 169 + 495 = 664
So, the triangle is acute.
9.2 Special Right Triangles
Find the value of x. Write your answer in simplest form.
Question 7.
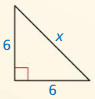
Answer:
hypotenuse = leg • √2
x = 6√2
Question 8.
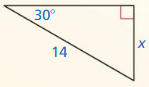
Answer:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
14 = x • √3
x = 8.08
Question 9.
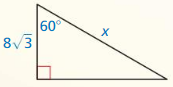
Answer:
longer leg = shorter leg • √3
x = 8√3 • √3
x = 24
9.3 Similar Right Triangles
Identify the similar triangles. Then find the value of x.
Question 10.
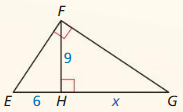
Answer:
9 = √(6x)
81 = 6x
x = \(\frac { 27 }{ 2 } \)
Question 11.
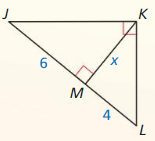
Answer:
x = √(6 x 4)
x = 2√6
Question 12.
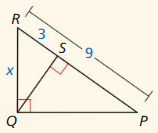
Answer:
\(\frac { RP }{ RQ } \) = \(\frac { SP }{ RS } \)
\(\frac { 9 }{ x } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 3 } \)
x = 3.5
Question 13.
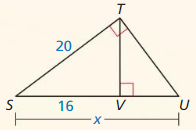
Answer:
\(\frac { SU }{ ST } \) = \(\frac { SV }{ VU } \)
\(\frac { 16 }{ 20 } \) = \(\frac { x }{ (x – 16) } \)
4(x – 16) = 5x
x = 16
Find the geometric mean of the two numbers.
Question 14.
9 and 25
Answer:
mean = √(9 x 25)
= 15
Question 15.
36 and 48
Answer:
mean = √(36 x 48)
= 24√3
Question 16.
12 and 42
Answer:
mean = √(12 x 42)
= 6√14
9.4 The Tangent Ratio
Find the tangents of the acute angles in the right triangle. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to four decimal places.
Question 17.
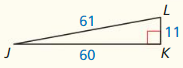
Answer:
tan J = \(\frac { Opposite side }{ Adjacent side } \)
tan J = \(\frac { LK }{ JK } \) = \(\frac { 11 }{ 60 } \)
tan L = \(\frac { JK }{ LK } \) = \(\frac { 60 }{ 11 } \)
Question 18.
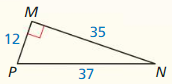
Answer:
tan P = \(\frac { MN }{ MP } \) = \(\frac { 35 }{ 12 } \)
tan N = \(\frac { MP }{ MN } \) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 35 } \)
Question 19.
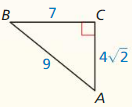
Answer:
tan A = \(\frac { BC }{ AC } \) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 4√2 } \)
tan B = \(\frac { AC }{ BC } \) = \(\frac { 4√2 }{ 7 } \)
Find the value of x. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Question 20.
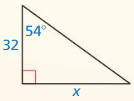
Answer:
tan 54 = \(\frac { x }{ 32 } \)
1.37 = \(\frac { x }{ 32 } \)
x = 43.8
Question 21.
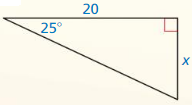
Answer:
tan 25 = \(\frac { x }{ 20 } \)
0.46 x 20 = x
x = 9.2
Question 22.
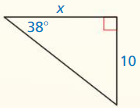
Answer:
tan 38 = \(\frac { 10 }{ x } \)
x = 12.82
Question 23.
The angle between the bottom of a fence and the top of a tree is 75°. The tree is 4 let from the fence. How tall is the tree? Round your answer to the nearest foot.
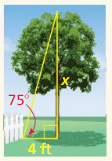
Answer:
tan 75 = \(\frac { x }{ 4 } \)
x = 14.92
9.5 The Sine and Cosine Ratios
Find sin X, sin Z, cos X, and cos Z. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal rounded to four decimal places.
Question 24.
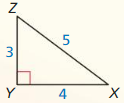
Answer:
sin X = \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
sin Z = \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 } \)
cos X = \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 } \)
cos Z = \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 } \)
Question 25.
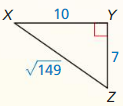
Answer:
sin X = \(\frac { 7 }{ √149 } \)
sin Z = \(\frac { 10 }{ √149 } \)
cos X = \(\frac { 10 }{ √149 } \)
cos Z = \(\frac { 7 }{ √149 } \)
Question 26.
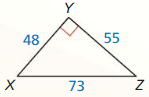
Answer:
sin X = \(\frac { 55 }{ 73 } \)
sin Z = \(\frac { 48 }{ 73 } \)
cos X = \(\frac { 48 }{ 73 } \)
cos Z = \(\frac { 55 }{ 73 } \)
Find the value of each variable using sine and cosine. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 27.
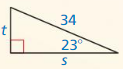
Answer:
sin 23 = \(\frac { t }{ 34 } \)
t = 13.26
cos 23 = \(\frac { s }{ 34 } \)
s = 31.28
Question 28.
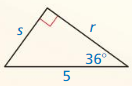
Answer:
sin 36 = \(\frac { s }{ 5 } \)
s = 2.9
cos 36 = \(\frac { r }{ 5 } \)
r = 4
Question 29.
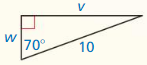
Answer:
sin 70 = \(\frac { v }{ 10 } \)
v = 9.39
cos 70 = \(\frac { w }{ 10 } \)
w = 3.42
Question 30.
Write sin 72° in terms of cosine.
Answer:
sin 72 = cos(90 – 72)
= cos 18 = 0.95
Question 31.
Write cos 29° in terms of sine.
Answer:
sin 29 = cos(90 – 29)
= cos 61 = 0.48
9.6 Solving Right Triangles
Let ∠Q be an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of ∠Q to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Question 32.
cos Q = 0.32
Answer:
cos Q = 0.32
∠Q = inverse cos of .32
∠Q = 71.3
Question 33.
sin Q = 0.91
Answer:
sin Q = 0.91
∠Q = inverse sin of 0.91
∠Q = 65.5
Question 34.
tan Q = 0.04
Answer:
tan Q = 0.04
∠Q = inverse tan of 0.04
∠Q = 2.29
Solve the right triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 35.
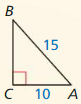
Answer:
a = 5√5, ∠A = 47.7, ∠B = 42.3
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
15² = a² + 10²
a² = 125
a = 5√5
sin A = \(\frac { 5√5 }{ 15 } \) = 0.74
∠A = 47.7
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
47.7 + ∠B + 90 = 180
∠B = 42.3
Question 36.
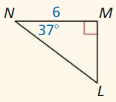
Answer:
NL = 7.59, ∠L = 53, ML = 4.55
Explanation:
cos 37 = \(\frac { 6 }{ NL } \)
NL = 7.59
∠N + ∠M + ∠L = 180
37 + 90 + ∠L = 180
∠L = 53
sin 37 = \(\frac { ML }{ 7.59 } \)
ML = 4.55
Question 37.
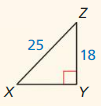
Answer:
XY = 17.34, ∠X = 46, ∠Z = 44
Explanation:
c² = a² + b²
25² = 18²+ b²
b² = 301
b = 17.34
sin X = \(\frac { 18 }{ 25 } \)
∠X = 46
sum of angles = 180
46 + 90 + ∠Z = 180
∠Z = 44
9.7 Law of Sines and Law of Cosines
Find the area of ∆ABC with the given side lengths and included angle.
Question 38.
m ∠ B = 124°, a = 9, c = 11
Answer:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ac sin B
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (9 x 11) sin 124
= 40.59
Question 39.
m ∠ A = 68°, b = 13, c = 7
Answer:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) bc sin A
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (13 x 7) sin 68
= 41.86
Question 40.
m ∠ C = 79°, a = 25 b = 17
Answer:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) ab sin C
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (25 x 17) sin 79
= 208.25
Solve ∆ABC. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 41.
m ∠ A = 112°, a = 9, b = 4
Answer:
∠B = 24, ∠C = 44, c = 6.76
Explanation:
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \)
\(\frac { sin B }{ 4 } \) = \(\frac { sin 112 }{ 9 } \)
sin B = 0.408
∠B = 24
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
112 + 24 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 44
\(\frac { sin 112 }{ 9 } \) = \(\frac { sin 44 }{ c } \)
c = 6.76
Question 42.
m ∠ 4 = 28°, m ∠ B = 64°, c = 55
Answer:
∠C = 88, b = 49.4, a = 25.5
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
28 + 64 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 88
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin 64 }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin 88 }{ 55 } \)
\(\frac { sin 64 }{ b } \) = 0.018
b = 49.4
\(\frac { sin 28 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 88 }{ 55 } \)
a = 25.5
Question 43.
m ∠ C = 48°, b = 20, c = 28
Answer:
∠B = 31.3, ∠A = 100.7, a = 37.6
Explanation:
\(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \)
\(\frac { sin B }{ 20 } \) = \(\frac { sin 48 }{ 28 } \)
\(\frac { sin B }{ 20 } \) = 0.026
sin B = 0.52
∠B = 31.3
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
∠A + 31.3 + 48 = 180
∠A = 100.7
\(\frac { sin 100.7 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 48 }{ 28 } \)
a = 37.6
Question 44.
m ∠ B = 25°, a = 8, c = 3
Answer:
b = 5.45, ∠A = 37.5, ∠C = 117.5
Explanation:
b² = a² + c²- 2ac cos B
b² = 8² + 3² – 2(8 x 3) cos 25 = 73 – 43.2 = 29.8
b = 5.45
\(\frac { sin A }{ 8 } \) = \(\frac { sin 25 }{ 5.45 } \)
sin A = 0.61
∠A = 37.5
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
37.5 + 25 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 117.5
Question 45.
m ∠ B = 102°, m ∠ C = 43°, b = 21
Answer:
∠A = 35, c = 14.72, a = 12.3
Explanation:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
∠A + 102 + 43 = 180
∠A = 35
\(\frac { sin 102 }{ 21 } \) = \(\frac { sin 43 }{ c } \)
0.046 = \(\frac { sin 43 }{ c } \)
c = 14.72
\(\frac { sin 102 }{ 21 } \) = \(\frac { sin 35 }{ a } \)
0.046 = \(\frac { sin 35 }{ a } \)
a = 12.3
Question 46.
a = 10, b = 3, c = 12
Answer:
∠B = 11.7, ∠C = 125.19, ∠A = 43.11
Explanation:
b² = a² + c²- 2ac cos B
3² = 10² + 12²- 2(10 x 12) cos B
9 = 100 + 144 – 240 cos B
cos B = 0.979
∠B = 11.7
a² = b² + c²- 2bc cos A
100 = 9 + 144 – 72 cos A
cos A = 0.73
∠A = 43.11
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180
43.11 + 11.7 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 125.19
Right Triangles and Trigonometry Test
Find the value of each variable. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 1.
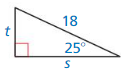
Answer:
sin 25 = \(\frac { t }{ 18 } \)
t = 7.5
cos 25 = \(\frac { s }{ 18 } \)
s = 16.2
Question 2.
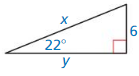
Answer:
sin 22 = \(\frac { 6 }{ x } \)
x = 16.21
cos 22 = \(\frac { y }{ 16.21 } \)
y = 14.91
Question 3.
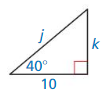
Answer:
tan 40 = \(\frac { k }{ 10 } \)
k = 8.3
cos 40 = \(\frac { 10 }{ j } \)
j = 13.15
Verity that the segment lengths form a triangle. Is the triangle acute, right, or obtuse?
Question 4.
16, 30, and 34
Answer:
34²= 16² + 30²
So, the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
Question 5.
4, √67, and 9
Answer:
9² = 81
4² + (√67)² = 83
So the triangle is acute
Question 6.
√5. 5. and 5.5
Answer:
5.5² = 30.25
√5² + 5² = 30
So the triangle is obtuse
Solve ∆ABC. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 7.
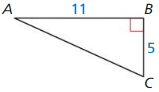
Answer:
c = 12.08, ∠A = 24.22, ∠C = 65.78
Explanation:
tan A = \(\frac { 5 }{ 11 } \)
∠A = 24.22
c² = 11²+ 5²
c = 12.08
24.22 + 90 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 65.78
Question 8.
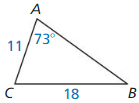
Answer:
∠B = 35.4, ∠C = 71.6, c = 17.9
Explanation:
\(\frac { sin 73 }{ 18 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 11 } \)
sin B = 0.58
∠B = 35.4
73 + 35.4 + ∠C = 180
∠C = 71.6
\(\frac { sin 73 }{ 18 } \) = \(\frac { sin 71.6 }{ c } \)
c = 17.9
Question 9.
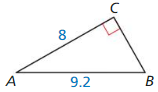
Answer:
BC = 4.54, ∠B = 59.3, ∠A = 30.7
Explanation:
9.2² = 8² + x²
x = 4.54
\(\frac { sin 90 }{ 9.2 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 8 } \)
sin B = 0.86
∠B = 59.3
∠A + 59.3 + 90 = 180
∠A = 30.7
Question 10.
m ∠ A = 103°, b = 12, c = 24
Answer:
a = 29, ∠B = 53.5
Explanation:
a² = b² + c²- 2bc cos A
a² = 144 + 24² – 2(12 x 24) cos 103
a = 29
\(\frac { sin B }{ 12 } \) = \(\frac { sin 103 }{ 29 } \)
∠B = 23.5
∠C = 180 – (103 + 23.5) = 53.5
Question 11.
m ∠ A = 26°, m ∠ C = 35°, b = 13
Answer:
∠B = 119, a = 6.42, c = 8.5
Explanation:
∠B + 26 + 35 = 180
∠B = 119
\(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) = \(\frac { sin 26 }{ a } \)
a = 6.42
\(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) = \(\frac { sin 35 }{ c } \)
c = 8.5
Question 12.
a = 38, b = 31, c = 35
Answer:
∠B=50.2, ∠C = 59.8, ∠A = 70
Explanation:
b² = a² + c²- 2ac cos B
31² = 38²+ 35²- 2(35 x 38) cos B
cos B = 0.64
∠B=50.2
a² = b² + c²- 2bc cos A
38² = 31²+ 35²- 2(31 x 35) cos A
cos A = 0.341
∠A = 70
∠C = 59.8
Question 13.
Write cos 53° in terms of sine.
Answer:
cos 53° = sin (90 – 53) = sin 37
Find the value of each variable. Write your answers in simplest form.
Question 14.
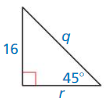
Answer:
sin 45 = \(\frac { 16 }{ q } \)
q = 22.6
cos 45 = \(\frac { r }{ q } \)
r = 16
Question 15.
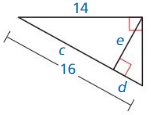
Answer:
Question 16.
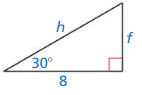
Answer:
sin 30 = \(\frac { f }{ 9.2 } \)
f = 4.6
cos 30 = \(\frac { 8 }{ h } \)
h = 9.2
Question 17.
In ∆QRS, m ∠ R = 57°, q = 9, and s = 5. Find the area of ∆QRS.
Answer:
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) qs sin R
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (9 x 5) sin 57 = 18.675
Question 18.
You are given the measures of both acute angles of a right triangle. Can you determine the side lengths? Explain.
Answer:
No.
Question 19.
You are at a parade looking up at a large balloon floating directly above the street. You are 60 feet from a point on the street directly beneath the balloon. To see the top of the balloon, you look up at an angle of 53°. To see the bottom of the balloon, you look up at an angle of 29°. Estimate the height h of the balloon.
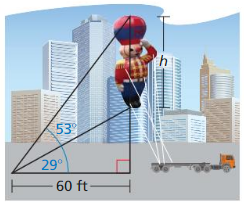
Answer:
The height of the balloon is 46 feet’s
The height from the ground to the top of the balloon is represented by x.
The trigonometric function is
Tan theta = opposite/adjacent
Tan 53 degrees = x/60
x = 60 x Tan 53 degrees.
= 79.6227
x = 79.62 feet
The height from the ground to the bottom of the balloon can be represented by t.
Tan theta = opposite/adjacent
Tan 29 degrees = y/60 degrees.
Y = 60 x tan 90 degrees.
= 33.2585
= 33.26 feet.
The height of the balloon is x – y
= 79.6227 – 33.2585
= 46.3642
The height of the balloon is 46 feet.
Question 20.
You warn to take a picture of a statue on Easter Island, called a moai. The moai is about 13 feet tall. Your camera is on a tripod that is 5 feet tall. The vertical viewing angle of your camera is set at 90°. How far from the moai should you stand so that the entire height of the moai is perfectly framed in the photo?

Answer:
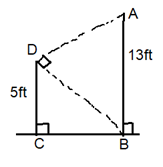
From the diagram, AB is the height of the statue on Easter Island, and CD is the height of the tripod.
Angle ABC = Angle DCB = 90 degrees.
AB//DC
Angle BDC = Angle ABD
ANGLE BDC = Angle ABD x Angle ADB = BCD = 90 degrees.
Angle ADB approximately equal to Angle BCD
AB/BD = BD/DC = 13/BD = BD/5
BD² = 5 x 13 = 80
BD = square root of (80) = 4 square root of (5)
BD² = DC² + BC²
BC = square root of (BD² – DC²)
Angle BCD = 90 degrees
DC = 5
BD = 4 square root of (5)
BC = square root of ((4(square root of (5)) ²
= square root of (80 – 25
= square root of (55)
= 7.42.
Therefore you can stand 7.42 feet away from the Moai. So, the entire height of the Moai is perfectly framed in the photo.
Right Triangles and Trigonometry Cummulative Assessment
Question 1.
The size of a laptop screen is measured by the length of its diagonal. you Want to purchase a laptop with the largest screen possible. Which laptop should you buy?
(A)

(B)

(C)

(D)

Answer:
(B)
Explanation:
(a) d = √9² + 12² = 15
(b) d = √11.25² + 20² = 22.94
(c) d = √12² + 6.75² = 13.76
(d) d = √8² + 6² = 10
Question 2.
In ∆PQR and ∆SQT, S is between P and Q, T is between R and Q, and \(\) What must be true about \(\overline{S T}\) and \(\overline{P R}\)? Select all that apply.
\(\overline{S T}\) ⊥ \(\overline{P R}\) \(\overline{S T}\) || \(\overline{P R}\) ST = PR ST = \(\frac{1}{2}\)PR
Answer:
Question 3.
In the diagram, ∆JKL ~ ∆QRS. Choose the symbol that makes each statement true.
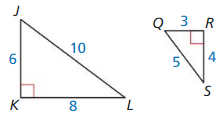
< = >
sin J ___________ sin Q sin L ___________ cos J cos L ___________ tan Q
cos S ___________ cos J cos J ___________ sin S tan J ___________ tan Q
tan L ___________ tan Q tan S ___________ cos Q sin Q ___________ cos L
Answer:
sin J = sin Q sin L = cos J cos L = tan Q
cos S > cos J cos J > sin S tan J = tan Q
tan L < tan Q tan S > cos Q sin Q = cos L
Question 4.
A surveyor makes the measurements shown. What is the width of the river.
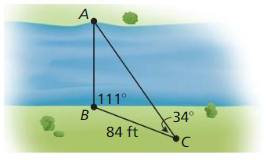
Answer:
tan 34 = \(\frac { AB }{ 84 } \)
AB = 56.28
Question 5.
Create as many true equations as possible.
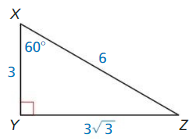
____________ = ______________
sin X cos X tan x \(\frac{X Y}{X Z}\) \(\frac{Y Z}{X Z}\)
Sin Z cos Z tan Z \(\frac{X Y}{Y Z}\) \(\frac{Y Z}{X Y}\)
Answer:
sin X = \(\frac{Y Z}{X Z}\) = cos Z
cos X = \(\frac{X Y}{X Z}\) = sin Z
tan x = \(\frac{Y Z}{X Y}\)
tan Z = \(\frac{X Y}{Y Z}\)
Question 6.
Prove that quadrilateral DEFG is a kite.
Given \(\overline{H E} \cong \overline{H G}\), \(\overline{E G}\) ⊥ \(\overline{D F}\)
Prove \(\overline{F E} \cong \overline{F G}\), \(\overline{D E} \cong \overline{D G}\)
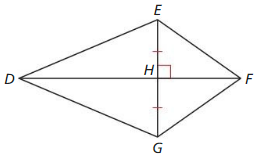
Answer:
Question 7.
What are the coordinates of the vertices of the image of ∆QRS after the composition of transformations show?
(A) Q’ (1, 2), R'(5, 4), S'(4, -1)
(B) Q'(- 1, – 2), R’ (- 5, – 4), S’ (- 4, 1)
(C) Q'(3, – 2), R’ (- 1, – 4), S’ (0, 1)
(D) Q’ (-2, 1), R'(- 4, 5), S'(1, 4)
Answer:
Question 8.
The Red Pyramid in Egypt has a square base. Each side of the base measures 722 feet. The height of the pyramid is 343 fee.
a. Use the side length of the base, the height of the pyramid, and the Pythagorean Theorem to find the slant height, AB, of the pyramid.
Answer:
343² = h² + 722²
h = 635.3
b. Find AC.
Answer:
AC = 343
c. Name three possible ways of finding m ∠ 1. Then, find m ∠ 1.
Answer:
Three possible ways are sin 1, cos 1 and tan 1
tan 1 = \(\frac { 722 }{ 635.3 } \)
∠1 = 48